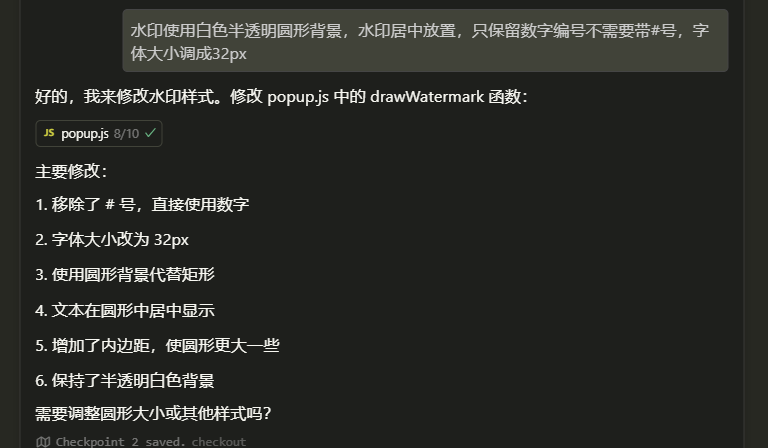
此类用于创建和启动一个HTTP代理服务
package org. example ; import org. apache. logging. log4j. LogManager ;
import org. apache. logging. log4j. Logger ; public class Bootstrap { private final Logger logger = LogManager . getLogger ( Bootstrap . class ) ; private AbstractEventLoop serverEventLoop; private int port; public Bootstrap ( ) { port = 8888 ; serverEventLoop = new ServerEventLoop ( this ) ; } public Bootstrap bindPort ( int port) { try { this . port = port; this . serverEventLoop. bind ( port) ; } catch ( Exception e) { logger. error ( "open server socket channel error." , e) ; } return this ; } public void start ( ) { serverEventLoop. getSelector ( ) . wakeup ( ) ; logger. info ( "Proxy server started at port {}." , port) ; } public AbstractEventLoop getServerEventLoop ( ) { return serverEventLoop; }
} 事件循环,单线程处理事件循环。包括客户端的连接和读写请求,目标服务器的连接和读写事件,在同一个事件循环中处理。
package org. example ; import org. apache. logging. log4j. LogManager ;
import org. apache. logging. log4j. Logger ;
import org. example. common. HttpRequestParser ; import java. io. IOException ;
import java. net. InetSocketAddress ;
import java. net. SocketAddress ;
import java. nio. ByteBuffer ;
import java. nio. channels. SelectableChannel ;
import java. nio. channels. SelectionKey ;
import java. nio. channels. ServerSocketChannel ;
import java. nio. channels. SocketChannel ; public class ServerEventLoop extends AbstractEventLoop { private final Logger logger = LogManager . getLogger ( ServerEventLoop . class ) ; public ServerEventLoop ( Bootstrap bootstrap) { super ( bootstrap) ; } @Override protected void processSelectedKey ( SelectionKey key) { if ( key. isValid ( ) && key. isAcceptable ( ) ) { if ( key. attachment ( ) instanceof Acceptor acceptor) { acceptor. accept ( ) ; } } if ( key. isValid ( ) && key. isReadable ( ) ) { if ( key. attachment ( ) instanceof ChannelHandler channelHandler) { channelHandler. handleRead ( ) ; } } if ( key. isValid ( ) && key. isConnectable ( ) ) { key. interestOpsAnd ( ~ SelectionKey . OP_CONNECT) ; if ( key. attachment ( ) instanceof ChannelHandler channelHandler) { channelHandler. handleConnect ( ) ; } } if ( key. isValid ( ) && key. isWritable ( ) ) { key. interestOpsAnd ( ~ SelectionKey . OP_WRITE) ; if ( key. attachment ( ) instanceof ChannelHandler channelHandler) { channelHandler. handleWrite ( ) ; } } } @Override public void bind ( int port) throws Exception { ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel . open ( ) ; serverSocketChannel. configureBlocking ( false ) ; SelectionKey key = serverSocketChannel. register ( this . selector, SelectionKey . OP_ACCEPT) ; key. attach ( new Acceptor ( serverSocketChannel) ) ; serverSocketChannel. bind ( new InetSocketAddress ( port) ) ; } class Acceptor { ServerSocketChannel ssc; public Acceptor ( ServerSocketChannel ssc) { this . ssc = ssc; } public void accept ( ) { try { SocketChannel socketChannel = ssc. accept ( ) ; socketChannel. configureBlocking ( false ) ; socketChannel. register ( selector, SelectionKey . OP_READ, new ClientChannelHandler ( socketChannel) ) ; logger. info ( "accept client connection" ) ; } catch ( IOException e) { logger. error ( "accept error" ) ; } } } abstract class ChannelHandler { Logger logger; SocketChannel channel; ByteBuffer writeBuffer; public ChannelHandler ( SocketChannel channel) { this . logger = LogManager . getLogger ( this . getClass ( ) ) ; this . channel = channel; this . writeBuffer = null ; } abstract void handleRead ( ) ; public void handleWrite ( ) { doWrite ( ) ; } public abstract void onChannelClose ( ) ; public ByteBuffer doRead ( ) { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer . allocate ( 4096 ) ; try { int len = channel. read ( buffer) ; if ( len == - 1 ) { logger. info ( "read end-of-stream, close channel {}" , channel) ; channel. close ( ) ; onChannelClose ( ) ; } if ( len > 0 ) { buffer. flip ( ) ; } } catch ( IOException e) { logger. error ( "read channel error" ) ; try { channel. close ( ) ; onChannelClose ( ) ; } catch ( IOException ex) { logger. error ( "close channel error." ) ; } } return buffer; } public void doWrite ( ) { if ( writeBuffer != null ) { try { while ( writeBuffer. hasRemaining ( ) ) { channel. write ( writeBuffer) ; } } catch ( IOException e) { logger. error ( "write channel error." ) ; try { channel. close ( ) ; onChannelClose ( ) ; } catch ( IOException ex) { logger. error ( "close channel error" ) ; } } writeBuffer = null ; } } public void handleConnect ( ) { } } class ClientChannelHandler extends ChannelHandler { HttpRequestParser requestParser; private SelectableChannel proxyChannel; public ClientChannelHandler ( SocketChannel sc) { super ( sc) ; this . channel = sc; this . requestParser = new HttpRequestParser ( ) ; this . proxyChannel = null ; } @Override public void handleRead ( ) { if ( requestParser. isParsed ( ) ) { if ( proxyChannel != null ) { SelectionKey proxyKey = proxyChannel. keyFor ( selector) ; if ( proxyKey != null && proxyKey. isValid ( ) && proxyKey. attachment ( ) instanceof ProxyChannelHandler proxyHandler) { if ( proxyHandler. writeBuffer == null ) { ByteBuffer buffer = doRead ( ) ; if ( buffer. hasRemaining ( ) && proxyKey. isValid ( ) ) { proxyHandler. writeBuffer = buffer; proxyKey. interestOpsOr ( SelectionKey . OP_WRITE) ; } } } } } else { ByteBuffer buffer = doRead ( ) ; requestParser. putFromByteBuffer ( buffer) ; if ( requestParser. isParsed ( ) ) { ByteBuffer buf = null ; if ( requestParser. getMethod ( ) . equals ( HttpRequestParser . HTTP_METHOD_CONNECT) ) { SelectionKey clientKey = channel. keyFor ( selector) ; if ( clientKey != null && clientKey. isValid ( ) && clientKey. attachment ( ) instanceof ClientChannelHandler clientHandler) { clientHandler. writeBuffer = ByteBuffer . wrap ( ( requestParser. getProtocol ( ) + " 200 Connection Established\r\n\r\n" ) . getBytes ( ) ) ; clientKey. interestOpsOr ( SelectionKey . OP_WRITE) ; } } else { byte [ ] allBytes = requestParser. getAllBytes ( ) ; buf = ByteBuffer . wrap ( allBytes) ; } this . proxyChannel = connect ( requestParser. getAddress ( ) , buf) ; } } } @Override public void onChannelClose ( ) { try { if ( proxyChannel != null ) { proxyChannel. close ( ) ; } } catch ( IOException e) { logger. error ( "close channel error" ) ; } } private SocketChannel connect ( String address, ByteBuffer buffer) { String host = address; int port = 80 ; if ( address. contains ( ":" ) ) { host = address. split ( ":" ) [ 0 ] . trim ( ) ; port = Integer . parseInt ( address. split ( ":" ) [ 1 ] . trim ( ) ) ; } SocketAddress target = new InetSocketAddress ( host, port) ; SocketChannel socketChannel = null ; SelectionKey proxyKey = null ; int step = 0 ; try { socketChannel = SocketChannel . open ( ) ; socketChannel. configureBlocking ( false ) ; step = 1 ; ProxyChannelHandler proxyHandler = new ProxyChannelHandler ( socketChannel) ; proxyHandler. setClientChannel ( channel) ; proxyHandler. writeBuffer = buffer; proxyKey = socketChannel. register ( selector, SelectionKey . OP_CONNECT, proxyHandler) ; proxyKey. interestOpsOr ( SelectionKey . OP_WRITE) ; step = 2 ; socketChannel. connect ( target) ; } catch ( IOException e) { logger. error ( "connect error." ) ; switch ( step) { case 2 : proxyKey. cancel ( ) ; case 1 : try { socketChannel. close ( ) ; } catch ( IOException ex) { logger. error ( "close channel error." ) ; } socketChannel = null ; break ; } } return socketChannel; } } class ProxyChannelHandler extends ChannelHandler { private SelectableChannel clientChannel; public ProxyChannelHandler ( SocketChannel sc) { super ( sc) ; clientChannel = null ; } @Override public void handleConnect ( ) { try { if ( channel. isConnectionPending ( ) && channel. finishConnect ( ) ) { SelectionKey proxyKey = channel. keyFor ( selector) ; proxyKey. interestOpsOr ( SelectionKey . OP_READ) ; } } catch ( IOException e) { try { channel. close ( ) ; onChannelClose ( ) ; } catch ( IOException ex) { logger. error ( "close channel error." ) ; } logger. error ( "finish connection error." ) ; } } @Override public void handleRead ( ) { if ( clientChannel != null ) { SelectionKey clientKey = clientChannel. keyFor ( selector) ; if ( clientKey != null && clientKey. isValid ( ) && clientKey. attachment ( ) instanceof ClientChannelHandler clientHandler) { if ( clientHandler. writeBuffer == null ) { ByteBuffer buffer = doRead ( ) ; if ( buffer. hasRemaining ( ) && clientKey. isValid ( ) ) { clientHandler. writeBuffer = buffer; clientKey. interestOpsOr ( SelectionKey . OP_WRITE) ; } } } } } @Override public void onChannelClose ( ) { try { if ( clientChannel != null ) { clientChannel. close ( ) ; } } catch ( IOException e) { logger. error ( "close channel error" ) ; } } public void setClientChannel ( SocketChannel client) { this . clientChannel = client; } }
}
事件循环的抽象类
package org. example ; import org. apache. logging. log4j. LogManager ;
import org. apache. logging. log4j. Logger ; import java. io. IOException ;
import java. nio. channels. SelectionKey ;
import java. nio. channels. Selector ;
import java. util. Iterator ;
import java. util. Set ;
import java. util. concurrent. Executors ; public abstract class AbstractEventLoop implements Runnable { private final Logger logger = LogManager . getLogger ( AbstractEventLoop . class ) ; protected Selector selector; protected Bootstrap bootstrap; public AbstractEventLoop ( Bootstrap bootstrap) { this . bootstrap = bootstrap; openSelector ( ) ; Executors . newSingleThreadExecutor ( ) . submit ( this ) ; } public void bind ( int port) throws Exception { throw new Exception ( "not support" ) ; } @Override public void run ( ) { while ( true ) { try { if ( selector. select ( ) > 0 ) { processSelectedKeys ( ) ; } } catch ( Exception e) { logger. error ( "select error." , e) ; } } } private void processSelectedKeys ( ) { Set < SelectionKey > = selector. selectedKeys ( ) ; Iterator < SelectionKey > = keys. iterator ( ) ; while ( iterator. hasNext ( ) ) { SelectionKey key = iterator. next ( ) ; iterator. remove ( ) ; processSelectedKey ( key) ; } } protected abstract void processSelectedKey ( SelectionKey key) ; public Selector openSelector ( ) { try { this . selector = Selector . open ( ) ; return this . selector; } catch ( IOException e) { logger. error ( "open selector error." , e) ; } return null ; } public Selector getSelector ( ) { return selector; }
} 用于解析HTTP请求报文中的请求头,可以获取主机和端口号
package org. example. common ; import org. apache. logging. log4j. LogManager ;
import org. apache. logging. log4j. Logger ; import java. nio. ByteBuffer ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. List ; public class HttpRequestParser { private final Logger logger = LogManager . getLogger ( HttpRequestParser . class ) ; public static final String COLON = ":" ; public static final String REQUEST_HEADER_HOST_PREFIX = "host:" ; private UnboundedByteBuffer requestBytes = new UnboundedByteBuffer ( ) ; private List < String > = new ArrayList < > ( ) ; public static final String HTTP_METHOD_GET = "GET" ; public static final String HTTP_METHOD_POST = "POST" ; public static final String HTTP_METHOD_PUT = "PUT" ; public static final String HTTP_METHOD_DELETE = "DELETE" ; public static final String HTTP_METHOD_TRACE = "TRACE" ; public static final String HTTP_METHOD_OPTIONS = "OPTIONS" ; public static final String HTTP_METHOD_HEAD = "HEAD" ; public static final String HTTP_METHOD_CONNECT = "CONNECT" ; private String address; private String protocol; private String method; private boolean parsed = false ; private StringBuffer reqHeaderBuffer = new StringBuffer ( ) ; public void putFromByteBuffer ( ByteBuffer buffer) { for ( ; buffer. hasRemaining ( ) ; ) { byte b = buffer. get ( ) ; requestBytes. addByte ( b) ; reqHeaderBuffer. append ( ( char ) b) ; if ( b == '\n' && reqHeaderBuffer. charAt ( reqHeaderBuffer. length ( ) - 2 ) == '\r' ) { if ( reqHeaderBuffer. length ( ) == 2 ) { parsed = true ; logger. debug ( "Request header line end." ) ; break ; } String headerLine = reqHeaderBuffer. substring ( 0 , reqHeaderBuffer. length ( ) - 2 ) ; logger. debug ( "Request header line parsed {}" , headerLine) ; headers. add ( headerLine) ; if ( headerLine. startsWith ( HTTP_METHOD_GET) || headerLine. startsWith ( HTTP_METHOD_POST) || headerLine. startsWith ( HTTP_METHOD_PUT) || headerLine. startsWith ( HTTP_METHOD_DELETE) || headerLine. startsWith ( HTTP_METHOD_TRACE) || headerLine. startsWith ( HTTP_METHOD_OPTIONS) || headerLine. startsWith ( HTTP_METHOD_HEAD) || headerLine. startsWith ( HTTP_METHOD_CONNECT) ) { this . protocol = headerLine. split ( " " ) [ 2 ] . trim ( ) ; this . method = headerLine. split ( " " ) [ 0 ] . trim ( ) ; } else if ( headerLine. toLowerCase ( ) . startsWith ( REQUEST_HEADER_HOST_PREFIX) ) { this . address = headerLine. toLowerCase ( ) . replace ( REQUEST_HEADER_HOST_PREFIX, "" ) . trim ( ) ; } reqHeaderBuffer. delete ( 0 , reqHeaderBuffer. length ( ) ) ; } } } public boolean isParsed ( ) { return parsed; } public String getAddress ( ) { return address; } public String getProtocol ( ) { return protocol; } public String getMethod ( ) { return method; } public byte [ ] getAllBytes ( ) { return requestBytes. toByteArray ( ) ; }
} 无界的字节缓冲区,每次会以两倍的容量扩容,可以用于追加存入客户端的请求数据,实现粘包
package org. example. common ; public class UnboundedByteBuffer { private byte [ ] bytes; private int size; private int cap; private final int DEFAULT_CAP = 4096 ; private final int MAX_CAP = 1 << 30 ; public UnboundedByteBuffer ( ) { this . cap = DEFAULT_CAP; this . bytes = new byte [ this . cap] ; this . size = 0 ; } public void addBytes ( byte [ ] data) { ensureCapacity ( data. length) ; System . arraycopy ( data, 0 , bytes, size, data. length) ; this . size += data. length; } private void ensureCapacity ( int scale) { if ( scale + this . size > this . cap) { int tmpCap = this . cap; while ( scale + this . size > tmpCap) { tmpCap = tmpCap << 1 ; } if ( tmpCap > MAX_CAP) { return ; } byte [ ] newBytes = new byte [ tmpCap] ; System . arraycopy ( this . bytes, 0 , newBytes, 0 , this . size) ; this . bytes = newBytes; } } public byte [ ] toByteArray ( ) { byte [ ] ret = new byte [ this . size] ; System . arraycopy ( this . bytes, 0 , ret, 0 , this . size) ; return ret; } public void addByte ( byte b) { ensureCapacity ( 1 ) ; this . bytes[ this . size++ ] = b; }
} 以上实现是在单个事件循环线程中处理所有事件,一个更好的方案是将客户端的Channel和代理服务器与目标服务器的Channel区分开,分别在两个事件循环中处理。基本实现也和本文中的代码大体一致,两者在理论上应该存在性能差距,实际经过本人测试可以每秒处理客户端的上千个连接。代码传送门