LCA - Lowest Common Ancestor
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/SP14932
题目描述
A tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one simple path. In other words, any connected graph without cycles is a tree. - Wikipedia
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) is a concept in graph theory and computer science. Let T be a rooted tree with N nodes. The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes v and w as the lowest node in T that has both v and w as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself). - Wikipedia
Your task in this problem is to find the LCA of any two given nodes v and w in a given tree T.
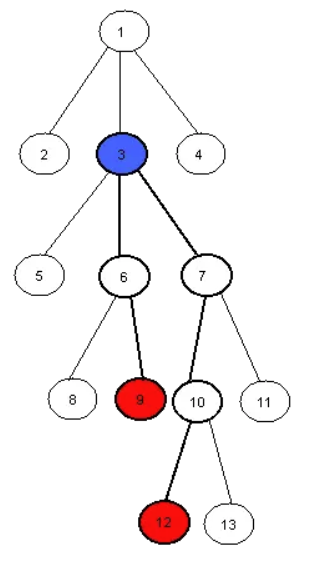
For example the LCA of nodes 9 and 12 in this tree is the node number 3.
Input
The first line of input will be the number of test cases. Each test case will start with a number N the number of nodes in the tree, 1 <= N <= 1,000. Nodes are numbered from 1 to N. The next N lines each one will start with a number M the number of child nodes of the Nth node, 0 <= M <= 999 followed by M numbers the child nodes of the Nth node. The next line will be a number Q the number of queries you have to answer for the given tree T, 1 <= Q <= 1000. The next Q lines each one will have two number v and w in which you have to find the LCA of v and w in T, 1 <= v, w <= 1,000.
Input will guarantee that there is only one root and no cycles.
Output
For each test case print Q + 1 lines, The first line will have “Case C:” without quotes where C is the case number starting with 1. The next Q lines should be the LCA of the given v and w respectively.
Example
Input:
1
7
3 2 3 4
0
3 5 6 7
0
0
0
0
2
5 7
2 7
Output:
Case 1:
3
1
输入格式
无
输出格式
无
代码
倍增算法
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
vector<int> dep; // 存储深度
vector<vector<int>> fa; // 存储跳跃点
vector<vector<int>> e; // 存储边
void dfs(int x, int y) {for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {fa[x][i] = fa[fa[x][i - 1]][i - 1];}for (auto i : e[x]) {dfs(i, x);}
}int lca(int u, int v) {if (dep[u] < dep[v]) swap(u, v);for (int i = 9; i >= 0; i--) {if (dep[fa[u][i]] >= dep[v]) u = fa[u][i];}if (u == v) return v;for (int i = 9; i >= 0; i--) {if (fa[u][i] != fa[v][i]) {u = fa[u][i];v = fa[v][i];}}return fa[u][0];
}void solve() {int N; // 节点数cin >> N;dep = vector<int>(N + 1);fa = vector<vector<int>>(N + 1, vector<int>(10, 0));e = vector<vector<int>>(N + 1);dep[1] = 1;for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {int sonNum; // 子节点数量cin >> sonNum;while (sonNum--) {int sonNode;cin >> sonNode;e[i].push_back(sonNode);fa[sonNode][0] = i;dep[sonNode] = dep[i] + 1;}}dfs(1, 0);int queryNum;cin >> queryNum; // 查询次数while (queryNum--) {int u, v;cin >> u >> v;cout << lca(u, v) << endl;}
}int main() {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);int T;cin >> T;for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) {cout << "Case " << i << ":" << endl;solve();}return 0;
}
tarjan算法
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
vector<bool> vis; // 存储是否访问
vector<int> fa; // 存储父节点
vector<vector<int>> e; // 存储子节点
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> query; // 需要查询的
vector<int> ans; // 存储答案int find(int x) {if (x == fa[x]) return x;return fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}void tarjan(int x) {vis[x] = true;for (auto son : e[x]) {if (!vis[son]) {tarjan(son);fa[son] = x;}}for (auto q : query[x]) {int y = q.first, id = q.second;if (vis[y]) {ans[id] = find(y);}}
}
void solve() {int N; // 节点数cin >> N;fa = vector<int>(N + 1);e = vector<vector<int>>(N + 1);query.resize(N + 1);vis = vector<bool>(N + 1, false);for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {fa[i] = i;}// 输入子节点for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {int sonNum;cin >> sonNum;while (sonNum--) {int sonNode;cin >> sonNode;e[i].push_back(sonNode);}}int queryNum;cin >> queryNum;ans = vector<int>(queryNum + 1);for (int i = 1; i <= queryNum; i++) {int u, v;cin >> u >> v;query[u].push_back({ v, i });query[v].push_back({ u, i });}tarjan(1);for (int i = 1; i <= queryNum; i++) {cout << ans[i] << endl;}
}int main() {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);int T;cin >> T;for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) {cout << "Case " << i << ":" << endl;solve();}return 0;
}




![11.20[JAVAEXP3]重定向细究【DEBUG】](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/265fa5ad8b784e6a9e7658f61909fcdd.png)