HarmonyOS Next 关于页面渲染的性能优化方案
HarmonyOS Next 应用开发中,用户的使用体验至关重要。其中用户启动APP到呈现页面主要包含三个步骤:
- 框架初始化
- 页面加载
- 布局渲染
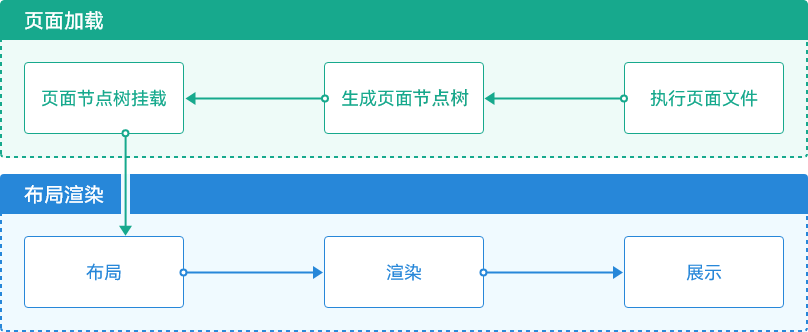
从页面加载到布局渲染中,主要包含了6个环节:
- 执行页面文件
- 生成页面节点树
- 页面节点树挂载
- 布局
- 渲染
- 展示
页面节点树挂载的速度取决于节点的数量,我们可以理解给1个自定义组件在渲染时,后端同时会生成一个对应的
节点。该节点后期会用来diff。
渲染的速度取决于布局属性。如果布局属性越复杂、冗余。那么就越慢。
节点的数量优化
HarmonyOS Next 会根据自定义节点的数量在后端生成对应的节点。那么如果我们在实际开发中,可以考虑尽量的将自定义组件的数量减少,替换成 @Builder 自定义构建函数。
那么哪些自定义节点可以替换成**@Builder**自定义构建函数呢,看下表:
| 分类 | 自定义组件 | @Builder |
|---|---|---|
| 复用布局结构 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 复用样式 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 导出使用 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 生命周期 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 状态管理 | 支持 | 不支持 |
所以,当我们对于封装的需求,不需要导出使用、不需要使用生命周期、不需要独立的状态管理时。就可以使用**@Builder**来代替自定义组件。
@Builder的基本使用

@Entry
@Component
struct Index {@BuilderCustomBtn(text:string){Button(text).width(100).height(50).linearGradient({colors:[[Color.Black,0],[Color.Red,1]]})}build() {Column({space:10}){this.CustomBtn("登录")this.CustomBtn("注册")}.width("100%").height("100%").justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)}
}
自定义组件的基本使用

@Component
struct CustomBtn {text: string = ""build() {Button(this.text).width(100).height(50).linearGradient({colors: [[Color.Black, 0], [Color.Red, 1]]})}
}@Entry
@Component
struct Index {build() {Column({ space: 10 }) {CustomBtn({text:"登录"})CustomBtn({text:"注册"})}.width("100%").height("100%").justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)}
}
布局属性的优化
这里的优化,主要是指性能的优化,也就是用户体验的优化,不是对于开发者来讲的开发体验的优化。
HarmonyOS Next 有提供 @Styles 和 @Extends 来实现代码层面的优化,也就是样式代码的简单封装。
但是无论是用户层面的优化和代码层面的优化。@Styles 和 @Extends 都存在一定的限制。因此HarmonyOS
Next 又推出了 AttributeModifier 和 AttributeUpdater(AttributeUpdater 是AttributeModifier的继承 )
AttributeModifier
- AttributeModifier是一个接口,需要我们主动实现它相关的方法。如默认态(Normal)、按压态(Pressed)、焦点态(Focused)、禁用态(Disabled)、选择态(Selected)
- AttributeModifier 可以实现样式属性的按需注册
- 支持和@Observed和@ObjectLink配套使用
AttributeModifier 基本使用
-
定义MyButtonModifier类,继承AttributeModifier接口,并且声明是对Button进行的样式属性封装
export class MyButtonModifier implements AttributeModifier<ButtonAttribute> { -
MyButtonModifier中声明变量,用来注册不同的样式属性
isDark: boolean = false -
定义正常态的样式 (applyNormalAttribute 是接口AttributeModifier中定义的 )
applyNormalAttribute(instance: ButtonAttribute): void {if (this.isDark) {instance.backgroundColor(Color.Black).fontColor(Color.White).border({width:10,color:Color.Brown}).borderRadius(20).padding(10).margin(20)} else {instance.backgroundColor(Color.White).fontColor(Color.Black)}}
-
组件中开始复用(完整代码)
export class MyButtonModifier implements AttributeModifier<ButtonAttribute> {isDark: boolean = falseconstructor(dark?: boolean) {this.isDark = !!dark}applyNormalAttribute(instance: ButtonAttribute): void {if (this.isDark) {instance.backgroundColor(Color.Black).fontColor(Color.White).border({width:10,color:Color.Brown}).borderRadius(20).padding(10).margin(20)} else {instance.backgroundColor(Color.White).fontColor(Color.Black)}} }@Entry @Component struct attributeDemo {@State modifier: MyButtonModifier = new MyButtonModifier(false);build() {Row() {Column() {Button("Button")// 注册属性.attributeModifier(this.modifier).onClick(() => {// 点击切换this.modifier.isDark = !this.modifier.isDark})}.width('100%')}.height('100%')} } -
效果

AttributeModifier 其他状态
多态样式中除了默认态(Normal)还有 、按压态(Pressed)、焦点态(Focused)、禁用态(Disabled)、选择态(Selected)。我们一并实现。
// 按压applyPressedAttribute(instance: ButtonAttribute): void {instance.backgroundColor(Color.Red)}// 获得焦点applyFocusedAttribute(instance: ButtonAttribute): void {}// 选择applySelectedAttribute(instance: ButtonAttribute): void {}// 禁用applyDisabledAttribute(instance: ButtonAttribute): void {}

搭配 @Observed和@ObjectLink
上述案例中,样式的变更是根据 变量 isDark来实现的。如果想要根据对象中某个属性来实现样式的变更。我们可以搭配@Observed和@ObjectLink
对象嵌套对象
以下代码主要利用了 @Observed和@ObjectLink 可以监听深层次属性的改变,然后当深层次属性改变后,触发
AttributeModifier 跟随改变。
-
声明子类 Son,代表深层次属性的载体
@Observed class Son {// 控制样式切换的关键变量isShow: boolean = false } -
使用 @Observed 修饰 Person类 (父类),拥有Son子类
@Observed class Person {son: Son = new Son() } -
声明 BtnModifier 类,需要实现 AttributeModifier 接口,实现样式优化和复用。接收 son属性。用来响应状态变化
class BtnModifier implements AttributeModifier<ButtonAttribute> {son: Sonconstructor(son: Son) {this.son = son}applyNormalAttribute(instance: ButtonAttribute): void {if (this.son.isShow) {instance.backgroundColor(Color.Red)} else {instance.backgroundColor(Color.Green)}} } -
完整代码
import { promptAction } from '@kit.ArkUI';// 定义一个名为 'BtnModifier' 的类,实现对 'ButtonAttribute' 的属性修改 class BtnModifier implements AttributeModifier<ButtonAttribute> {// 存储一个 'Son' 类型的实例son: Son;// 构造函数,接收一个 'Son' 类型的参数并初始化 'son' 属性constructor(son: Son) {this.son = son;}// 应用普通属性的方法,接收一个 'ButtonAttribute' 类型的实例作为参数applyNormalAttribute(instance: ButtonAttribute): void {// 如果 'son' 的 'isShow' 属性为 true,则将按钮背景颜色设置为红色if (this.son.isShow) {instance.backgroundColor(Color.Red);} else {// 否则将按钮背景颜色设置为绿色instance.backgroundColor(Color.Green);}} }// 使用 '@Observed' 装饰器标记的类,表示该类的变化可以被观测到 @Observed class Son {// 定义一个布尔类型的属性 'isShow',初始值为 falseisShow: boolean = false; }// 使用 '@Observed' 装饰器标记的类,表示该类的变化可以被观测到 @Observed class Person {// 创建一个 'Son' 类型的实例并初始化son: Son = new Son(); }@Component struct CustomBtn {// 使用 '@ObjectLink' 装饰器标记的属性,表示与外部对象的链接@ObjectLinkson: Son;// 可空的 'BtnModifier' 类型属性modify: BtnModifier | null = null;// 在组件即将出现时执行的方法aboutToAppear(): void {// 创建一个新的 'BtnModifier' 实例并赋值给 'modify' 属性this.modify = new BtnModifier(this.son);}// 构建组件的方法build() {// 创建一个按钮,并将按钮的文本设置为 'son.isShow' 的字符串表示形式Button(this.son.isShow.toString())// 设置按钮的属性修改器为 'modify'.attributeModifier(this.modify);} }@Entry @Component struct Index {// 使用 '@State' 装饰器标记的属性,表示该属性的变化会触发组件的重新渲染@Stateperson: Person = new Person();build() {// 创建一个列容器Column() {// 创建一个自定义按钮组件,并传入 'person.son' 作为参数CustomBtn({ son: this.person.son })// 为按钮添加点击事件处理函数.onClick(() => {// 切换 'person.son.isShow' 的值this.person.son.isShow = !this.person.son.isShow;// 显示一个提示信息promptAction.showToast({ message: `${this.person.son.isShow}` });});}.width("100%").height("100%").justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center);} }

数组嵌套对象
数组嵌套对象的写法类似上面示例,但是可以通过简单的一些编程技巧来进一步优化。如单例
// 定义一个名为 'BtnModifier' 的类,实现对 'ButtonAttribute' 的属性修改
class BtnModifier implements AttributeModifier<ButtonAttribute> {// 静态变量,用于存储单例实例static instance: BtnModifier;// 表示是否在交谈的布尔属性,初始值为 falseisTalk: boolean = false;// 静态方法,用于获取单例实例static getInstance(): BtnModifier {// 如果单例实例不存在,则创建一个新的实例if (!BtnModifier.instance) {BtnModifier.instance = new BtnModifier();}// 返回单例实例return BtnModifier.instance;}// 设置 isTalk 属性的方法setTalk(isTalk: boolean): BtnModifier {// 更新 isTalk 属性值this.isTalk = isTalk;// 返回当前实例,以便进行链式调用return this;}// 应用普通属性的方法,接收一个 'ButtonAttribute' 类型的实例作为参数applyNormalAttribute(instance: ButtonAttribute): void {// 如果 isTalk 为 true,则将按钮背景颜色设置为红色if (this.isTalk) {instance.backgroundColor(Color.Red);} else {// 否则将按钮背景颜色设置为绿色instance.backgroundColor(Color.Green);}}
}// 使用 '@Observed' 装饰器标记的类,表示该类的变化可以被观测到
@Observed
class Person {// 用户名属性,初始值为 "人类"userName: string = "人类";// 表示是否在交谈的布尔属性,初始值为 falseisTalk: boolean = false;
}@Component
struct CustomBtn {// 使用 '@ObjectLink' 装饰器标记的属性,表示与外部对象的链接@ObjectLinkperson: Person;// 存储 'BtnModifier' 的实例,通过单例模式获取modify: BtnModifier = BtnModifier.getInstance();// 构建组件的方法build() {// 创建一个按钮,并将按钮的文本设置为 'person.userName'Button(this.person.userName)// 设置按钮的属性修改器,并根据 'person.isTalk' 的值设置是否在交谈状态.attributeModifier(this.modify.setTalk(this.person.isTalk));}
}@Entry
@Component
struct Index {// 使用 '@State' 装饰器标记的属性,表示该属性的变化会触发组件的重新渲染@StatepersonList: Person[] = [new Person(), new Person()];// 构建组件的方法build() {// 创建一个列容器Column() {// 遍历 'personList',为每个 'Person' 实例创建一个 'CustomBtn' 组件,并添加点击事件处理函数ForEach(this.personList, (person: Person) => {CustomBtn({ person: person }).onClick(() => {// 切换 'person.isTalk' 的值person.isTalk = !person.isTalk;});});}.width("100%").height("100%").justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center);}
}
AttributeModifier 和 @Styles 、@Extend的比较
| 能力 | @Styles | @Extend | AttributeModifier |
|---|---|---|---|
| 跨文件导出 | 不支持 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 通用属性设置 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 通用事件设置 | 支持 | 支持 | 部分支持 |
| 组件特有属性设置 | 不支持 | 支持 | 部分支持 |
| 组件特有事件设置 | 不支持 | 支持 | 部分支持 |
| 参数传递 | 不支持 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 多态样式 | 支持 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 业务逻辑 | 不支持 | 不支持 | 支持 |
基于以上对比,可以看见 AttributeModifier 几乎可以满足以上所有场景。唯一缺点就是代码量稍多一些些。
接口定义
declare interface AttributeModifier<T> {applyNormalAttribute?(instance: T): void;applyPressedAttribute?(instance: T): void;applyFocusedAttribute?(instance: T): void;applyDisabledAttribute?(instance: T): void;applySelectedAttribute?(instance: T): void;}
AttributeUpdater
如果设计大量的样式属性修改,如果都是基于状态变量,那么在实现修改前,还是会导致diff的对比,性能损耗验证。因此引入了 AttributeUpdater,它继承了AttributeModifier基本能力,还拓展了直接修改属性和组件构造函数的能力。用来根据单一状态来批量修改样式属性。
简单实用
- 声明 MyButtonUpdater 类,继承 AttributeUpdater
- 组件中实例化 MyButtonUpdater 类
- 直接修改组件样式属性
import { AttributeUpdater } from '@kit.ArkUI';// 注意,这里是继承 AttributeUpdater 类
class MyButtonUpdater extends AttributeUpdater<ButtonAttribute> {
}@Entry
@Component
struct attributeDemo {@State modifier: MyButtonUpdater = new MyButtonUpdater();build() {Row() {Column() {Button("直接修改批量样式属性").attributeModifier(this.modifier).onClick(() => {// 直接修改this.modifier.attribute?.backgroundColor(Color.Green).width(200).fontColor(Color.Red)})}.width('100%')}.height('100%')}
}

重新调用组件构造函数
提供了updateConstructorParams 接口,可以让我们重新调用该组件的构造函数。实现组件的重新渲染
-
继承 AttributeUpdater 类时,同时传入两个泛型 ButtonAttribute 和 ButtonInterface
class MyButtonUpdater extends AttributeUpdater<ButtonAttribute,ButtonInterface> {} -
直接调用要组件的构造函数 updateConstructorParams
import { AttributeUpdater } from '@kit.ArkUI';// 注意,这里是继承 AttributeUpdater 类 class MyButtonUpdater extends AttributeUpdater<ButtonAttribute,ButtonInterface> {}@Entry @Component struct attributeDemo {@State modifier: MyButtonUpdater = new MyButtonUpdater();build() {Row() {Column() {Button("重新渲染组件").attributeModifier(this.modifier).onClick(() => {this.modifier.updateConstructorParams("文本也可以改变")})}.width('100%')}.height('100%')} }

接口定义
export declare class AttributeUpdater<T, C = Initializer<T>> implements AttributeModifier<T> {applyNormalAttribute?(instance: T): void;initializeModifier(instance: T): void;get attribute(): T | undefined;updateConstructorParams: C;
}
总结
后期如果要考虑实现样式复用,可以优先使用 AttributeModifier 和 AttributeUpdater
作者
作者:万少
链接:https://www.nutpi.net/
來源:坚果派 著作权归作者所有。
商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。