- 🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊
具体实现
(一)环境
语言环境:Python 3.10
编 译 器: PyCharm
框 架:
(二)具体步骤
from absl.logging import warning
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.data import AUTOTUNE from utils import GPU_ON
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 第一步:准备环境
GPU_ON() # ##########output#############################################
# Tensorflow Version: 2.10.0# [PhysicalDevice(name='/physical_device:GPU:0', device_type='GPU')]
# [PhysicalDevice(name='/physical_device:GPU:0', device_type='GPU')]
# ##########end output##########################################
# 支持中文
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号 import os, PIL, pathlib # 隐藏警告
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # 第二步:导入数据
data_dir = "./datasets/365-7-data"
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
image_count = len(list(data_dir.glob('*/*')))
print("图片总数为:", image_count)
# ########output##############################################
# 图片总数为: 3400# ########end output########################################## # 第三步:数据预处理
batch_size = 8
img_height, img_width = 224, 224
train_ds = tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory( data_dir, validation_split=0.2, subset="training", seed=123, image_size=(img_height, img_width), batch_size=batch_size,
)
# ############output##########################################
# Found 3400 files belonging to 2 classes.
# Using 2720 files for training.
##############end output###################################### val_ds = tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory( data_dir, validation_split=0.2, subset="validation", seed=123, image_size=(img_height, img_width), batch_size=batch_size,
)
# ############output##########################################
# Found 3400 files belonging to 2 classes.
# Using 680 files for validation.
# ###############end output##################################
# 获取名称标签
class_names = train_ds.class_names
print(class_names)
# #################output######################################
# ['cat', 'dog']
###################end output###################################
# 检查一下数据
for image_batch, labels_batch in train_ds: print(image_batch.shape) print(labels_batch.shape) break
# #############output########################################
# (8, 224, 224, 3) ---每一批8张图片,长224,宽224,RGB彩色通道(3)
# (8,) --- 标签就是一批8张图片的标签
# #############end output###################################
# 预处理
AUTOTUNE = tf.data.AUTOTUNE def preprocess_image(image, label): return (image / 255.0, label) # 归一化处理
train_ds = train_ds.map(preprocess_image, num_parallel_calls=AUTOTUNE)
val_ds = val_ds.map(preprocess_image, num_parallel_calls=AUTOTUNE) # cache() ----将数据集缓存到内存当中 加速运行
# shuffle() ----打乱数据
# prefetch() ----预取数据,加速运行
train_ds = train_ds.cache().shuffle(1000).prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE)
val_ds = val_ds.cache().prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE) # 可视化数据
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10)) # 创建一个顶层容器,大小是15*20英寸
for images, labels in train_ds.take(1): for i in range(8): # 向当前图添加坐标轴, 我们想在1行显示8张图片,所以是1行8列 ax = plt.subplot(1, 8, i + 1) print(images[i]) # imshow()--将数据显示为图像,支持的数据类型(M,N)标量数据/(M,N,3)RGB数据/(M,N,4)RGBA数据。本例中是RGB plt.imshow(images[i]) plt.title(class_names[labels[i]]) # 显示坐标轴标签 plt.axis('off') # 隐藏所有的轴信息 plt.show()

# 第四步:构建VGG16网络模型
from tensorflow.keras import layers, models, Input
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
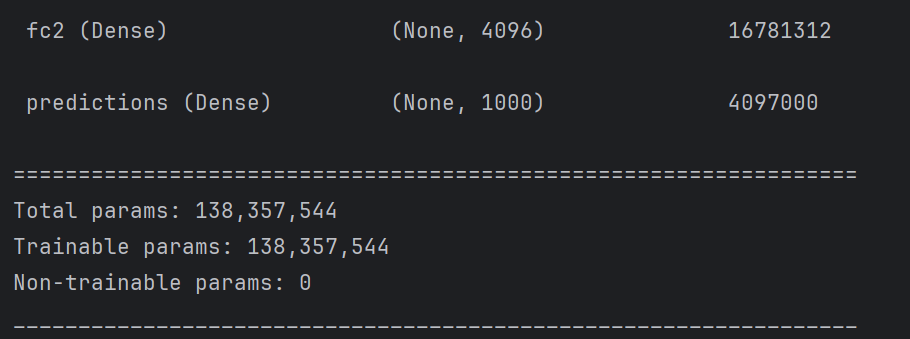
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Dense, Flatten, Dropout def VGG16(nb_classes, input_shape): input_tensor = Input(shape=input_shape) # 1st block x = Conv2D(64, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block1_conv1')(input_tensor) x = Conv2D(64, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block1_conv2')(x) x = MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2), name = 'block1_pool')(x) # 2nd block x = Conv2D(128, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block2_conv1')(x) x = Conv2D(128, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block2_conv2')(x) x = MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2), name = 'block2_pool')(x) # 3rd block x = Conv2D(256, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block3_conv1')(x) x = Conv2D(256, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block3_conv2')(x) x = Conv2D(256, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block3_conv3')(x) x = MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2), name = 'block3_pool')(x) # 4th block x = Conv2D(512, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block4_conv1')(x) x = Conv2D(512, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block4_conv2')(x) x = Conv2D(512, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block4_conv3')(x) x = MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2), name = 'block4_pool')(x) # 5th block x = Conv2D(512, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block5_conv1')(x) x = Conv2D(512, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block5_conv2')(x) x = Conv2D(512, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block5_conv3')(x) x = MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2), name = 'block5_pool')(x) # full connection x = Flatten()(x) x = Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='fc1')(x) x = Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='fc2')(x) output_tensor = Dense(nb_classes, activation='softmax', name='predictions')(x) model = Model(input_tensor, output_tensor) return model model=VGG16(1000, (img_width, img_height, 3))
model.summary()
# 第五步:编译
model.compile(loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', # 损失函数 optimizer='adam', # 优化函数 metrics=['accuracy']) # 模型评估的指标,一般是accuracy
# 第六步:训练模型
from tqdm import tqdm
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K epochs = 10
lr = 1e-4 # 记录训练数据,方便后面分析
history_train_loss = []
history_val_loss = []
history_train_accuracy = []
history_val_accuracy = [] for epoch in range(epochs): train_total = len(train_ds) val_total = len(val_ds) """ total: 预期的迭代数目 ncols: 控制进度条宽度 mininterval: 进度条更新最小间隔,以秒为单位(默认为0.1) """ with tqdm(total=train_total, desc=f'Epoch {epoch + 1}/{epochs}', mininterval=1, ncols=100) as pbar: lr = lr * 0.92 K.set_value(model.optimizer.lr, lr) for image, label in train_ds: history = model.train_on_batch(image, label) train_loss = history[0] train_accuracy = history[1] pbar.set_postfix({ "loss": "%.4f" % train_loss, "accuracy": "%.4f" % train_accuracy, "lr": K.get_value(model.optimizer.lr), }) pbar.update(1) history_train_loss.append(train_loss) history_train_accuracy.append(train_accuracy) print('开始验证!') with tqdm(total=val_total, desc=f'Epoch {epoch + 1}/{epochs}', mininterval=0.3, ncols=100) as pbar: for image, label in val_ds: history = model.test_on_batch(image, label) val_loss = history[0] val_accuracy = history[1] pbar.set_postfix({ "loss": "%.4f" % val_loss, "accuracy": "%.4f" % val_accuracy }) pbar.update(1) history_val_loss.append(val_loss) history_val_accuracy.append(val_accuracy) print('结束验证!') print('验证loss为:%.4f'%val_loss) print('验证准确率为:%.4f'%val_accuracy)
# 第七步:评估模型 [# 采用加载的模型(new_model)来看预测结果
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 3)) # 图形的宽为18高为5
plt.suptitle("预测结果展示") for images, labels in val_ds.take(1): for i in range(8): ax = plt.subplot(1, 8, i + 1) # 显示图片 plt.imshow(images[i].numpy()) # 需要给图片增加一个维度 img_array = tf.expand_dims(images[i], 0) # 使用模型预测图片中的人物 predictions = model.predict(img_array) plt.title(class_names[np.argmax(predictions)]) plt.axis("off")
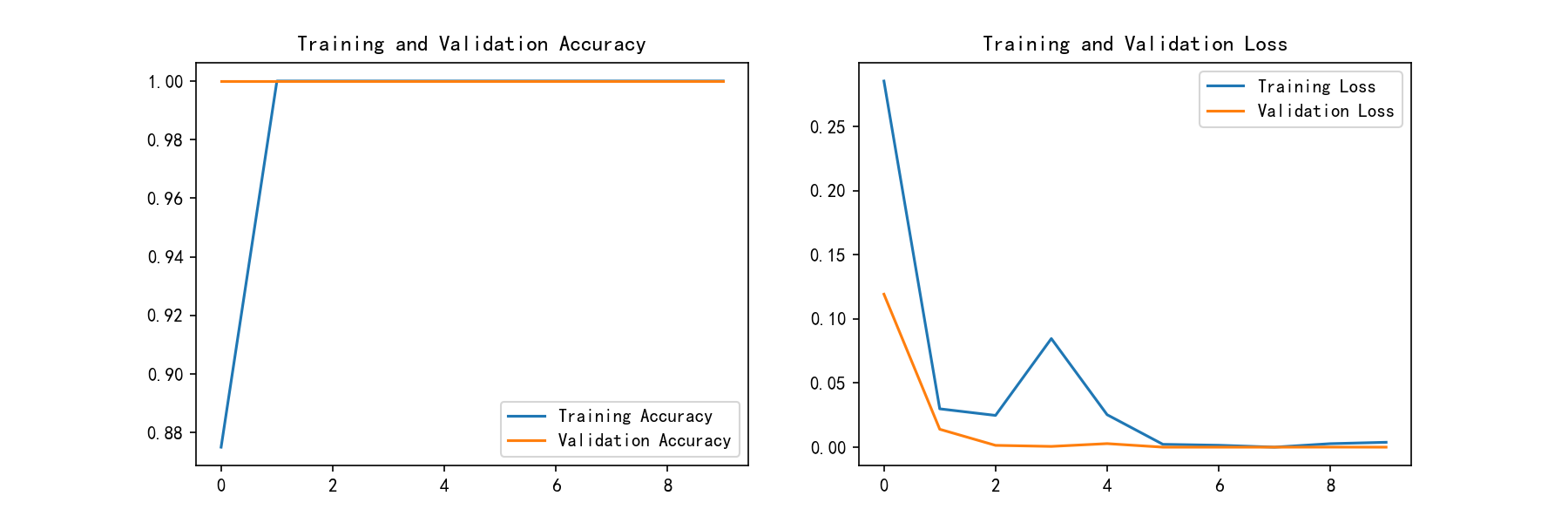
plt.show()](<epochs_range = range(epochs)plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)plt.plot(epochs_range, history_train_accuracy, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, history_val_accuracy, label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs_range, history_train_loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, history_val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.show()>)

# 第八步:预测
import numpy as np
# 采用加载的模型(new_model)来看预测结果
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 3)) # 图形的宽为18高为5
plt.suptitle("预测结果展示") for images, labels in val_ds.take(1): for i in range(8): ax = plt.subplot(1, 8, i + 1) # 显示图片 plt.imshow(images[i].numpy()) # 需要给图片增加一个维度 img_array = tf.expand_dims(images[i], 0) # 使用模型预测图片中的人物 predictions = model.predict(img_array) plt.title(class_names[np.argmax(predictions)]) plt.axis("off")
plt.show()