此笔记来自于B站黑马程序员 good
Java 历史版本及其优势

函数式编程, Stream API
一.函数伊始函数、函数对象
函数对象
行为参数法
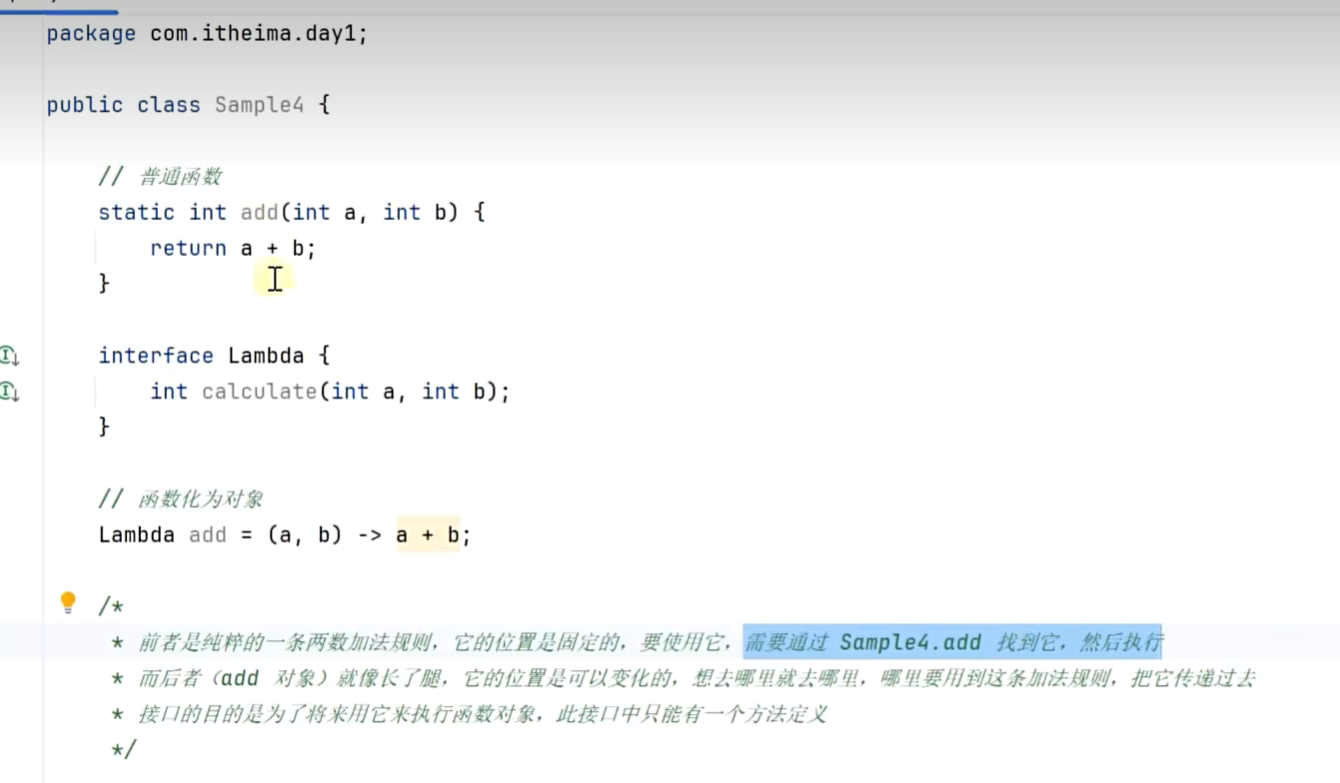
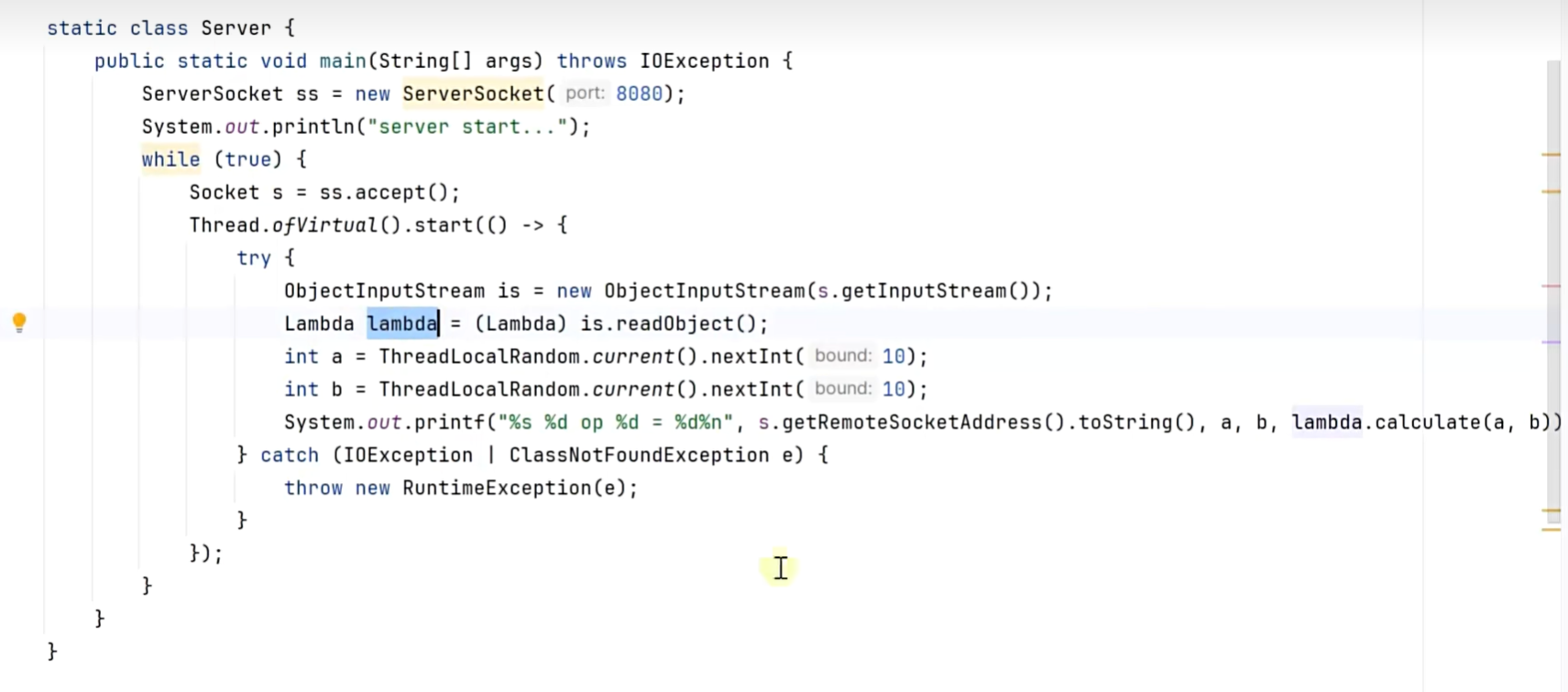
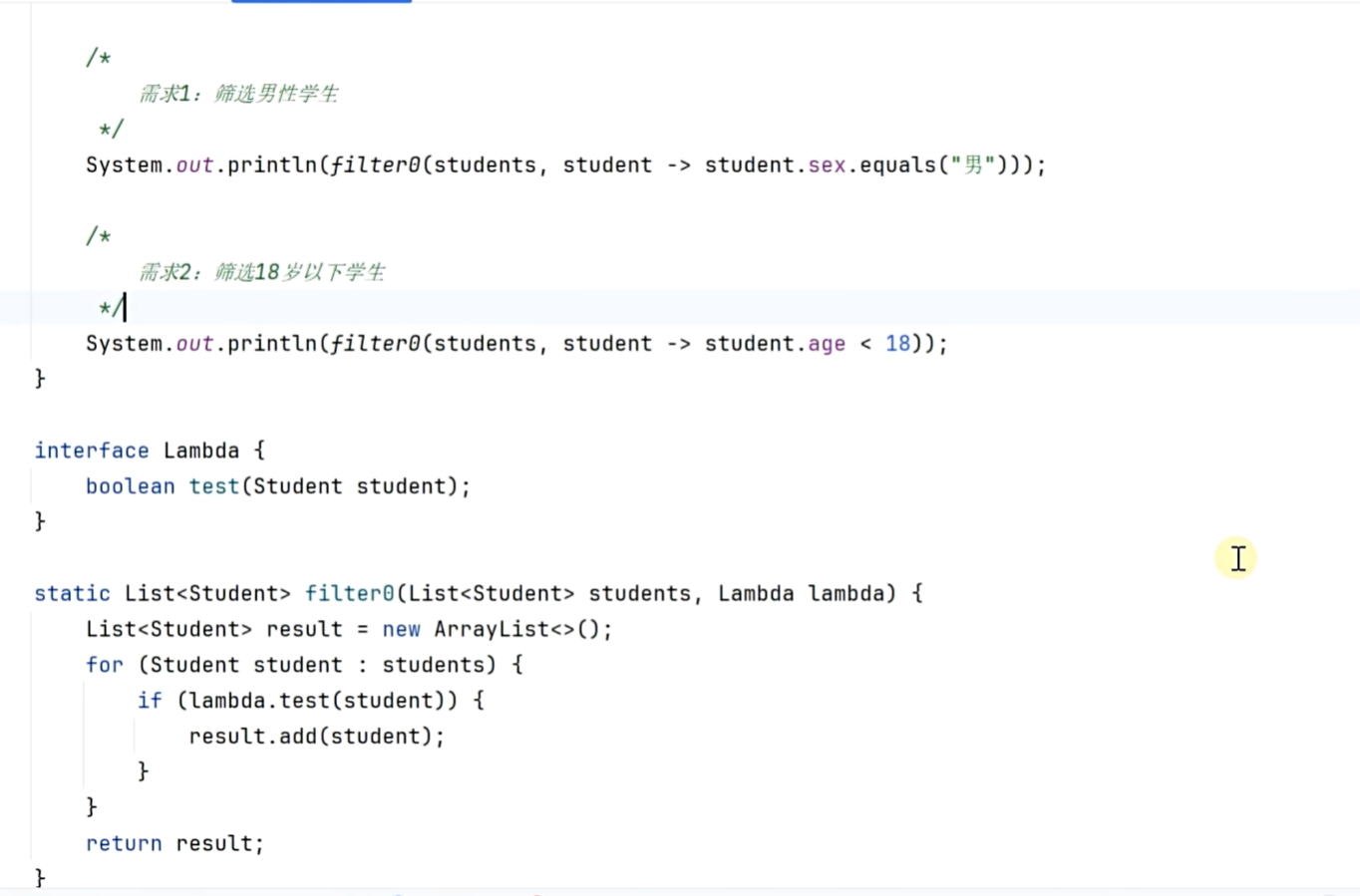
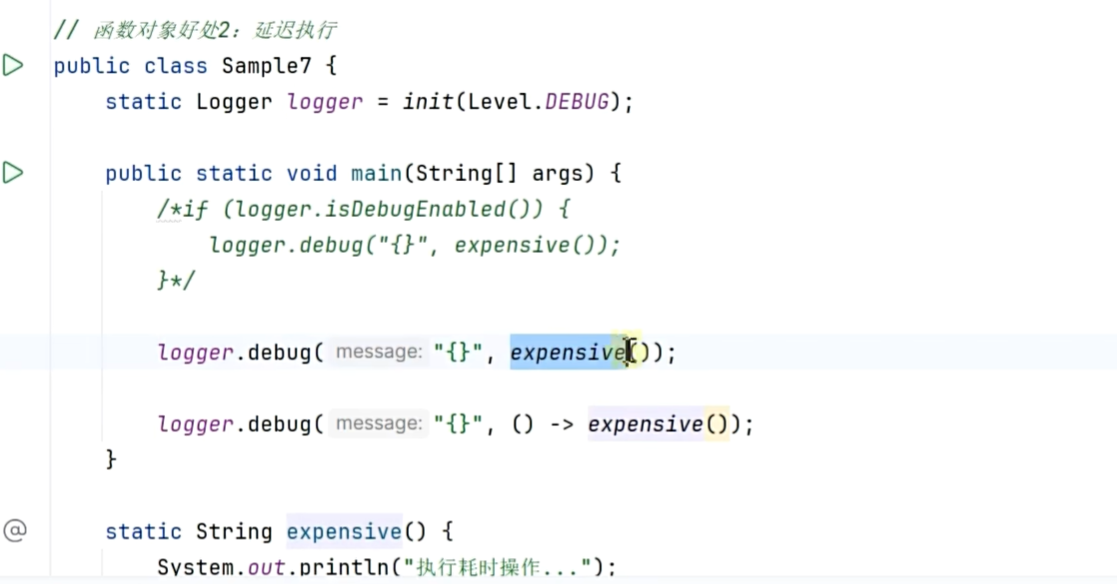
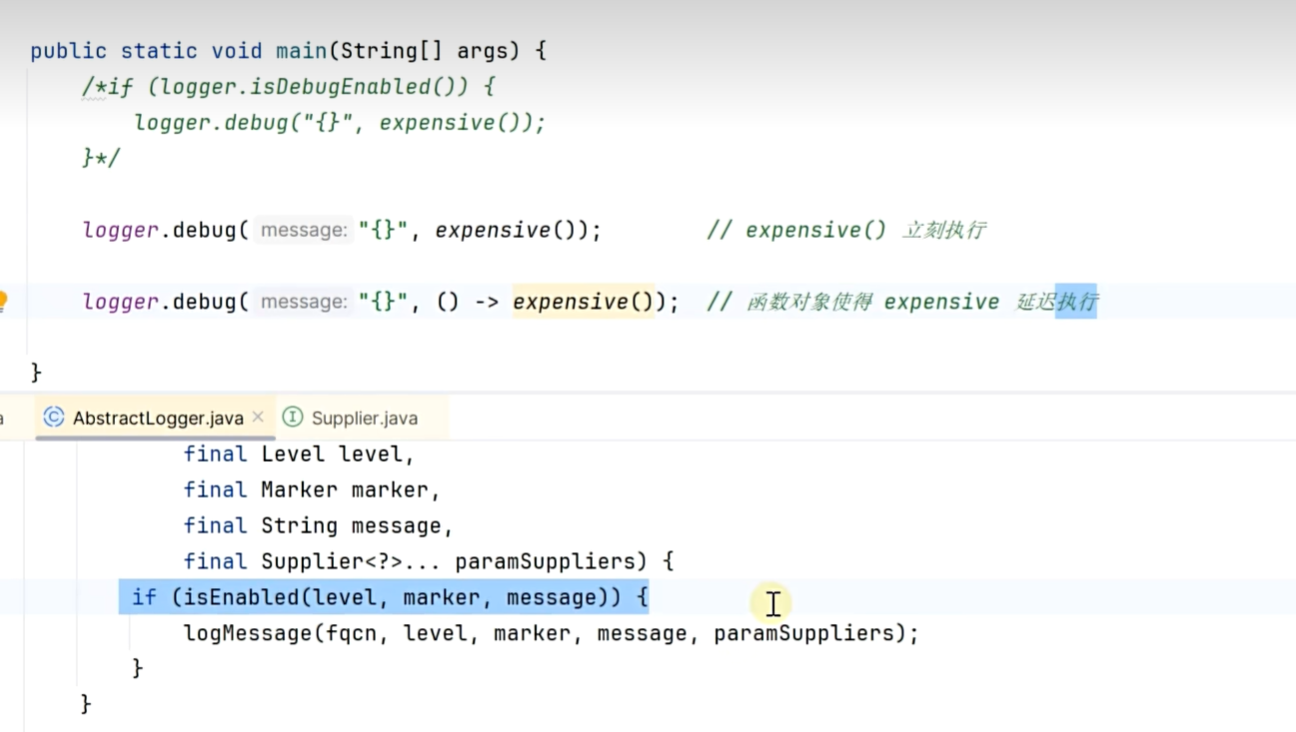
延迟执行
a-lambda

b-方法引用

复习小测
- Math::random
() -> Math.random() - Math::sqrt
(double number) -> Math.sqrt(number) - Student::getName
(student stu) -> stu.getName() - Student::setName
(Student stu,String newName) -> stu.setName(newName) - Student::hashcode
(student stu) -> stu.hashcode() - Student::equals
(Student stu, object o) -> stu.equals(o)
假设已有对象 Student stu = new Student(“张三”);
- stu::getName
() -> stu.getName()
- stu::setName
(String newName) -> stu.setName(newName)
- Student::new
(String name) -> new Student(name)
二.函数编程语法 Lambda、方法引用、闭包、柯里化、高阶函数
函数对象类型
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.math.BigInteger;
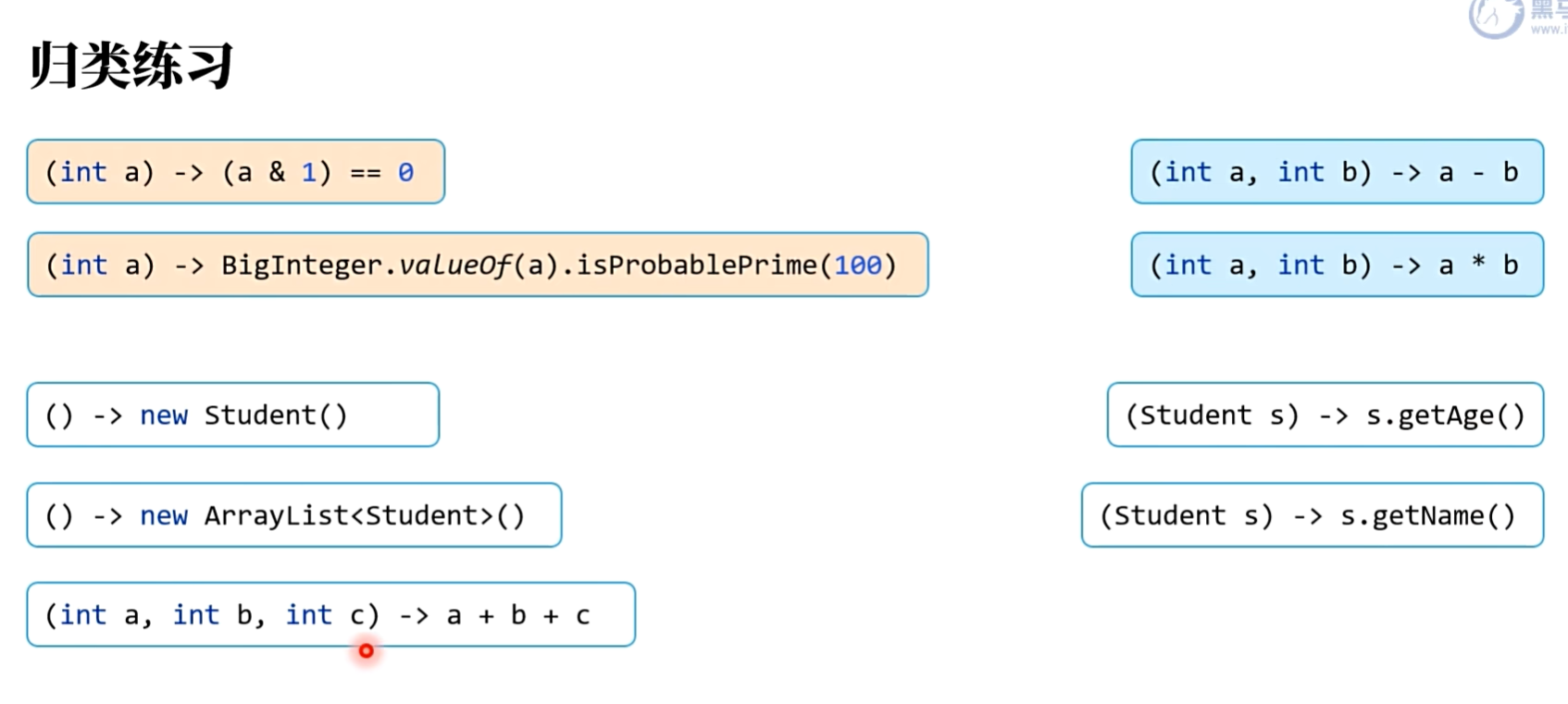
import java.util.ArrayList;public class CategoryTest {static class Student{private String name;public Student(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getName() { return name; }public void setName(String name) {this.name=name;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(object o){...}@0verridepublic int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name);}}public static void main(String[] args) {IntPredicate(int a) -> (a & 1) == 0;IntPredicate(int a) -> BigInteger.valueOf(a).isProbablePrime(100);(int a, int b, int c) -> a + b + c;IntBinaryOperator(int a, int b) -> a - b;IntBinaryOperator(int a, int b) -> a * b;Supplier<Student>() -> new Student();Supplier<List<Student>>() -> new ArrayList<Student>();Function<Studetn, String> obj8 <String, Student> obj8 = (Student s) -> s.getName();Function<Student, Integer> obj9 (Type7)<Integer, Student> obj9 = (Student s) -> s.getAge();}@FunctionalInterfaceinterface Type1 {boolean op(int a); // 只能有一个抽象方法}@FunctionalInterfaceinterface Type7<O, I> {O op(I input);}
}
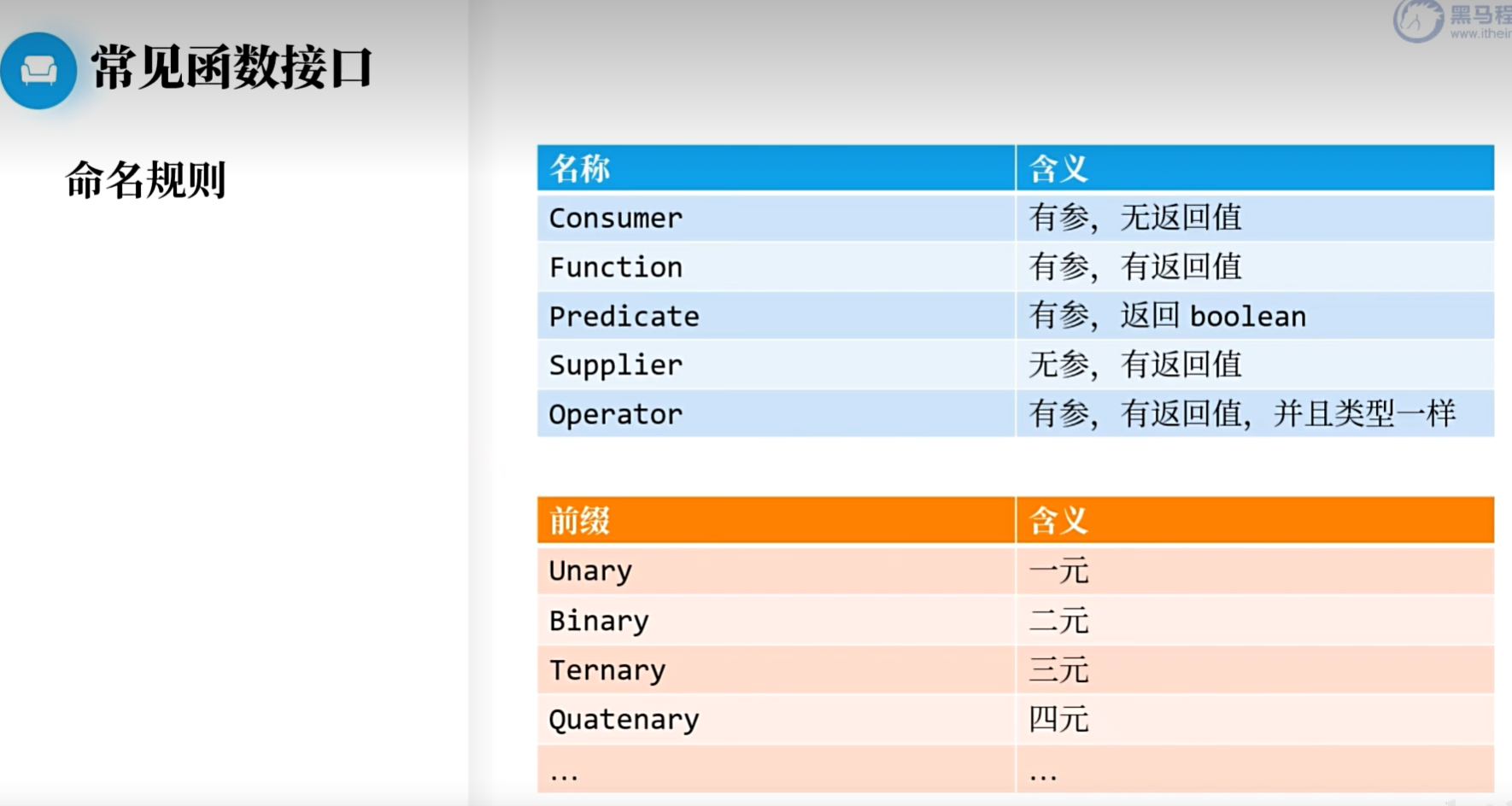
常见的函数接口

使用函数接口来解决问题
public class test04 {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> result = supply(5, () -> ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt());System.out.println(result);}static List<Integer> filter(List<Integer> list, Predicate<Integer> predicate) { ... };static List<String> map(List<Integer> list, Function<Integer, String> func) { ... };static void consume(List<Integer> list, Consumer<Integer> consumer) { ... }static List<Integer> supply(int count, Supplier<Integer> supplier) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {// 生成:随机数,但以后可能改变生成规则result.add(supplier.get());}return result;/**() -> ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt();*/}
}
方法引用

类名:静态方法

public class MethodRef1 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*需求:挑选出所有男性学生*/Stream.of (new Student("张无忌", "男"),new Student("周芷若", "女"),new Student("宋青书","男"))// .filter(stu -> stu.sex().equals("男")); lambda 表达式方式.filter(MethodRef1::isMale);// .forEach(sut -> System.out.println(sut)) lambda 表达式方式.forEach(MethodRef1::abc); // 静态方法引用方式/*(Student stu) -> stu.sex().equals("男")(Student stu) -> MethodRef1.isMale(stu)*/public static boolean isMale(Student stu) {return stu.sex().equals("男"); }public static void abc(Student stu) {System.out.println(stu);}}
}
类名:非静态方法

public class MethodRef1 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*需求:挑选出所有男性学生*/Stream.of (new Student("张无忌", "男"),new Student("周芷若", "女"),new Student("宋青书","男"))// .filter(stu -> stu.sex().equals("男")); lambda 表达式方式.filter(MethodRef1::isMale);// .forEach(sut -> System.out.println(sut)) lambda 表达式方式// .forEach(MethodRef1::abc); // 静态方法引用方式.forEach(Student::print);/*(Student stu) -> stu.sex().equals("男")(Student stu) -> MethodRef1.isMale(stu)*/public static boolean isMale(Student stu) {return stu.sex().equals("男"); }public static void abc(Student stu) {System.out.println(stu);}record Student(String name, String sex) {public void print() {System.out.println(this);}/*** Student::print* (stu) -> stu.print()*/}}
}

public class MethodRef3 {static class Util {public boolean isMale(Student stu) {return stu.sex().equals("男");}}public static void main(String[] args) {Util uitl = new Util();Stream.of (new Student("张无忌", "男"),new Student("周芷若", "女"),new Student("宋青书","男")).filter(util::isMale).map(Student::getName).forEach(System.out::println);}/*** (stu) -> util.isMale(stu)*/record Student(String name, String sex) {public String getName() {return this.name;}/*** Student::name* stu -> stu.name()*/}
}
构造方法

import java.util.function.Supplier;@toString
public class MethodRef4 {static class Student {private final String name;private final Integer age;public Student() { ... }public Student(String name) { this.name = name }public Student(String name, Integer age) {this.name = name; this.age = age}@Overridepublic String toString() {}}public static void main(String[] args) {Supplier<Student> s1 = Student::new;Function<String, Student> s2 = Student::new;BiFunction<String, Integer, Student> s3 = Student::new;System.out.println(s1.get());System.out.println(s2.apply("张三"));System.out.println(s3.apply("李四", 25));}
}

public class MethodRef5 {public static void main(String[] args) {Util util = new UtilExt();util.hiOrder(Stream.of (new Student("张无忌", "男"),new Student("周芷若", "女"),new Student("宋青书","男")));}record Student(String name, String sex) { }static class Util {// 过滤男性学生并打印private bollean isMale(Student stu) {return stu.sex().equals("男");}private boolean isFemale(Student stu) {return stu.sex().equals("女");}void hiOrder(Stream<Student> stream) {stream// .filter(stu->this.isMale(stu)).filter(this.isMale).forEach(System.out::println);}}static class UtilExt extends Util {// 过滤女性学生并打印void hiOrder(Stream<Student> stream) {stream.filter(super::isFemale).forEach(System.out::println);}}
}

对于无需返回值的函数接口,例如 Consumer 和 Runnable 它们可以配合有返回值的函数对象使用
import java.util.function.Consumer;public class MethodRef7 {public static void main(String[] args) {Consumer<Object> x = MethodRef7::print1;Function<Object, Integer> y = MethodRef7::print2;Consumer<Object> z = MethodRef7::print2;static void print1(Object obj) {System.out.println(obj);}static int print2(Object obj) {System.out.println(obj);return 1;}}
}
public class Exercise4 {record Student(String name) { }// 写出与下列 lamdba表达式 等价的方法引用public static void main(String[] args) {Function<String, Integer> lambda1 = Integer::parseInt;// Function<String, Integer> lambda = (String s) -> Integer.parseInt(S);// BiPredicate<List<String>, String> lambda2 = (list, element) -> list.contains(element);BiPredicate<List<String>, String> lambda2 = List::contains;// BiPredicate<Student, Object> lambda3 = (stu, obj) -> stu.equals(obj);BiPredicate<Student, Object> lambda3 = Student::equals;// Predicate<File> lambda4 = (file) -> file.exists();Predicate<File> lambda4 = File::exists;// Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();// Supplier<Long> lambda5 = () -> runtime.freeMemory();Supplier<Long> lambda5 = Runtime.getRuntime()::freeMemory;}
}
例二
public class Exercise5 {record Color(Integer red, Integer green, Integer blue) { }// 如果想用 'Color::new' 来构造 Color 对象,还应当补充哪些代码public static void main(Stirng[] args) {TrenaryFunction lambda = Color::new; // (Integer, Integer, Integer) -> ColorColor white = lambda.create(255, 255, 255);System.out.println(white);}@FunctionalInterfaceinterface TernaryFunction {Color create(Integer red, Integer green, Integer blue);}
}
public class Exercise6 {/*** 传入参数时,分别用* 类名::静态方法* 类名::非静态方法* 来表示 [学生年龄大于等于18] 的条件*/static void highOrder(Predicate<Student> predicate) {List<Student> list = List.of(new Student("张三", 18),new Student("张三", 17),new Student("张三", 20));for (Student stu : list) {if (predicate.test(stu)) {System.out.println(stu + "通过测试");}}record Student(String name, int age) {boolean abc() {return this.age() >= 18;}}static boolean ageGreaterOrEquals18(Student student) {return studetn.age() >= 18;}public static void main(String[] args) {highOrder(Exercise6::abc);/*** (Exercise6 obj, Student student) -> obj.abc(student)*/}}}
闭包

public class ClosureTest1 {@FunctionalInterfaceinterface Lambda {int op(int y);}static void highOrder(Lambda lambda) { System.out.println(lambda.op(1)); }public static void main(String[] args) {/**** 函数对象 (int y) -> x + y 与它外部的变量 x 形成闭包* effective final <===> final*/final int x = 10;highOrder((int y) -> x + y);stu.d = 40;highOrder(lambda);}static int a = 1;int b = 2;static class Student {int d;public Student(int d) {this.d = d;}}public static void test(int c) {highOrder(y -> a + y);highOrder(y -> b + y);highOrder(y -> c + y);}
}
public class ClosureTest2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 闭包作用:给函数对象提供参数以外的数据List<Runnable> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {int k = i + 1;Runnable task = () -> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "执行任务" + k);list.add(task);}ExecutorService service = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExcutor();for (Runnable task : list) {service.submit(task);}System.in.read();} }
public class CarryingOTest {@FunctionalInterfaceinterface F2 {int op(int a, int b);}@FunctionalInterfaceinterface Fa {Fb op(int a);}@FunctionalInterfaceinterface Fb {int op(int b);}public static void main(String[] args) {// 两个参数的函数对象F2 f2 = (a, b) -> a + b;System.out.println(f2.op(10, 20));/*** 改造* (a) -> 返回另一个参数* (b) -> a + b*/ Fa fa = (a) -> (b) -> a + b;Fb fb = fa.op(10);int r = fb.op(20);System.out.println(r);}}
示例二
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class Carrying1Test {@FunctionalInterfaceinterface Fa {Fb op(List<Integer> a);}@FunctionalInterfaceinterface Fb {Fc op(List<Interger> b);}@FunctionalInterfaceinterface Fc {List<Integer> op(List<Integer> c);}static Fc step2(Fb fb) {List<Integer> y = List.of(4, 5, 6);return fb.op(y);}static void step3(Fc fc) {List<Integer> z = List.of(7, 8, 9);List<Integer> result = fc.op(z);System.out.println(result);}public static void main(String[] args) {step3(step2(step1()));}}
高阶函数
所谓高阶,就是指它是其它函数对象的使用者
- 将通用、复杂的逻辑隐含在高阶函数内
- 将易变、未定的逻辑放在外部的函数对象中

public class InnerLoop {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7);// 需求:逆序遍历集合,只想负责元素处理,不改变集合hiOrder(list, (value) -> System.out.println(value));}public static void void hiOrder(List<Integer> list, Consumer<Integer> consumer) {ListIterator<Integer> iterator = list.listInterator(list.size());while (iterator.hasPrevious()) {Integer value = iterator.previous();consumer.accept(value);}}
}

import java.util.LinkedList;public class BinaryTree {public record TreeNode(int value, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {public String toString() { return "%d".formatted(value); }}enum Type {PRE, IN, POST}public static void traversal(TreeNode root, Type type, Consumer<TreeNode> consumer) { // 用来记住回去的路LinkedList<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();// 当前节点TreeNode curr = root;// 记录最近一次处理完的节点TreeNode last = null;while (curr != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {// 左边未走完if (curr != null) {// 记住来时的路stack.push(curr);if (type == Type.PRE) {consumer.accept(curr);}// 下次向左走curr = curr.left;} else {TreeNode peek = stack.peek();if (peek.right == null) {if (type == Type.IN || type == Type.POST) {consumer.accept(peek);}last = stack.pop();} else if (peek.right == last) {if (type == Type.POST) {consumer.accept(peek);}last = stack.pop();} else {if (type == Type.POST) {consumer.accept(peek);}curr = peek.right;}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {/* 1/ \2 3/ / \ 4 5 6**/TreeNode root = new TreeNode(new TreeNode(2, new TreeNode(4, null, null), null),new TreeNode(3, new TreeNode(5, null, null), new TreeNode(6, null, null)));traversal(root, Type.PRE, System.out::print);System.out.println();traversal(root, Type.IN, System.out::print);System.out.println();traversal(root, Type.POST, System.out::print);System.out.println();}
}
stream

import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;public class SimpleStream<T> {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);SimpleStream.of(list).filter(x -> (x & 1) == 1) .map(x -> x * x).forEach(System.out::println);}public static <T> SimpleStream<T> of(Collection<T> collection) {return new SimpleStream<>(Collection);}private Collection<T> collection;private SimpleStream(Collection<T> collection) {this.collection = collection;}public SimpleStream filter(Predicate<T> predicate) {List<T> result = new ArrayList<>();for (T t : collection) {if (predicate.test(t)) {result.add(t);}}return new SimpleStream<>(result);}public <U> SimpleStream<U> map(Function<T, U> function) {List<U> result = new ArrayList<>();for (T t : collection) {U u = function.apply(t);result.add(U);}return new SimpleStream<>(result);}public void forEach(Consumer<T> consumer) {for (T t : collection) {consumer.accept(t);}}
}

import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;public class SimpleStream<T> {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);HashSet<Integer> collect = SimpleStream.of(list).collect(HashSet::new, HashSet::add); // HashSet::add (set, t) -> set.add(t)System.out.println(collect);StringBuilder collect2 = SimpleStream.of(list).collect(StringBuilder::new, StringBuilder::append);System.out.println(collect2);SimpleStream.of(list).collect(() -> new StringJoiner("-"), (joiner, t) -> joiner.add(String.valueOf(t)));SimpleStream.of(list).map(t->String.valueOf(t)).collect(()->new StringJoiner("-"), StringJoiner::add);System.out.println(collect3);// (StringJoiner, Integer) -> void// (StringJoiner, CharSequence) -> voidSimpleStream.of(list).filter(x -> (x & 1) == 1) .map(x -> x * x).forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println(SimpleStream.of(list).reduce(0, Integer::sum));System.out.println(SimpleStream.of(list).reduce(Integer.MAX_VALUE, Math::min));System.out.println(SimpleStream.of(list).reduce(Integer.MIN_VALUE, Math.max));}public static <T> SimpleStream<T> of(Collection<T> collection) {return new SimpleStream<>(Collection);}private Collection<T> collection;private SimpleStream(Collection<T> collection) {this.collection = collection;}// C 代表容器类型,supplier 用来创建容器public <C> C collect(Supplier<C> supplier, BiConsumer<C, T> consumer) {C c = supplier.get(); //创建了容器for (T t : collection) {consumer.accept(c, t); // 向容器中添加元素}return c;}// 新增public T reduce(T o, BinaryOperator<T> operator) {T p = o;for (T t : collection) { // t是本次遍历的元素p = operator.apply(p, t); // 累加器}return p;}public SimpleStream filter(Predicate<T> predicate) {List<T> result = new ArrayList<>();for (T t : collection) {if (predicate.test(t)) { // 过滤器result.add(t);}}return new SimpleStream<>(result);}public <U> SimpleStream<U> map(Function<T, U> function) {List<U> result = new ArrayList<>();for (T t : collection) {U u = function.apply(t);result.add(U);}return new SimpleStream<>(result);}public void forEach(Consumer<T> consumer) {for (T t : collection) {consumer.accept(t); // 遍历}}}

public class SimpleStream<T> {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3);/*key value1 12 23 24 15 1*/HashMap<Integer, Integer> collect = SimpleStream.of(list).collect(HashMap::new, (map, t) -> {if (!map.containsKey(t)) {map.put(t, 1);} else {Integer v = map.get(t);map.put(t, v + 1);}});System.out.println(collect);HashMap<Integer, AtomicInteger> collect2 = SimpleStream.of(List).collect(HashMap::new, (map, t) -> map.computeIfAbsent(t, k -> new AtomicInteger()).getAndIncrement());System.out.println(collect2);}
}
三. Stream API

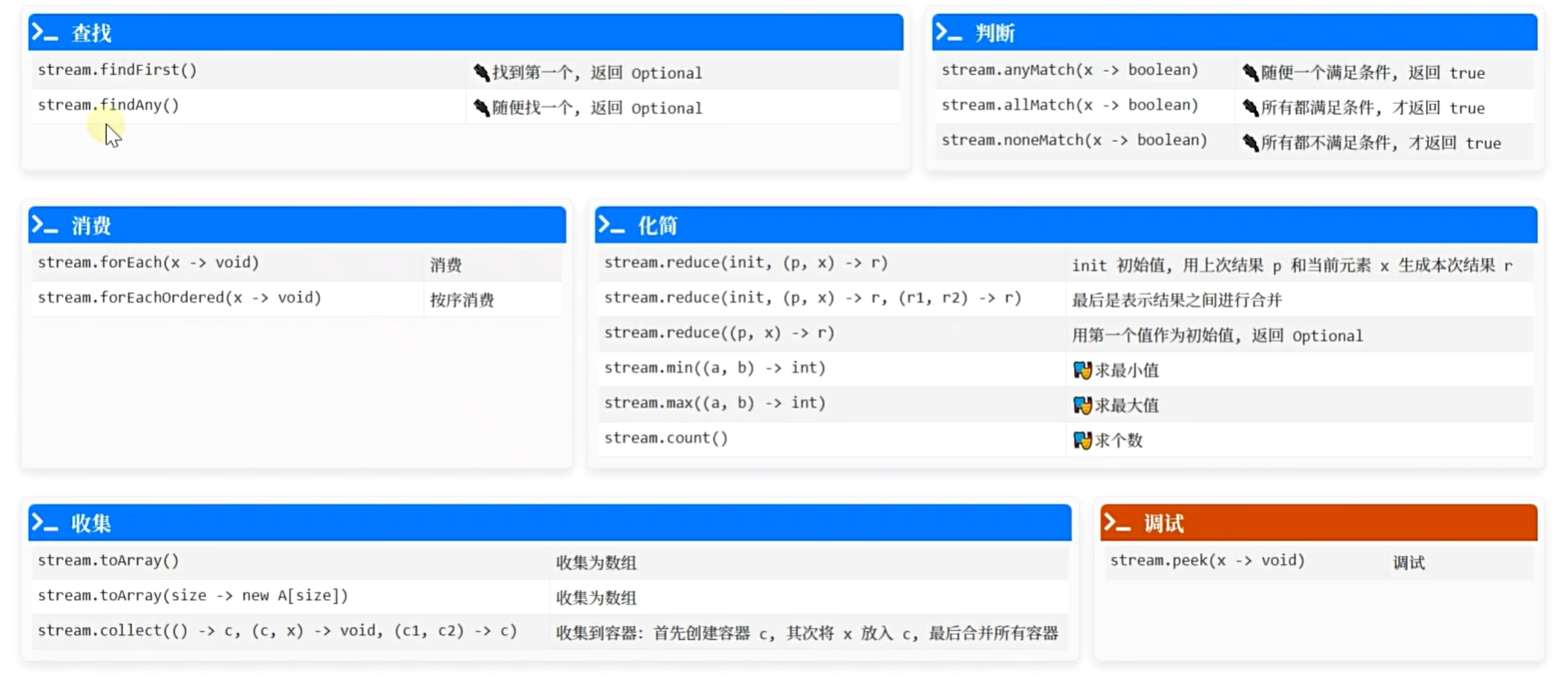
filter过滤 Predicate
public class FilterTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Stream.of (new Fruit(cname: "草莓", name: "Strawberry", category: "浆果", color: "红色"),new Fruit(cname: "桑葚", name: "Mulberry", category: "浆果", color: "紫色"),new Fruit(cname: "杨梅", name: "Waxberry", category: "浆果", color: "红色"),new Fruit(cname: "核桃", name: "Walnut", category: "坚果", color: "棕色"),new Fruit(cname: "花生", name: "Peanut", category: "坚果", color: "棕色"),new Fruit(cname: "蓝莓", name: "Blueberry", category: "浆果", color: "蓝色")).filter(f->f.category().equals("浆果")) // && f.color().equals("蓝色").filter(f->f.color().equals("蓝色")).forEach(System.out::println);}// Java 17新特性record Fruit(String cname, String name, String category, String color) {}
}
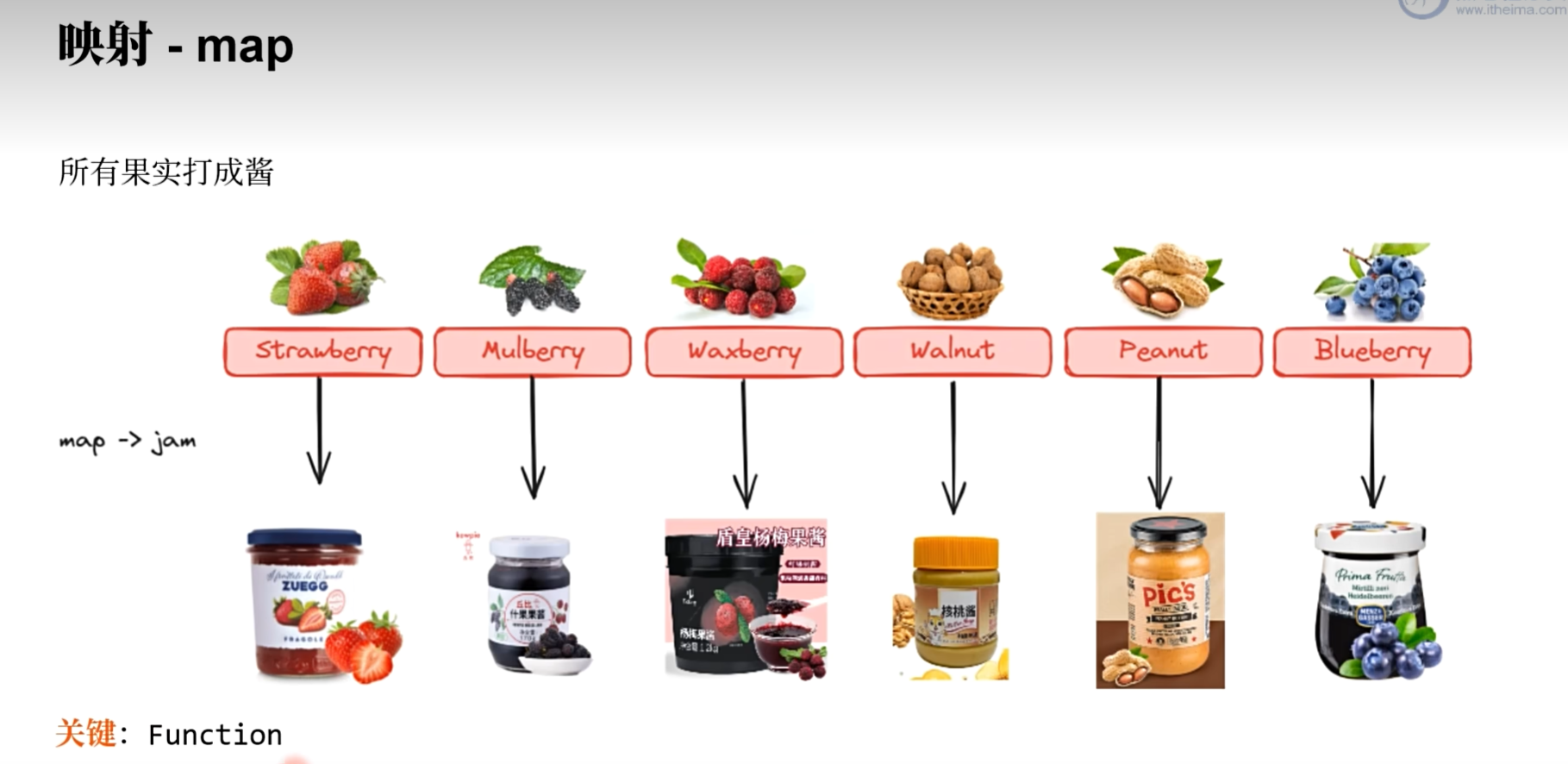
public class FilterTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Stream.of (new Fruit(cname: "草莓", name: "Strawberry", category: "浆果", color: "红色"),new Fruit(cname: "桑葚", name: "Mulberry", category: "浆果", color: "紫色"),new Fruit(cname: "杨梅", name: "Waxberry", category: "浆果", color: "红色"),new Fruit(cname: "核桃", name: "Walnut", category: "坚果", color: "棕色"),new Fruit(cname: "花生", name: "Peanut", category: "坚果", color: "棕色"),new Fruit(cname: "蓝莓", name: "Blueberry", category: "浆果", color: "蓝色")).map(f->f.cname()+"酱") // Stream<String>.forEach(System.out::println);}// Java 17新特性record Fruit(String cname, String name, String category, String color) {}
}
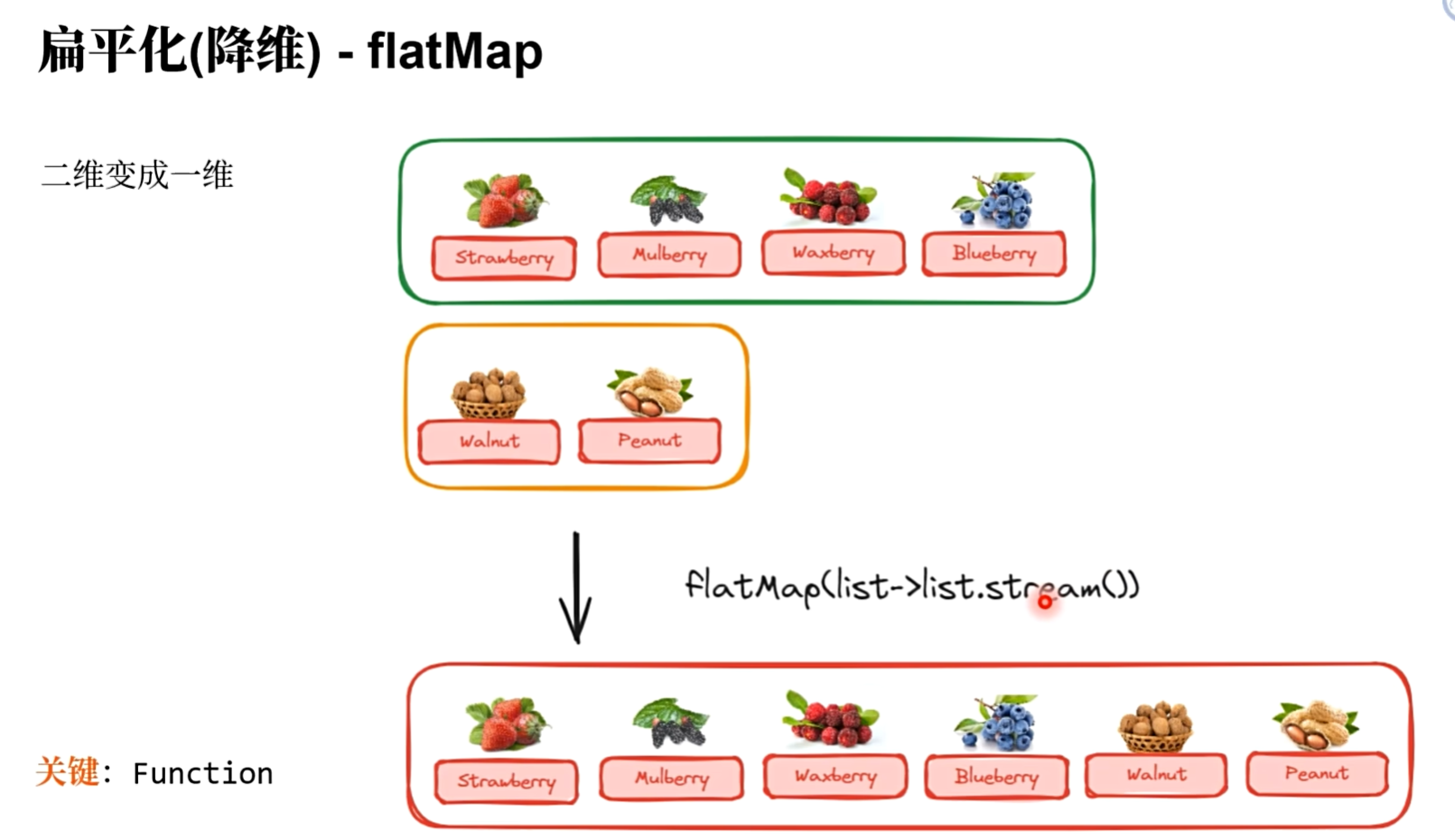
public class FilterTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer[][] array2D = {{1, 2, 3},{4, 5, 6},{7, 8, 9},};Arrays.stream(array2D).flatMap(array -> Arrays.stream(array)).forEach(System.out::println);// Java 17新特性record Fruit(String cname, String name, String category, String color) {}
}

import java.util.List;public class BuildStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 从集合构建Set.of(1, 2, 3).stream().forEach(System.out::println);Map.of("a", 1, "b", 2).entrySet().stream().forEach(System.out::println);int[] array = {1, 2, 3}Arrays.stream(array).forEach(System.out::println);// 3. 从对象构建Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).forEach(System.out::println);}
}
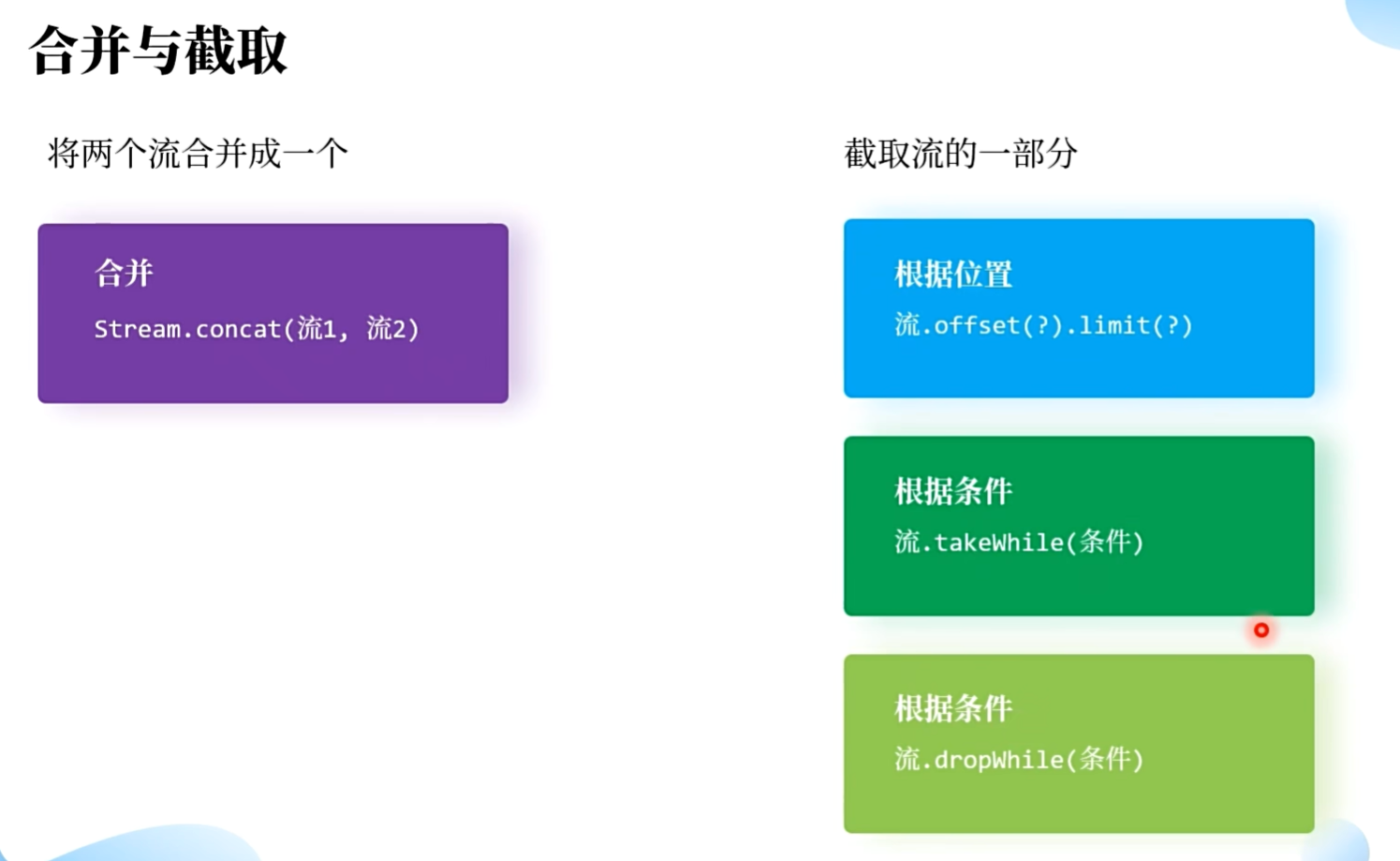
public class ConcatSplitTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 合并Stream<Integer> s1 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3);Stream<Integer> s2 = Stream.of(4, 5);Stream<Integer> concat = Stream.concat(s1, s2);concat.forEach(System.out::println);/*2. 截取 - 直接给出截取位置skip(long n) 跳过 n 个数据, 保留剩下的limit(long n) 保留 n 个数据,剩下的不要*/// concat.skip(2).forEach(System.out::print);concat.limit(2).forEach(System.out::print);/**takeWhile(Predicate p) 条件成立保留,一旦条件不成立,剩下的不要dropWhile(Predicate p) 条件成立舍弃,一旦条件不成立,剩下的保留*/concat.takeWhile(x -> x < 3).forEach(System.out::print);concat.dropWhile(x -> x < 3).forEach(System.out::print);}
}

public class GenerateTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. IntStream.rangeIntStream.rang(1, 10).forEach(System.out::println);IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 1).forEach(System.out::println);// 2. IntStream.iterate 生成 1 3 5 7 9 ... 奇数序列 可以根据上一个元素值来生成当前元素InStream.iterator(1, x -> x + 2).forEach(System.out::println); InStream.iterator(1, x -> x <= 9, x -> x + 2).forEach(System.out::println);// IntStream.generateIntStream.generate(() -> ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100)).limit(5).forEach(System.out::println);ThreadLocalRandom.current().ints(streamSize: 5, randomNumberOrigin: 0, randomNumber: 100).forEach(System.out::println);}
}

import java.util.stream.IntStream;public class FindTest {public static void main(String[] args) {IntStream stream = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);// 找到第一个偶数System.out.println(stream.filter(x -> (x & 1) == 0).findFirst().orElse(-1));stream.filter(x -> (x & 1) == 0).findFirst().ifPresent((x)->System.out.println(x));// 找到任意一个偶数stream.filter(x -> (x & 1) == 0).findAny().ifPresent((x) -> System.out.println(x));// 见名知意System.out.println(stream.anyMatch(x -> (x&1) == 0));System.out.println(stream.allMatch(x -> (x & 1)) == 0);System.out.println(stream.noneMatch(x -> (x & 1)) == 0);}
}
去重与排序
public class SortTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 去重IntStream.of(1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5).distince().forEach(System.out::println);// 排序Stream.of (// 排序new Hero(name: "令狐冲", strength: 90),new Hero(name: "风清扬", strength: 98),new Hero(name: "独孤求败", strength: 100),new Hero(name: "方证", strength: 92),new Hero(name: "东方不败", strength: 98),new Hero(name: "冲虚", strength: 90),new Hero(name: "向问天", strength: 88),new Hero(name: "任我行", strength: 92),new Hero(name: "不戒", strength: 88))// 重要:简洁但可能存在溢出问题。.sorted((a, b) -> a.strength() - b.strength()) // a.strenght < b.strength ? -1 : a.strength() == b.strength() ? 0 : 1// .sorted((a, b) -> Integer.compare(a.strength(), b.strength()))// .sorted((Comparator.comparingInt(h -> h.strength())).sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(Hero::strength).reverse().thenComparingInt(h->h.name.length())) .forEach(System.out::println);// Hero::strength <==> (h) -> h.strength();record Hero(String name, int strength) {}}
}
reduce
import java.util.stream.Stream;/*简化:两两合并,只剩下一个适合:最大值,最小值,求和,求个数....reduce((p, x) -> r) p 上次的合并结果,x 当前元素, r 本次合并结果.reduce(init, (p, x) -> r).reduce(init, (p, x) -> r, (r1, r2) -> r)
*/
public class ReduceTest {record Hero(String name, int strength) { ... }public static void main(String[] args) {Stream<Hero> result = Stream.of (new Hero(name: "令狐冲", strength: 90),new Hero(name: "风清扬", strength: 98),new Hero(name: "独孤求败", strength: 100),new Hero(name: "方证", strength: 92),new Hero(name: "东方不败", strength: 98),new Hero(name: "冲虚", strength: 90),new Hero(name: "向问天", strength: 88),new Hero(name: "任我行", strength: 92),new Hero(name: "不戒", strength: 88));// 1.求武力最高的 heroOptional<Hero> result = stream.reduce((h1, h2) -> h1.strength() > h2.strength() ? h1 : h2)Hero result = stream.reduce(new Hero("-", -1), (h1, h2) -> h1.strength() > h2.strength() ? h1 : h2);System.out.println(result);// 求高手总数System.out.println(stream.map(h -> 1).reduce(0, (a, b) -> a + b));System.out.println(stream.count());stream.max(Comparator.comparingInt(Hero::strength));stream.min(Comparator.comparingInt(Hero::strength));stream.mapToInt(Hero::strength).sum());stream.mapToInt(Hero::strength).average());}
}
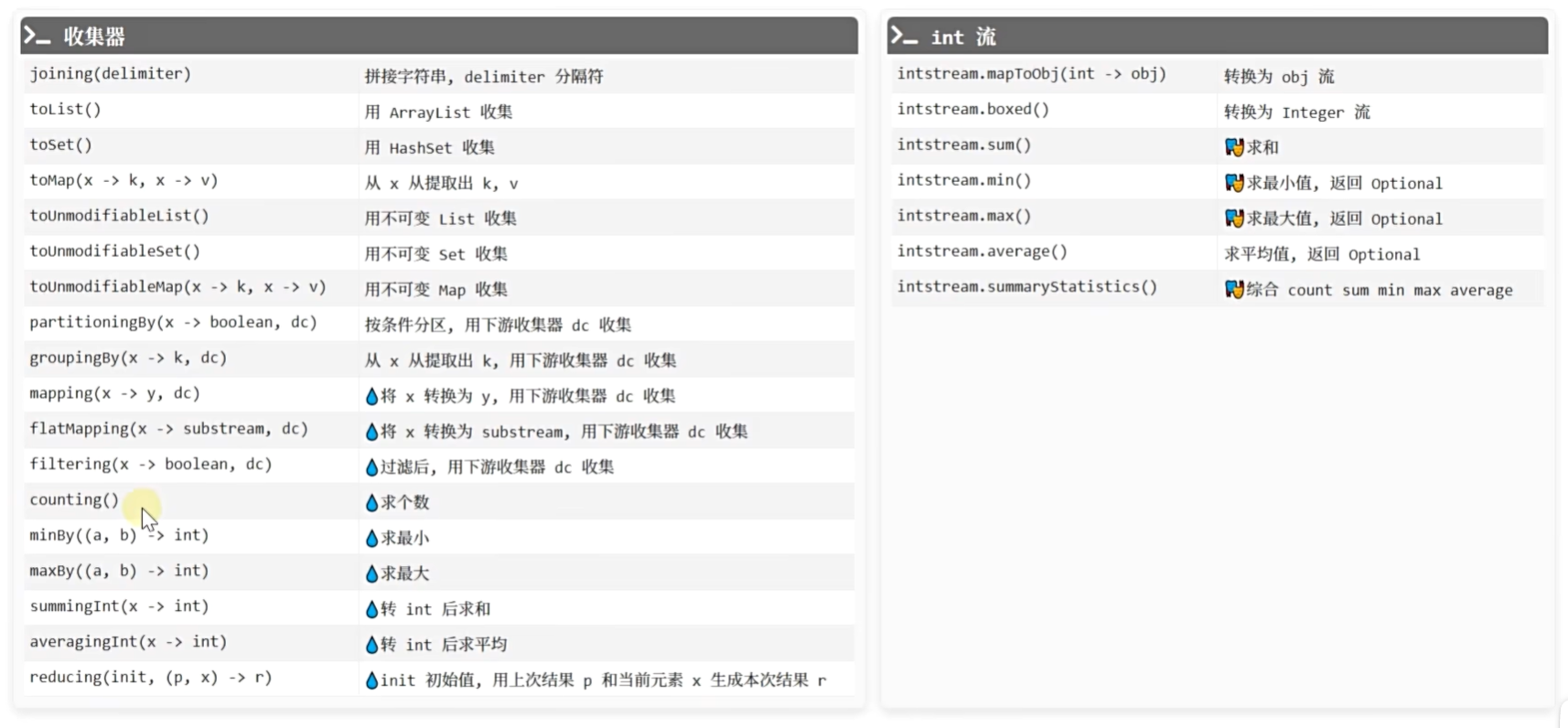
收集器

import java.util.stream.Stream;public class C11CollectTest {record Hero(String name, int strength) { ... }/*收集:将元素收集入容器.collect(() -> c, (c, x) -> void, ?)() -> c 创建容器 c(c, x) -> void 将元素 x 加入 容器 c*/public static void main(String[] args) {Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("令狐冲", "风清扬", "孤独求败", "方证", "东方不败","冲虚","向问天","任我行","不戒");// 1.收集到 ListList<String> result = stream.collect(() -> new ArrayList<>(), (list, x) -> list.add(x), (a, b) -> { });/*ArrayList::new () -> new ArrayList()ArrayList::add (list, x) -> list.add(x)能等价就等价看自己的风格或要求*/ // 缺点:不太方便调试List<String> result = stream.collect(ArrayList::new, ArrayList::add, (a, b) -> { });Set<String> result = stream.collect(LinkeeHashSet::new, Set::add, (a, b) -> { });Map<String, Integer> result = stream.collect(HashMap::new, (map, x) -> map.put(x, 1), (a, b) -> { });// 流空,不实现stream.collect(StringBuilder::new, StringBuilder::append, (a, b) -> { });stream.collect(() -> new StringJoiner(","), StringJoiner:add, (a, b) -> { });}
}
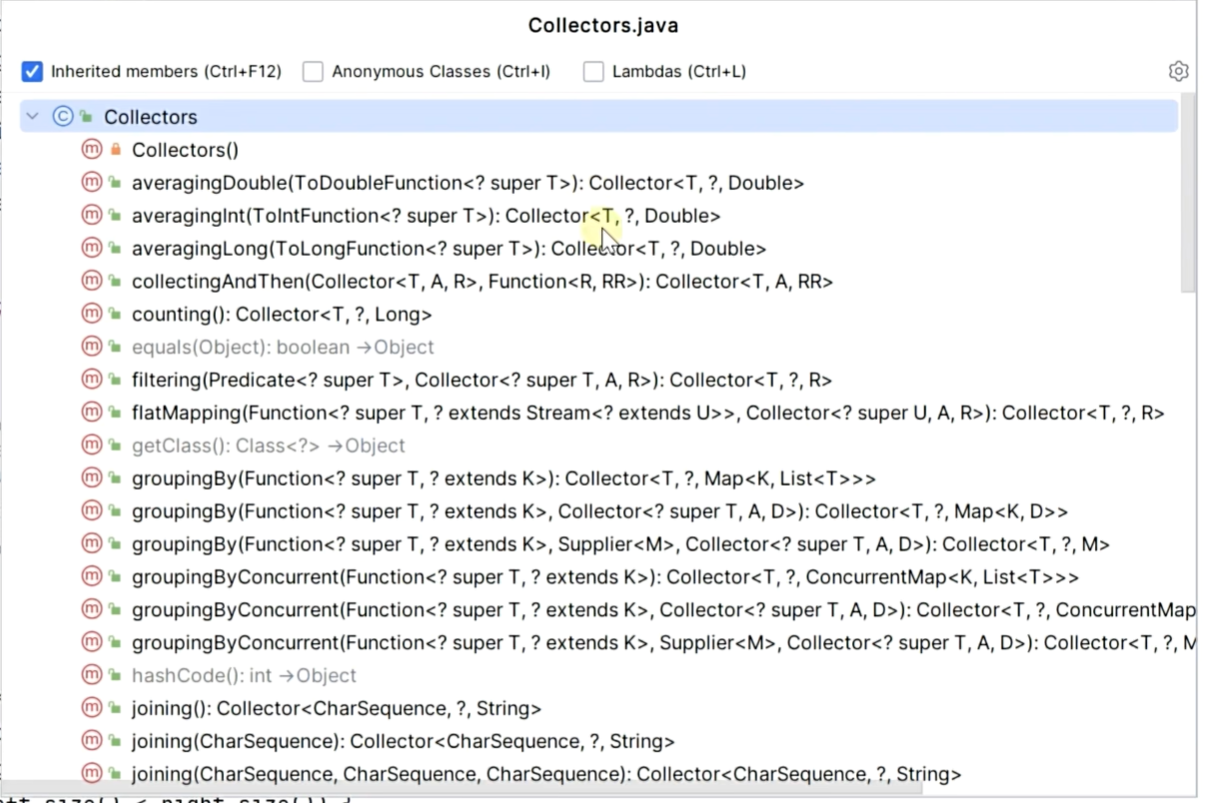
import java.util.stream.Stream;// 收集器 Collectors
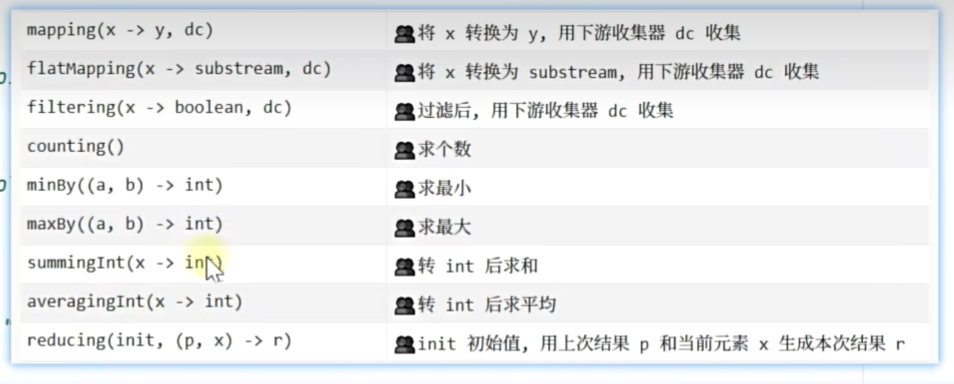
public class C11CollectTest {record Hero(String name, int strength) { ... }/*收集:将元素收集入容器.collect(() -> c, (c, x) -> void, ?)() -> c 创建容器 c(c, x) -> void 将元素 x 加入 容器 c*/public static void main(String[] args) {Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("令狐冲", "风清扬", "孤独求败", "方证", "东方不败","冲虚","向问天","任我行","不戒");// 1.收集到 ListList<String> result = stream.collect(() -> new ArrayList<>(), (list, x) -> list.add(x), (a, b) -> { });/*ArrayList::new () -> new ArrayList()ArrayList::add (list, x) -> list.add(x)能等价就等价看自己的风格或要求*/ // 缺点:不太方便调试List<String> result = stream.collect(ArrayList::new, ArrayList::add, (a, b) -> { }); List<String> result = stream.collect(Collectors.toList());Set<String> result = stream.collect(LinkeeHashSet::new, Set::add, (a, b) -> { });Set<String> result = stream.collect(Collectors.toSet());Map<String, Integer> result = stream.collect(HashMap::new, (map, x) -> map.put(x, 1), (a, b) -> { });Map<String, Integer> result = stream.collect(Collectors.toMap(x -> x, x -> 1));// 流空,不实现stream.collect(StringBuilder::new, StringBuilder::append, (a, b) -> { });stream.collect(Collectors.joining;stream.collect(() -> new StringJoiner(","), StringJoiner:add, (a, b) -> { });stream.collect(Collectors.joining(","));/*3:new ArrayList(["令狐冲", “风清扬", “向问天",“任我行"])4:new ArrayList(["独孤求败","东方不败"])2: new ArrayList(["方证",“冲虚",“不戒"])*/Map<Integer, List<String>> result = stream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(x -> x.length(), Collectors.toList()));for (Map.Entry<Integer, List<String>> e : result.entrySet()) {System.out.println(e);}/**1. mapping(x->y, dc) 需求:根据名字长度分组,分组后组内只保留他们的武力值new Hero("令狐冲", 90) -> 90dc 下游收集器 down collector */Map<Integer, List<Integer>> collect = stream.collect (groupingBy(h -> h.name().length(), mapping(h -> h.strength(), toList())));for (Map.Entry<Integer, List<Integer>> e : collect.entrySet()) {System.out.println(e);}/** 2. filtering(x -> boolean, dc) 需求:根据名字长度分组,分组后组内过滤掉武力小于 90 的*/// 在分组收集的过程中,执行过滤Map<Integer, List<Hero>> collect1 = stream.collect (groupingBy(h -> h.name().length(), filtering(h -> h.strength() >= 90, toList()));)// 先过滤,再来分组收集Map<Integer, List<Hero>> collect1 = stream.filter(h -> h.strength() >= 90).collect(groupingBy(h -> h.name().length(), toList()));for (Map.Entry<Integer, List<Hero>> e : collect1.entrySet()) {System.out.println(e);}/*** 3. flatMapping(x -> substream, dc) 需求:根据名字长度分组,分组后组内保留人名,并且人名切分成单个字符*/// Character::toString (x) -> x.toString(); "令狐冲".chars().mapToObj(Character.toString.forEach(System.out::println);stream.collect(groupingBy(h -> h.name().length(), flatMapping(h->h.name().chars().mapToObj(Character::toString), toList())));for (Map.Entry<Integer, List<String>> e : collect.entrySet()) {System.out.println(e);}/** 4. counting() 需求:根据名字长度分组,分组后求每组个数*/Map<Integer, Long> collect = stream.collect(groupingBy(h -> h.name().length(), count()));for (Map.Entry<Integer, Long> e : collect.entrySet()) {System.out.println(e);}/** minBy((a, b) -> int) 需求:根据名字长度分组,分组后求每组武功最低的人* maxBy((a, b) -> int) 需求:根据名字长度分组,分组后求每组武功最高的人*/stream.collect(groupingBy(h -> h.name().length(), maxBy(Comparator.comparingInt(Hero::strength))));/** 7. summingInt(x -> int) 需求:根据名字长度分组,分组后求每组武力和* 8. averagingDouble(x -> double) 需求:根据名字长度分组,分组后求每组武力平均值** stream.collect(groupingBy(h -> h.name().length(), averagingDouble(h -> h.strength())));*/for (Map.Entry<Integer, Optional<Hero>> e : collect.entrySet()) {System.out.println(e);}/** 9. reducing(init, (p, x) -> r)*/stream.collect(groupingBy(h -> h.name().length(), mapping(h -> h.strength(), reducing(0, (p, x) -> p + x))));}
}
基本流
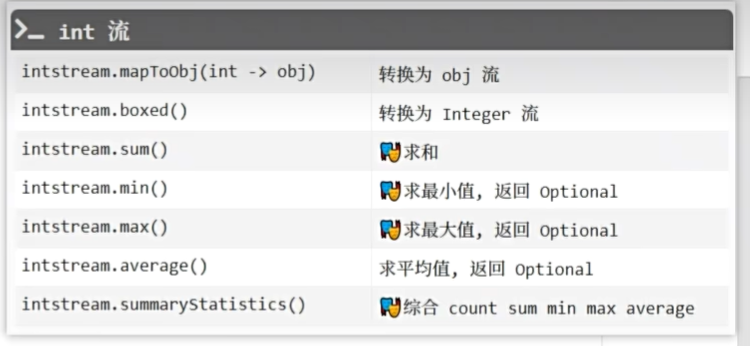

import java.util.stream.DoubleStream;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
import java.uyil.stream.LongStream;
import java.util.stream.Stream;public class C14Effective {/*三种基本流*/public static void main(String[] args) {IntStream a = IntStream.of(97, 98, 99);LongStream b = LongStream.of(1L, 2L, 3L);DoubleStream c = DoubleStream.of(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);Stream<Integer> d = Stream.of(1, 2, 3);a.mapToObj(Character::toString).forEach(System.out::println);IntSummaryStatistics stat = a.summaryStatistics();System.out.println(stat.getSum());System.out.println(stat.getCount());System.out.println(stat.getMax());System.out.println(stat.getMin());System.out.println(stat.getAverage());Stream<Hero> stream = Stream.of(new Hero("令狐葱", 90),new Hero("风清扬", 98));stream.mapToInt(Hero::strength).forEach(System.out::println);}
}
流的特性
import java.util.stream.Stream;public class C15Summary {public static void main(String[] args) {/*** 掌握 Stream 流的特性* 1. 一次使用* 2. 两类操作(中间操作 lazy 懒惰, 终结操作 eager 迫切)*/Stream<Integer> s1 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);s1.map(x -> x + 1).filter(x -> x <= 5).forEach(x -> System.out::println);}
}


stream 并行
import static java.util.stream.Collectors.toList;// 并行流
public class C16Parallel {public static void main(String[] args) {/* ... */List<Integer> collect = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).parallel().collect(Collector.of (() -> new ArrayList(), // 如何创建容器(list, x) -> list.add(x), // 如何向容器添加数据(list1, list2) -> {list1.addAll(list2);return list1;}, // 如何合并两个容器的数据list -> list // 收尾// 特性:并发,是否需要收尾,是否要保证收集顺序 (默认)容器不支持并发,需要收尾,要保证收集顺序));System.out.println(collect);}private static String simple() { }
}
import static java.util.stream.Collectors.toList;// 并行流
public class C16Parallel {public static void main(String[] args) {/* ... */List<Integer> collect = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4).parallel().collect(Collertor.of)(() -> {System.out.printf("%-12s %s%n", simple(), "create"); // 1.如何创建容器return new ArrayList<Integer>();},(list, x) -> {List<Integer> old = new ArrayList<>(list);list.add(x);System.out.printf("%-12s %s.add(%d)=>%s%n", simple(), old, x, list);}, // 2. 如何向容器添加数据(list1, list2) -> {List<Integer> old = new ArrayList<>(list1);list1.addAll(list2);System.out.println("%-12s %s.add(%s)=>%s%n", simple(), lod, list2, list3);return list1;} // 3.如何合并两个容器的数据list -> {System.out.printf("%-12s finish: %s=>%s%n", simple(), list, list);return list;} // 4.收尾// 5. 特性:容器不支持并发,需要收尾,要保证收集顺序)System.out.println(e);}private static String simple() { }
}

public class C16Parallel {public static void main(String[] args) {/** 1. 数据量问题:数据量大时才建议用并行流* 2. 线程会无限增加吗:跟 cpu 能处理的线程数相关* 3. 收尾的意义: 转不可变集合,StringBuilder 转 String* 4. 是否线程安全: 不会有线程安全问题* 5. 特性* 是否需要收尾(默认收尾),是否需要保证顺序(默认保证)容器是否支持并发(默认不支持)到达选择哪一种?A. Characteristics.CONCURRENT + Characteristics.UNORDERED + 线程安全容器B. 默认 + 线程不安全容器*/List<Integer> collect = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12).parallel().collect(Collertor.of(() -> {System.out.printf("%-12s %s%n", simple(), "create"); // 1.如何创建容器return new ArrayList<Integer>();},(list, x) -> {List<Integer> old = new ArrayList<>(list);list.add(x);System.out.printf("%-12s %s.add(%d)=>%s%n", simple(), old, x, list);}, // 2. 如何向容器添加数据(list1, list2) -> {List<Integer> old = new ArrayList<>(list1);list1.addAll(list2);System.out.println("%-12s %s.add(%s)=>%s%n", simple(), lod, list2, list3);return list1;} // 3.如何合并两个容器的数据list -> {System.out.printf("%-12s finish: %s=>%s%n", simple(), list, list);return Collections.unmodifiableList(list);} // 4.收尾// 5. 特性:容器不支持并发,需要收尾,要保证收集顺序, Collector.Characteristics.IDENTITY_FINISH // 不需要收尾,Collector.Characteristics.UNORDERED // 不需要保证顺序, Collector.Characteristics.CONCURRENT // 容器需要支持并发)System.out.println(e);collect.add(100);}private static String simple() { }
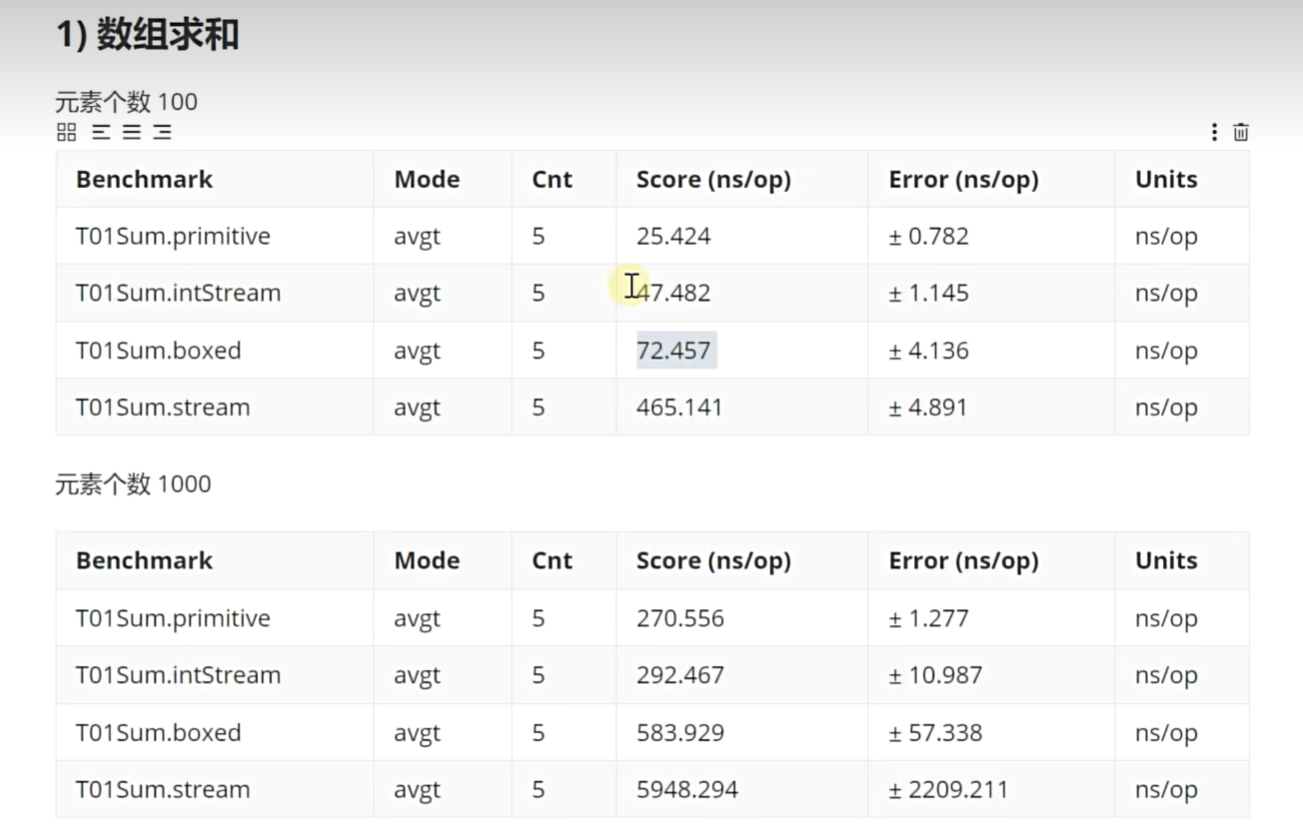
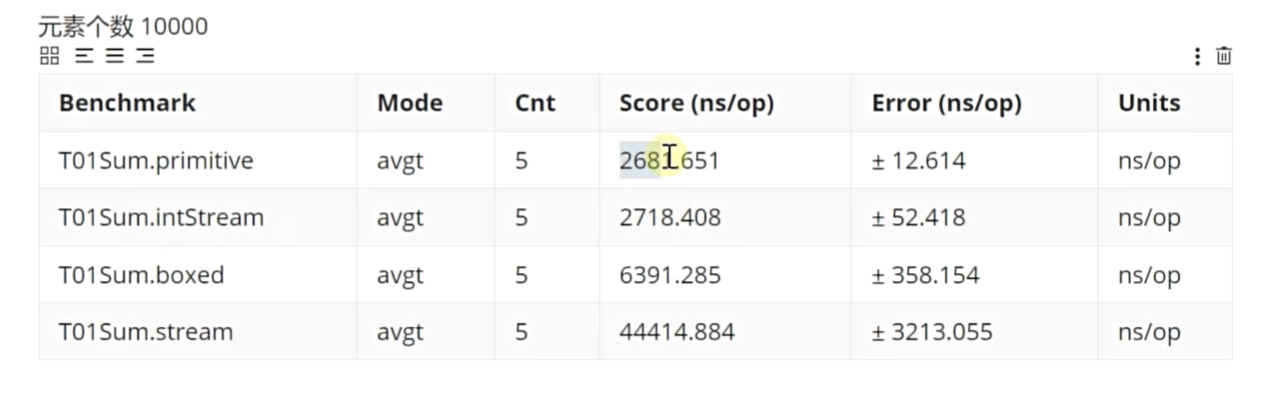
Stream 流的性能
// 性能: 求和 JMH
public class T01Sum {@State(Scope.Benchmark)public static class MyState { ... }@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public int primitive(MyState state) {int sum = 0;for (int number : state.numbers) {sum += number;}return sum;}@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AveragetTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public int boxed(MyState state) { int sum = 0;for (Integer i : state.numberList) {sum += i;}return sum;}@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public int stream(MyState state) {return state.numberList.stream().reduce(0, (a, b) -> a + b);}@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public int intStream(MyState state) {return IntStream.of(state.numbers).sum();}public static void main(String[] args) throws RunnerException {Options opt = new OptionsBuilder().include(TO1Sum.class.getSimpleName()).forks(1).build();new Runner(opt).run();}
}
pubilc class T02Parallel {static final int n = 1000000;@State(Scope.Benchmark)pubilc static class MyState {int[] numbers = new int[n];{for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {numbers[i] = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10000000);}}}@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public int primitive(MyState state) {int max = 0;for (int number : state.numbers) {if (number > max) {max = number;}}return max;}@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public int sequence(MyState state) {return IntStream.of(state.numbers).max().orElse(0);}@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public int parallel(MyState state) {return IntStram.of(state.number).parallel().max().orElse(0);}@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public int custom(Mystate state) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {int[] numbers = state.numbers;int step = n / 10;ArrayList<Future<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();try (ExecutorService service = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j += step) {int k = j;result.add(service.submit(() -> {int max = 0;for (int i = k; i < k + step; i++) {if (numbers[i] > max) {max = numbers[i];}}return max;}));}System.out.println(result.size());int max = 0;for (Future<Integer> future : result) {if (future.get() > max) {max = future.get();}}return max;}}
}
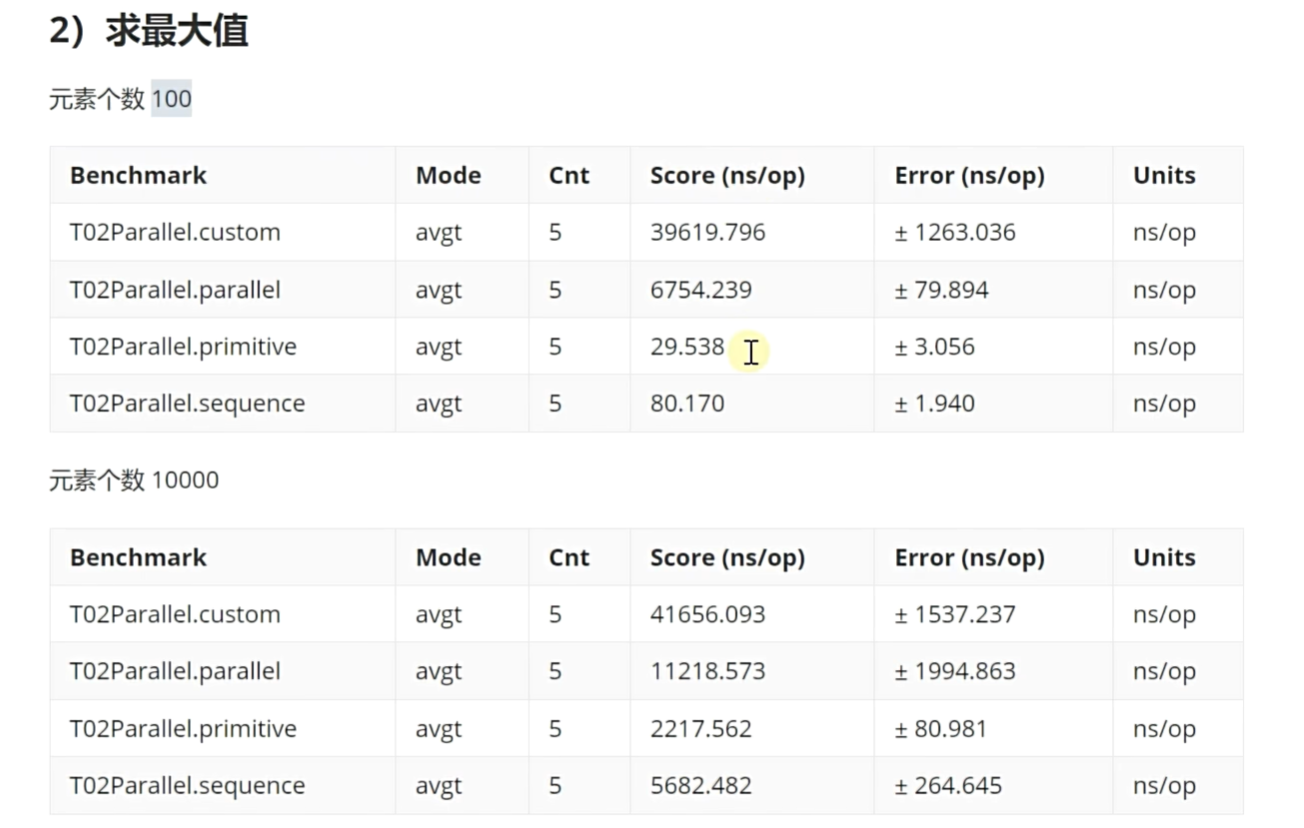
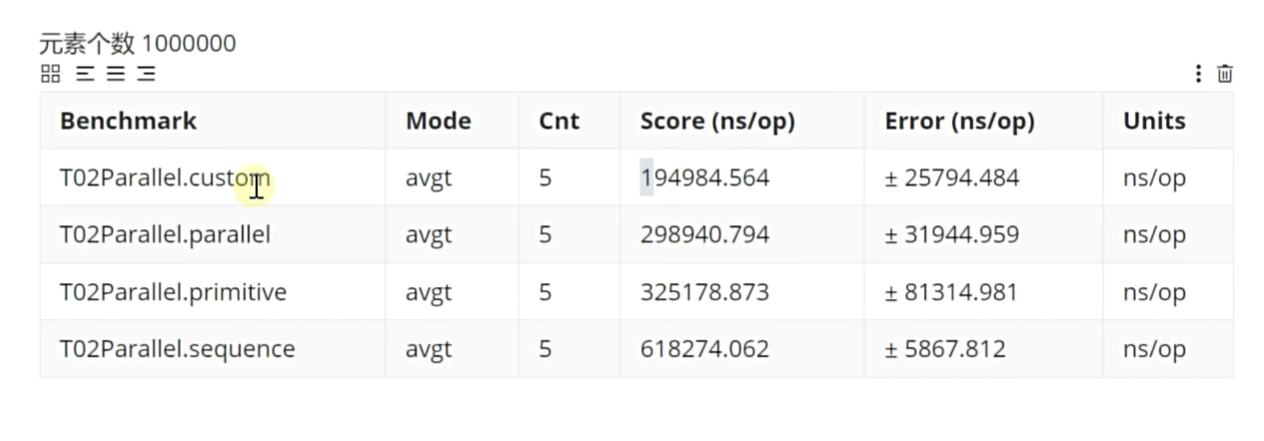
import static java.util.stream.Collectors.*;public class T03Concurrent {static final int n = 1000000;@State(Scope.Benchmark)public static class MyState {int[] numbers = new int[n];{for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {numbers[i] = ThreadLocalRandom().current().nextInt(n / 10);}}}@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public Map<Integer, Integer> loop1(MyState state) {Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();for (int number : state.numbers) {map.merge(number, 1, Integer::sum);}return map;}@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public Map<Integer, Integer> loop1(MyState state) {Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();for (int number : state.numbers) {map.computeIfAbsent(number, k -> new AtomicInteger()).getAndIncrement();}return map;} @Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public Map<Integer, Long> sequence(MyState state) {return Arrays.stream(state.numbers).boxed().collect(groupingBy(Function.identity(), counting()));}@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public Map<Integer, Long> parallelNoConcurrent(MyState state) {return Arrays.stream(state.numbers).boxed().parallel().collect(groupingBy(Function.identity(), counting()));}@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)public ConcurrentMap<Integer, Long> parallelConcurrent(MyState state) {return Arrays.stream(state.numbers).boxed().parallel().collect(groupingByConcurrent(Function.identity(), counting()));}public static void main(String[] args) throws RunnerException, ExecutionException, InterruptedException {}
}
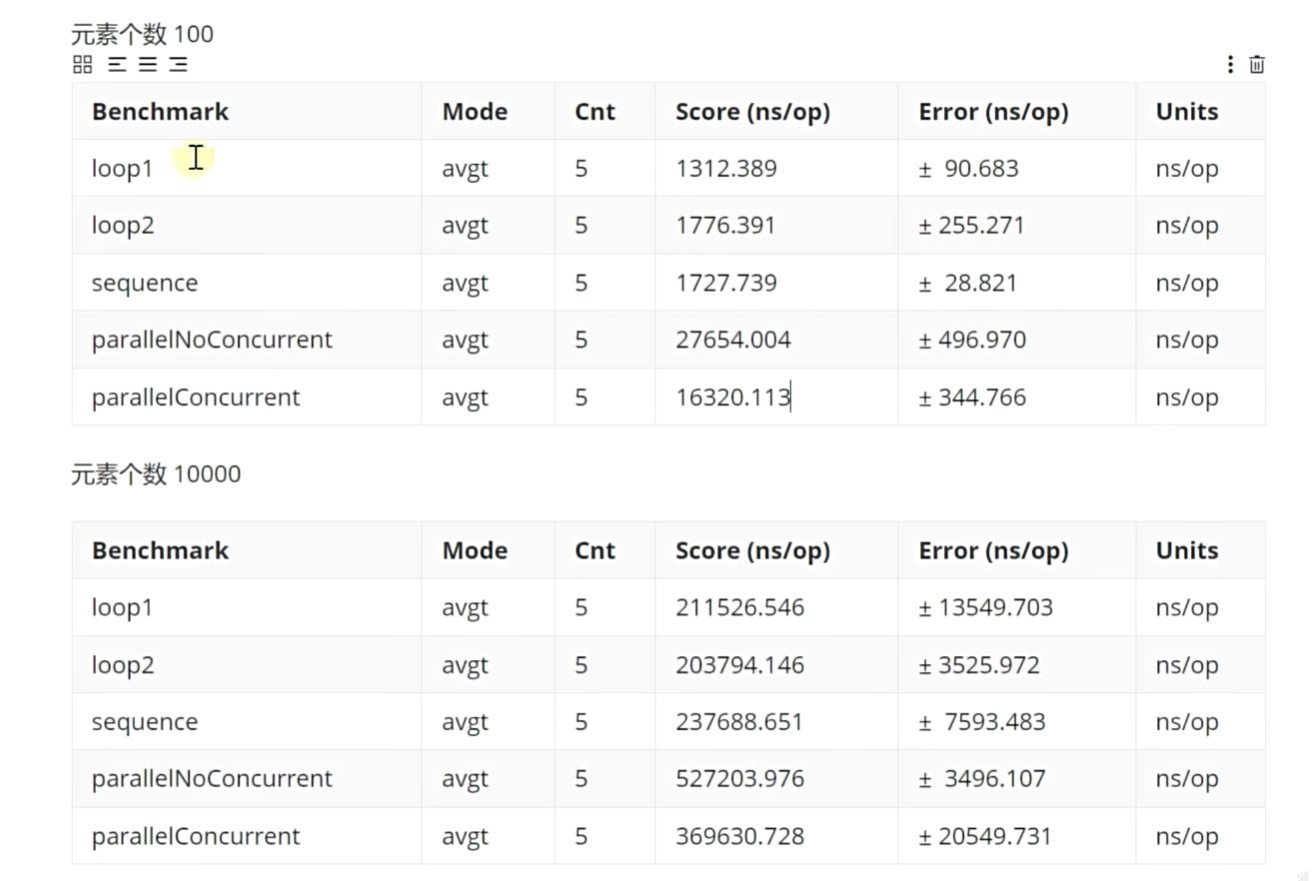
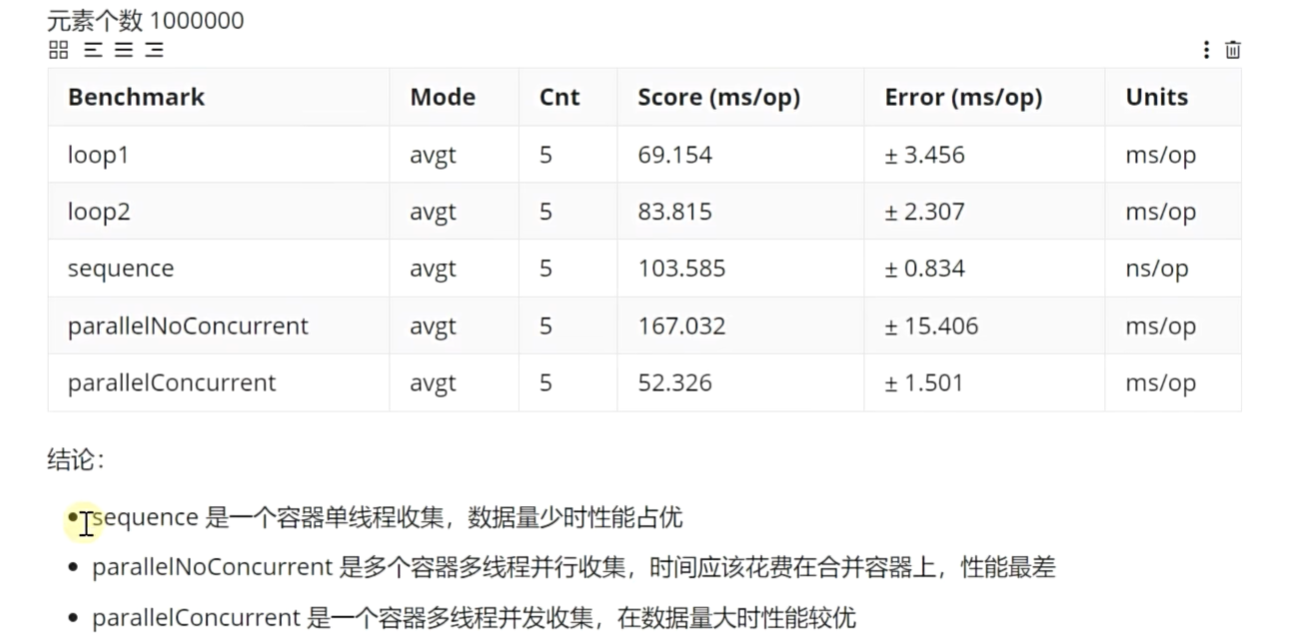
四.实际应用统计、异步、框架、并行、事件
统计
static final int INDEX = 0;
static final int TIME = 1;
static final int ORDER_ID = 2;
static final int PRODUCT_ID = 3;
static final int CATEGORY_ID = 4;
static final int CATEGORY_CODE = 5;
static final int BRAND = 6;
static final PRICE = 7;
static final int USER_ID = 8;
static final int USER_AGE = 9;
static final int USER_SEX = 10;
static final int USER_REGION = 11;
static final int DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss z");public static void main(String[] args) {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Path.of("./data.txt"))) {lines.skip(1).limit(5).forEach(line->System.out.println(line));} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
每月的销售量
static final int INDEX = 0;
static final int TIME = 1;
static final int ORDER_ID = 2;
static final int PRODUCT_ID = 3;
static final int CATEGORY_ID = 4;
static final int CATEGORY_CODE = 5;
static final int BRAND = 6;
static final PRICE = 7;
static final int USER_ID = 8;
static final int USER_AGE = 9;
static final int USER_SEX = 10;
static final int USER_REGION = 11;
static final int DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss z");public static void main(String[] args) {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Path.of("./data.txt"))) {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();Map<YearMonth, Long> collect = lines.skip(1).map(line -> line.split(",")).collect(groupingBy(array -> YearMonth).from(formatter.parse(array[TIME]), TreeMap::new, counting()));System.out.println("花费" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));for (Map.Entry<YearMoth, Long> e : collect.entrySet()) {System.out.println(e);}} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
统计销量最高的月份
static final int INDEX = 0;
static final int TIME = 1;
static final int ORDER_ID = 2;
static final int PRODUCT_ID = 3;
static final int CATEGORY_ID = 4;
static final int CATEGORY_CODE = 5;
static final int BRAND = 6;
static final PRICE = 7;
static final int USER_ID = 8;
static final int USER_AGE = 9;
static final int USER_SEX = 10;
static final int USER_REGION = 11;
static final int DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss z");public static void main(String[] args) {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Path.of("./data.txt"))) {lines.skip(1).map(line -> line.split(",")).collect(groupingBy(array -> YearMonth.from(formatter.parse(array[TIME])), counting())).entrySet().stream()// .max(Comparator.comparingLong(e -> e.getValue()));.max(Map.Entry.comparingByValue()).ifPresent(x -> System.out.println(x));} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
销量最高的商品
static final int INDEX = 0;
static final int TIME = 1;
static final int ORDER_ID = 2;
static final int PRODUCT_ID = 3;
static final int CATEGORY_ID = 4;
static final int CATEGORY_CODE = 5;
static final int BRAND = 6;
static final PRICE = 7;
static final int USER_ID = 8;
static final int USER_AGE = 9;
static final int USER_SEX = 10;
static final int USER_REGION = 11;
static final int DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss z");public static void main(String[] args) {case3();
}
private static void case3() {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get("./data.txt")) {lines.skip(1).map(line->line.split(",")).collect(groupingBy(array->array[PRODUCT_ID], counting())).entrySet().stream().max(Map.Entry.comparingByValue()).ifPresent(System.out::println);} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
下单最多的前10用户
static final int INDEX = 0;
static final int TIME = 1;
static final int ORDER_ID = 2;
static final int PRODUCT_ID = 3;
static final int CATEGORY_ID = 4;
static final int CATEGORY_CODE = 5;
static final int BRAND = 6;
static final PRICE = 7;
static final int USER_ID = 8;
static final int USER_AGE = 9;
static final int USER_SEX = 10;
static final int USER_REGION = 11;
static final int DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss z");public static void main(String[] args) {case4();
}
private static void case4() {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get("./data.txt")) {lines.skip(1).map(line -> line.split(",").collect(groupingBy(array -> array[USER_ID], counting));for (Map.Entry<String, Long> e : collect.entrySet()) {System.out.println(e);}collect.entrySet().stream().sorted(Map.Entry.<String, Long>comparingByValue().reversed()).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
最小堆
static class MyQueue<E> extends PriorityQueue<E> {private int max;public MyQueue(Comparator<? super E> comparator, int max) {super(comparator);this.max = max;}@Overridepublic boolean offer(E e) {boolean r = supper.offer(e);if (this.size() > max) {this.poll();}return r;}}
private static void case4() {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Path.of("./data.txt"))) {Map<String, Long> collect = lines.skip(1).map(line -> line.split(",")).collect(groupingBy(array -> array[USER_ID], counting()));// 小顶推MyQueue<Map.Entry<String, Long>> map = collect.entrySet().stream().collect (() -> new MyQueue<Map.Entry<String, Long>(Map.Entry.comparingByValue())(queue, x) -> queue.offer(x),(q1, q2) -> q1.addAll(q2));while(!queue.isEmpty()) {System.out.println(queue.poll());}} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
每个地区下单最多的用户
static final int INDEX = 0;
static final int TIME = 1;
static final int ORDER_ID = 2;
static final int PRODUCT_ID = 3;
static final int CATEGORY_ID = 4;
static final int CATEGORY_CODE = 5;
static final int BRAND = 6;
static final PRICE = 7;
static final int USER_ID = 8;
static final int USER_AGE = 9;
static final int USER_SEX = 10;
static final int USER_REGION = 11;
static final int DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss z");public static void main(String[] args) {case5();
}
private static void case5() {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get("./data.txt")) {Map<String, Map<String, Long>> collect = lines.skip(1).map(line -> line.split(",")).collect(groupingBy(array -> array[USER_GEGION], groupingBy(array -> array[USER_ID], counting())));collect.entrySet().stream.map(e -> Map.entry(e.getKey(),e.getValue().entrySet().stream().max(Map.Entry.comparingByValue()))).forEach(System.out::println);} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
每个地区下单最多的前3用户
static final int INDEX = 0;
static final int TIME = 1;
static final int ORDER_ID = 2;
static final int PRODUCT_ID = 3;
static final int CATEGORY_ID = 4;
static final int CATEGORY_CODE = 5;
static final int BRAND = 6;
static final PRICE = 7;
static final int USER_ID = 8;
static final int USER_AGE = 9;
static final int USER_SEX = 10;
static final int USER_REGION = 11;
static final int DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss z");public static void main(String[] args) {case5();
}
private static void case5() {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get("./data.txt")) {Map<String, Map<String, Long>> collect = lines.skip(1).map(line -> line.split(",")).collect(groupingBy(array -> array[USER_GEGION], groupingBy(array -> array[USER_ID], counting())));collect.entrySet().stream.map(e -> Map.entry(e.getKey(),// e.getValue().entrySet().stream()// .sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue().reverse())// .limit(3)// .collect(toList())e.getValue().entrySet().stream().collect (() -> new MyQueue<Map.Entry<String, Long>> (Map.Entry.comparingByValue(), 3)MyQueue::offerMyQueue::addAll))).forEach(System.out::println);} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
按一级类别统计销量
static final int INDEX = 0;
static final int TIME = 1;
static final int ORDER_ID = 2;
static final int PRODUCT_ID = 3;
static final int CATEGORY_ID = 4;
static final int CATEGORY_CODE = 5;
static final int BRAND = 6;
static final PRICE = 7;
static final int USER_ID = 8;
static final int USER_AGE = 9;
static final int USER_SEX = 10;
static final int USER_REGION = 11;
static final int DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss z");public static void main(String[] args) {case6();
}
static String firstCategory(String[] array) {String c = array[CATEGORY_CODE];int idx = c.indexOf(".");return c.substring(0, idx);
}
private static void case6() {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get("./data.txt")) {Map<String, Long> collect = lines.skip(1).map(line -> line.split(",")).filter(array -> !array[CATEGORY_CODE].isEmpty()).collect(groupingBy(TestData::firstCategory, TreeMap::new, counting()));for (Map.Entry<String, Long> e : collect.entrySet()) {System.out.println(e);}} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
按区间统计销量
static final int INDEX = 0;
static final int TIME = 1;
static final int ORDER_ID = 2;
static final int PRODUCT_ID = 3;
static final int CATEGORY_ID = 4;
static final int CATEGORY_CODE = 5;
static final int BRAND = 6;
static final PRICE = 7;
static final int USER_ID = 8;
static final int USER_AGE = 9;
static final int USER_SEX = 10;
static final int USER_REGION = 11;
static final int DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss z");public static void main(String[] args) {case7();
}
static String priceRange(Double price) {if (price < 100) {return "[0, 100)";} else if (price >= 100 && price < 500) {return "[100, 500)"} else if (price >= 500 && price < 1000) {return "[500, 1000)";} else {return "[1000, 无穷)";}
}
private static void case6() {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get("./data.txt")) {lines.skip(1).map(line -> line.split(",")).map(array->Double.valueOf(array[PRICE])).collect(groupingBy(TestData::priceRange, counting()));// 打印集合 略} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
不同年龄段女性下不同类别订单
static final int INDEX = 0;
static final int TIME = 1;
static final int ORDER_ID = 2;
static final int PRODUCT_ID = 3;
static final int CATEGORY_ID = 4;
static final int CATEGORY_CODE = 5;
static final int BRAND = 6;
static final PRICE = 7;
static final int USER_ID = 8;
static final int USER_AGE = 9;
static final int USER_SEX = 10;
static final int USER_REGION = 11;
static final int DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss z");public static void main(String[] args) {case8();
}
static String ageRange(Double price) {int age = Double.valueOf(array[USER_AGE]).intValue();if (age < 18) {return "[0, 18)";} else if (age < 30) {return "[18, 30)";} else if (age < 50) {return "[30, 50)";} else {return "[50, 无穷)"}
}
private static void case8() {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get("./data.txt")) {lines.skip(1).map(line -> line.split(",")).filter(array->array[USER_SEX].equals("女")).filter(array-> array[CATEGORY_CODE].isEmpty()).collect(groupingBy(TestData::ageRange, groupingBy(TestData::firstCategory, TreeMap::new, counting())));for (Map.Entry<String, Map<String, Long>> e1 : map.entrySet()) {for (Map.Entry<String, Long> e2 : e1.getValue().entrySet()) {System.out.println("%-12s%-15s%d%n", e1.getKey(), e2.getKey(), e2.getValue());}}// 打印集合 略} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
异步处理
static final int INDEX = 0;
static final int TIME = 1;
static final int ORDER_ID = 2;
static final int PRODUCT_ID = 3;
static final int CATEGORY_ID = 4;
static final int CATEGORY_CODE = 5;
static final int BRAND = 6;
static final PRICE = 7;
static final int USER_ID = 8;
static final int USER_AGE = 9;
static final int USER_SEX = 10;
static final int USER_REGION = 11;
static final int DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss z");static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger("Test");// 1. 显式使用了线程池
// 2. 函数对象嵌套使用,可读行差
public static void main(String[] args) {logger.info("开始统");// monthlySalesReport();new Thread()->monthlySalesReport().start(); // 异步代码调用logger.info("执行其他操作");/*目标:将处理结果的逻辑放在 monthlySalesReport 之外做法1:将结果作为方法的返回值返回做法2:将处理结果的逻辑作为函数对象传递给方法*/try (ExcutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3)) {logger.info("开始统计");service.submit(()-> {monthlySalesReport((map) -> {logger.info(e.toString());});});logger.info("执行其他操作");}}private static void monthlySalesReport(Counsumer<Map<YearMonth, Long>> consumer) {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get("./data.txt")) {Map<YearMonth, Long> map = lines.skip(1).map(line -> line.split(",")).collect(groupingBy(array -> YearMonth.from(formatter.parse(array[TIME], TreeMap::new, counting())));return collect; } catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
异步优化
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import java.util.concurrent.CompletebleFuture;public class C03CompletableFutureTest {static Logger logger = loggerFactory.getLogger("Test");public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 异步执行CompletableFuture.runAsync() // 在任务不需要返回结果时CompletableFuture.supplyAsync() // 在任务需要处理结果时CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> logger.info("异步操作1")); CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {logger.info("异步操作2");return "结果";}).thenApply(r -> r + "转换后").thenAccept(r -> logger.info(r));System.in.read(); // 不让主线程立刻结束// 2.处理异步任务的结果/*thenApply(Function)thenApplyAsyncthenAccept(Consumer)thenAcceptAsunc(Consumer)*/}
}
static final int INDEX = 0;
static final int TIME = 1;
static final int ORDER_ID = 2;
static final int PRODUCT_ID = 3;
static final int CATEGORY_ID = 4;
static final int CATEGORY_CODE = 5;
static final int BRAND = 6;
static final PRICE = 7;
static final int USER_ID = 8;
static final int USER_AGE = 9;
static final int USER_SEX = 10;
static final int USER_REGION = 11;
static final int DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM--dd HH:mm:ss z");static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger("Test");// 1. 显式使用了线程池
// 2. 函数对象嵌套使用,可读行差
public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> monthlySalesReport()).thenAccept(map -> {for (Map.Entry<YearMonth, Long> e : map.entrySet()) {logger.info(e.toString());}});System.in.read();try (ExcutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3)) {logger.info("开始统计");CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> monthlySalesReport).thenAccept(map -> {for (Map.Entry<YearMonth, Long> e : map.entrySet()) {logger.info(e. toString());}});logger.info("执行其他操作");System.in.read();}}private static void monthlySalesReport(Counsumer<Map<YearMonth, Long>> consumer) {try (Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get("./data.txt")) {Map<YearMonth, Long> map = lines.skip(1).map(line -> line.split(",")).collect(groupingBy(array -> YearMonth.from(formatter.parse(array[TIME], TreeMap::new, counting())));return collect; } catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}
框架 跳过 博主 还没学呢 😂(预计11月份开Spring全家桶)
- 什么是框架?
- 半成品软件,帮助开发者快速构建应用程序
- 框架提供的都是固定不变的、已知的、可以重用的代码
- 而那些每个应用不同的业务逻辑,变化的、未知的部分,则在框架外由开发者自己实现
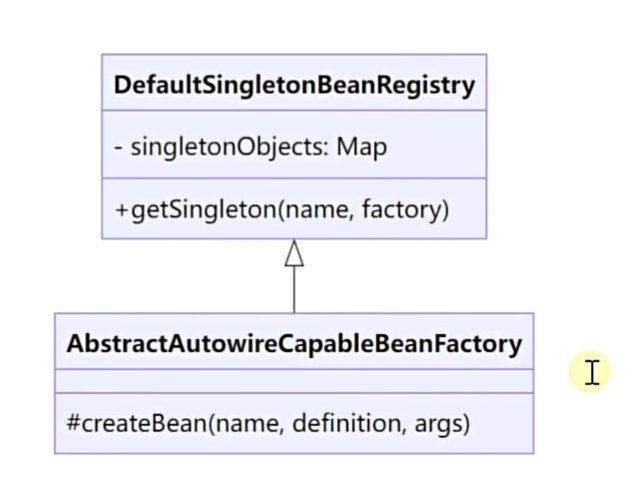
将未知交给子类
- Spring 延迟创建 bean
-
public class C01JdbcTemlate {public static void main(String[] args) {HikariDataSoure dataSouce = new HikariDataSource();// 链接 mysql 服务器dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test")dataSource.setUsername("root")dataSource.setPassword("root");// try (Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection()) {// PreparedStatement stat = conn.prepareStatement("select * from student");// ResultSet rs = stat.executeQuery();// while (rs.next()) {// int id = rs.getInt("id");// String name = rs.getString("name");// String sex = rs.getString("sex");// list.add(new Student(id, name, sex));// }// } catch (SQLException e) {// throw new RuntimeException(e);// }JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);List<Student> list = template.query("select * from student", (rs, row) -> {int id = rs.getInt("id");String name = rs.getString("name");String sex = rs.getString("sex");return new Student(id, name, sex);});for (Student student : list) {System.out.println(student);}}record Student(int id, String name, String sex) {} }
- Spring
- SpringBoot
序列化
public class TestSerializable { public static void main(String[] args) throws Excepton {// 可序列化的函数对象Type1 lambda = (Type1 & Serializable) Student::getName;// 函数对象 <==> 字节码 会额外存储类和方法的信息,运行时就可以根据这些信息找到属性,从而进一步确定(列名)/*for (Method method : lambda.getClass().getDeclaredMethods()) {System.out.println(method);}*/SerializaedLambda invoke = (SerializedLambda) lambda.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("writeReplace").invoke(lambda);System.out.println(invoke.getClass()); // 哪个类使用了这个函数对象System.out.println(invoke.getImpClass()); // 哪个类实现了函数对象的逻辑System.out.println(invoke.getImplMethodName()); // 哪个方法实现了函数对象的逻辑}interface Type1 {String abc(Student student);}
}
并行
统计 Web 页面的访问次数
import static java.util.stream.Collectors.*;public class ParalletTest {static Pattern reg = Pattern.compile("(\\S+) - \\[(.+)] (.+) (.+)");private static final int FILES = 100;public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {Map<String, Long> map = one(0);for (Map.Entry<String, Long> e : map.entrySet()) {System.out.println(e);}}private static Map<String, Long> one(int i) {try(Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Path.of(String.format("web_server_access_%d.log", i)))) {return lines.map(line->reg.matcher(line)) // reg::matcher// .limit(10).filter(mather -> mather.find()) // Matcher::find.map(matcher -> new String[]{matcher.group(1), matcher.group(2), matcher.group(3), matcher.group(4)}).collect(groupingBy(array -> array[2], counting()));} catch {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}private static void sequence() {long start == System.currentTimeMillis();Map<String, Long> m0 = new HashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < FILES; i++) {Map<String, Long> mi = one(i);m0 = merge(m0, mi);}for (Map.Entry<String, Long> e : m0.entrySet()) {System.out.println(e);}System.our.println("cost: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));}static Map<String, Long> merge(Map<String, Long> m1, Map<String, Long> m2) {return Stream.of(m1, m2).flatMap(m -> m.entrySet().stream()).collect(toMap(Map.Entry::getKey, Map.Entry::getValue, (v1, v2) -> v1 + v2)); }private static void parallel() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {long start = System.currentTimeMillsi();for (int i = 0; i < FiLES; i++) {int k = i;CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> one(k));}Completablefuture<Map<String, Long>> f0 = futures.getFirst();for (int i = 1; i < futures.size(); i++) {CompletableFuture<Map<String, Long>> fi = futures.get(i);f0.thenCombine(fi, (m0, mi) -> merge(m0, mi));}Map<String, Long> map = f0.get();for (Map.Entry<String, Long> e : map.entrySet()) {System.out.println(e);}System.out.println("cost: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));}
}
UI 事件
import javax.swing.*;// 在 UI 设计时的应用
public class UITest {public static void main(String[] args) {JFrame frame = new JFrame();JButton button = new JButton("点我");button.addActionListener(e -> System.out.println("已点击"));frame.add(button);frame.setSize(300, 200);frame.setVisible(true);}
}
五.实现原理 Lambda、方法引用、闭包、可切分迭代器
原理 Lambda
import java.util.function.BinaryOperator;public class C01Lambda1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {BinaryOperator<Integer> lambda = (a, b) -> a + b;/*lambda 表达式是一种语法糖, 它仍然会被翻译成 类,对象,方法1. 方法从哪来:编译器发现代码中出现了 lambda, 就会在当前类中生成 private static 方法,方法内包含的就是 lambda 的逻辑实验代码for (Method method : C01Lambda1.class.getDeclaredMethods()) {System.out.println(method);}2. 类和对象从哪来: 运行期间动态生成MethodHandleMethodHandle 的执行权限与上下文相关原本有权限调用的方法,正常能运行,通过 MethodHandle 反射也能调用原本没权限调用的方法,正常不能调用, MethodHandle 反射也调用不了3. 1. 反射调用静态方法MethodHandle mh = MethodHandles.lookup().findStatic(C01Lambda1.class, "lambda$main$2"),MethodType.methodType(Integer.class, Integer.class, Integer.class);System.out.println(mh.invoke(1, 2));// 反射调用非静态方法MethodHandle mh2 = MethodHandles.lookup().findVirtual(MyLambda.class, "apply", MethodType.methodType(Integer.class, Integer.class, Integer.class));// 反射调用构造器方法MethodHandle mh3 = MethodHandles.lookup().findConstructor(MyLambda.class, MethodType.methodType(void.class));System.out.println(mh3.invoke()); //new MyLambda()System.out.println(new MyLambda());*/MethodHandles.Lookup lookup = MethodHandles.lookup();MethodHandle imp1 = lookup.findStatic(CO1Lambda1.class, "lambda$main$2",MethodType.methodType(Integer.class, Integer.class, Integer.class));// 内部: 生成函数对象所需的类LambdaMetafactory.metafactory (, // 1. lookup, // 2. 接口方法名, // 3. 创建函数对象工厂方法长相 BinaryOperator factory(), // 4. 接口方法长相, // 5. 实现方法(本例就是下面的静态方法 lambda$main$2), // 6. 函数对象实际长相lookup,"apply",MethodType.methodType(BinaryOperator.class),MetodType.methodType(Object.class, Object.class, Object.class)impl,MethodType.methodType(Integer.class, Integer.class, Integer.class));// BinaryOperator factory() { return new MyLambda() }MethodHandle mh = cs.getTarget(); // 就是函数对象工厂方法BinaryOperator<Integer> invoke = (BinaryOperator<Integer>) mh.invoke();System.out.println(invoke.apply(5, 6));}static final class MyLambda implements BinaryOperator<Integer> {private MyLambda() { }@Overridepublic Integer apply(Integer e, Integer b) {returen lambda$main$0(a, b);}}private static Integer lambda$main$2(Integer a, Integer b) {return a + b;}
}
函数入口
import java.util.function.BinaryOperator;public class C01Lambda1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {BinaryOperator<Integer> lambda = (a, b) -> a + b;}static final class MyLambda implements BinaryOperator<Integer> {private MyLambda() { }@Overridepublic Integer apply(Integer e, Integer b) {returen lambda$main$0(a, b);}}private static Integer lambda$main$2(Integer a, Integer b) {return a + b;}
}
重定向

方法引用
public class C02MethodReference {public static void main(String[] args) {// 方法引用是一种语法糖,它仍然会被翻译成 类,对象,方法// 1.方法从哪来// 2.类,对象从哪来Function<Student, String> func = Student::getName(); // stu-> stu.getName()MethodHandles.Lookup lookup = MethodHandles.lookup();// 反射调用非静态方法MethodHandle impl = lookup.findVirtual(Student.class, "getName", MethodType.methodType(String.class));CallSite cs = LambdaMetafactory.metafactory (lookup,"apply",MethodType.methodType(Function.class),MethodType.methodType(Object.class, Object.class), // 实现接口:两个泛型参数impl, MethodType.methodType(String.class, Student.class) // 返回类型 + 参数类型);Function<Student, String> invoke = (Function<Student, String>) cs.getTarget().invoke();Student stu = new Student();stu.name = "张三";System.out.println(invoke.apply(stu));}static final class MyMethodReference implements Function<Student, String> {@Overridepublic String apply(Student student) {return student.getName();}}static class Student {private String name;public String getName() {return name;}}
}

闭包
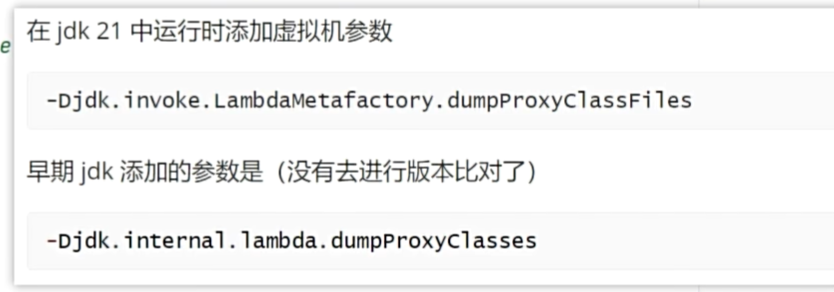
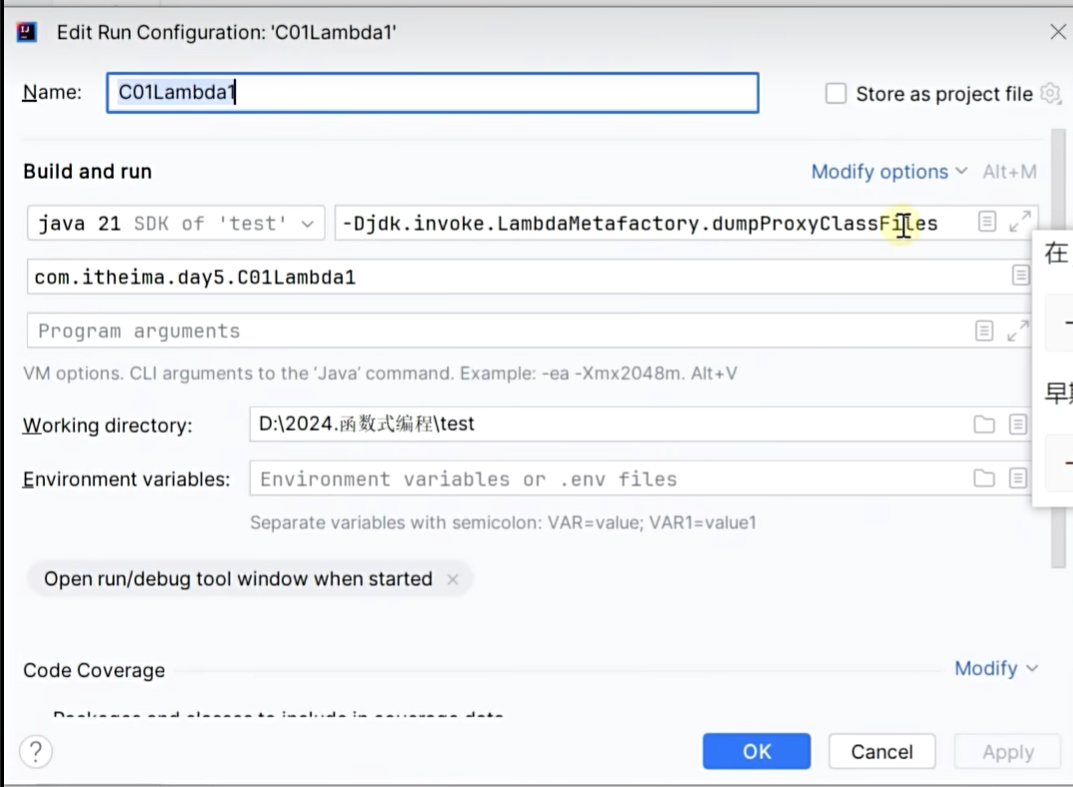
import java.util.function.BinaryOperator;// -Djdk.invoke.LambdaMetafactory.dumpProxyClassFiles
public class C03Closure {public static void main(String[] args) {int c = 10;BinaryOperator<Integer> lambda = (a, b) -> a + b + c; // invoke dynamictest(lambda);for (Method method : C03Closure.class.getDeclaremethods()) {System.out.println(method);}// 1.方法// 2.类和对象static void test(BinaryOperator<Integer> lambda) {}final static class C03Closure$$Lambda implements BinaryOperator {private final int c;private C03Closure$$Lambda(int c) { this.c = c;}public Object apply(Object a, Object b) {return C03Clsure.lambda$main$1(this.c, (Integer)a, (Integer)b);}}// 反编译static private Integer lambda$main$1(int c, Integer a, Integer b) {reutrn a + b + c;}}
}
静态变量
public class C04Closure {static int c = 10;public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryOperator<Integer> lambda = (a, b) - a + b + c;/*System.out.println(lambda.apply(1, 2));c = 20;System.out.println(lambda.apply(1, 2));*/for (Method method : C04Closure.class.getDeclaredMethods()) {System.out.println(method);}static final class C04Closure$$Lambda implements BinaryOperator {private c04Closure$$Lambda() {}public Object apply(Object a, Object b) {return C04Closure.lambda$main$1((Integer)a, (Integer)b );}}}private static Integer lambda$1(Integer a, Integer b) {return a + b + C04Closure.c;}
}
可切分迭代器
public class C06Spliterator {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9);Integer[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};// Stream<Integer> s1 = list.stream();// Stream<Integer> s2 = Arrays.stream(array);Spliterator<Integer> sp1 = list.spliterator();Spliterator<Integer> sp2 = sp1.trySplit();Spliterator<Integer> sp3 = sp2.trySplit();System.out.println("sp1:");sp1.tryAdvance(System.out::println);System.out.println("sp2:");sp2.tryAdvance(System.out::println);System.out.println("sp3:")sp3.tryAdvance(System.out::println);System.out.println("==========================");CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> StreamSupport.stream(sp2, false).reduce(0, Integer::sum)).thenAccept(x -> logger.info("{}", x));CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> StreamSupport.stream(sp3, false).reduce(0, Integer::sum)).thenAccept(x -> logger.info("{}", x));System.in.read();}
}