基本使用
讲原理之前,我简单写个demo小程序
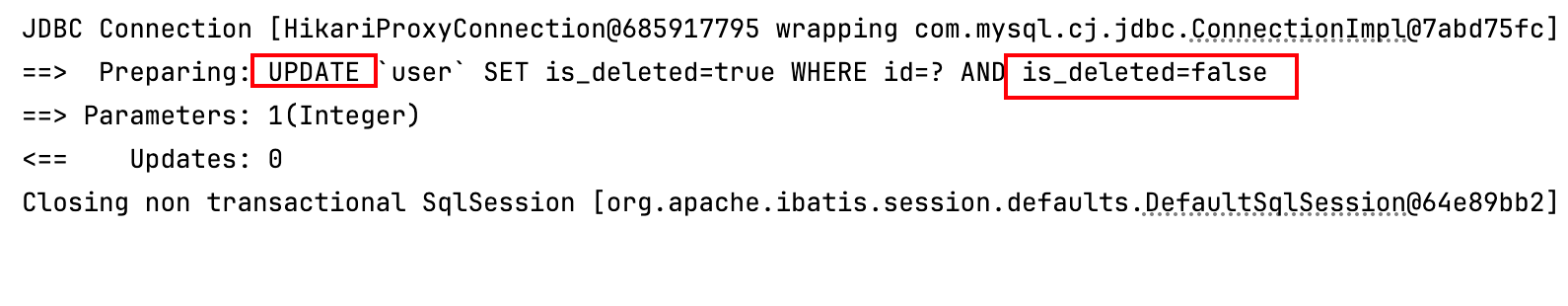
public class TestThreadLocal {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ThreadLocal<String> tl = new ThreadLocal();/**主线程设置了一个值*/tl.set("SSSSSs");//tl.set(new Integer(2));InheritableThreadLocal<String> itl = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();itl.set("itlValue");new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {/**子线程没有设置,所以肯定拿不到*/System.out.println("tl的值:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+tl.get());/**InheritableThreadLocal是可以传递到子线程的,所以这里可以拿到*/System.out.println("Itl的值:"+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + itl.get());}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {tl.set("ttttt");/**这个子线程设置了,是可以拿到*/System.out.println("tl的值:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+tl.get());/**InheritableThreadLocal是可以传递到子线程的,所以这里可以拿到*/System.out.println("Itl的值:"+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + itl.get());/**这里我们改一下看看主线程里的会不会修改*/itl.set("itl's Value changed By thread2");System.out.println("Itl的值:"+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + itl.get());}}).start();Thread.sleep(2000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+tl.get());/**这里我们可以看到子线程里修改InheritableThreadLocal的值是不会影响主线程的*/System.out.println("Itl的值:"+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + itl.get());}
}
运行结果
tl的值:Thread-0null
Itl的值:Thread-0itlValue
tl的值:Thread-1ttttt
Itl的值:Thread-1itlValue
Itl的值:Thread-1itl's Value changed By thread2
mainSSSSSs
Itl的值:mainitlValue
我们可以看到只有某个线程设置了 ThreadLocal的值才能取到,不设置是没有的,这就实现了线程间的隔离。另外对于InheritableThreadLocal它会继承父线程的 InheritableThreadLocal 变量的值(实际上是值的引用副本),所以修改对于主线程和其他子线程是无效的,但是对自己有效,个人觉得这很变态,不管了,这不是重点。
Thread和ThreadLocal的关系
ThreadLocal 和 Thread 是 Java 中处理多线程编程时的两个重要概念,它们在处理线程本地变量时有着不同的角色和用途。
Thread
Thread 是 Java 中用于表示线程的对象。每个 Thread 对象代表一个独立的执行路径,可以在并发环境中同时运行。Java 的多线程编程模型允许你创建多个 Thread 对象,以并行或并发的方式执行多个任务。
Thread 类提供了许多方法来管理和控制线程的行为,比如:
start(): 启动线程。run(): 线程的主体方法,包含线程要执行的任务代码。sleep(long millis): 使当前线程休眠指定的毫秒数。interrupt(): 中断线程。join(): 等待另一个线程终止。isAlive(): 检查线程是否还在运行。
ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal 是 Java 提供的一个工具类,用于创建线程局部变量。这些变量在每个线程中都有独立的初始值和副本,因此每个线程都可以独立地修改自己的变量副本,而不会影响到其他线程的副本。
ThreadLocal 提供了一种将变量与线程绑定的机制,这样每个线程都可以访问到属于自己的、独立的数据副本。这在多线程编程中特别有用,特别是在需要确保线程间数据隔离的场景中。
ThreadLocal 的主要方法包括:
get(): 获取当前线程所对应的值。set(T value): 设置当前线程的值。initialValue(): 提供线程局部变量的初始值,该方法是一个受保护的方法,通常需要在子类中重写。remove(): 移除当前线程的值。
ThreadLocal变量是Thread私有的,一个Thread里设置的值其他的Thread看不到(即使是子线程也不能看到,如果想要子线程看到,可以使用InheritableThreadLocal,这个也曾经被面试过),本文主要讲解ThreadLocal,也会把InheritableThreadLocal顺便讲一下,但是不会当成重点,毕竟面试的时候也不是重点。
下面是Thread类的定义的一部分
public
class Thread implements Runnable {/* Make sure registerNatives is the first thing <clinit> does. */private static native void registerNatives();static {registerNatives();}private volatile String name;private int priority;private Thread threadQ;private long eetop;/* Whether or not to single_step this thread. */private boolean single_step;/* Whether or not the thread is a daemon thread. */private boolean daemon = false;/* JVM state */private boolean stillborn = false;/* What will be run. */private Runnable target;/* The group of this thread */private ThreadGroup group;/* The context ClassLoader for this thread */private ClassLoader contextClassLoader;/* The inherited AccessControlContext of this thread */private AccessControlContext inheritedAccessControlContext;/* For autonumbering anonymous threads. */private static int threadInitNumber;private static synchronized int nextThreadNum() {return threadInitNumber++;}/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained* by the ThreadLocal class. 注意看这个变量,这就是我们的ThreadLocal变量的存放位置,按照它的注释,这个Map是存放在ThreadLocal里的*/ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;/** InheritableThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is* maintained by the InheritableThreadLocal class.*/ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;咱们怎么去理解呢,我们可以理解为这是一个 ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap类型的变量,它是在Thread里存放的,类型是 ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap,这个大家想想就能理解,如果不存放在Thread里怎么能实现线程自己用自己的呢。
ThreadLocal类里关于ThreadLocalMap的定义(每个Thread里都有一个ThreadLocalMap),可以说ThreadLocal关键是ThreadLocalMap,它自己只是定义了对外的接口,其他的逻辑都在ThreadLocalMap里(map的key是ThreadLocal的引用,value是我们在当前线程中设置的值),ThreadLocalMap里重点需要关注Entry,它继承了WeakReference,其实我们设置的值就是设置到这个弱引用的对象的value里,而弱引用只要垃圾回收,就会被回收掉:
网上借了一张图用来解释这些对象的关系

图的组成
- 左侧流程图:
- 初始化ThreadLocal对象:首先,通过
ThreadLocal的构造函数创建一个空的ThreadLocal对象。这个对象本身并不存储值,而是作为一个容器,用于在线程中存储和检索值。 - 设置值:接着,通过调用
ThreadLocal对象的set方法,可以为当前线程设置一个值。这个值是与当前线程相关联的,对其他线程不可见。
- 初始化ThreadLocal对象:首先,通过
- 右侧结构图:
- 线程局部变量结构:右侧展示了
ThreadLocal内部如何存储线程局部变量的结构。每个线程都有一个与之关联的ThreadLocalMap,这个映射表存储了键(ThreadLocal对象)和值(线程局部变量)的对应关系。 - 键(key):这里的键是
ThreadLocal对象本身。 - 值(value):与键相关联的值,即线程局部变量。
- 弱引用(weakReference):
ThreadLocalMap中的键(即ThreadLocal对象)是通过弱引用持有的。这意味着如果ThreadLocal对象没有其他强引用,它将被垃圾回收器回收,即使它仍然作为键存在于映射表中。
- 线程局部变量结构:右侧展示了
- 注释:
- 注释部分解释了为什么
ThreadLocalMap中的键要使用弱引用而不是强引用。如果使用强引用,即使ThreadLocal对象本身(即键)被设置为null(或不再被引用),它仍然会作为键存在于映射表中,导致内存泄漏。因为强引用会阻止垃圾回收器回收不再使用的对象。而使用弱引用,当ThreadLocal对象没有其他强引用时,它可以被垃圾回收器回收,从而避免内存泄漏。
- 注释部分解释了为什么
总结
这张图通过流程图和结构图相结合的方式,清晰地展示了ThreadLocal的工作原理以及为什么在其内部结构中使用了弱引用来避免内存泄漏。它强调了ThreadLocal在Java多线程编程中的重要性,以及如何使用它来管理线程内的共享数据,同时保持数据的线程隔离性。
ThreadLocal源码解析
static class ThreadLocalMap {/*** The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using* its main ref field as the key (which is always a* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.*/static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */Object value;Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {super(k);//new出来一个WeakReference对象,把ThreadLocal传给他 value = v;}}/*** The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two.*/private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;/*** The table, resized as necessary.* table.length MUST always be a power of two.*/private Entry[] table;/*** The number of entries in the table.*/private int size = 0;/*** The next size value at which to resize.*/private int threshold; // Default to 0/*** Set the resize threshold to maintain at worst a 2/3 load factor.*/private void setThreshold(int len) {threshold = len * 2 / 3;}/*** Increment i modulo len.*/private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);}/*** Decrement i modulo len.*/private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) {return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1);}/*** Construct a new map initially containing (firstKey, firstValue).* ThreadLocalMaps are constructed lazily, so we only create* one when we have at least one entry to put in it.*/ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);size = 1;setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);}/*** Construct a new map including all Inheritable ThreadLocals* from given parent map. Called only by createInheritedMap.** @param parentMap the map associated with parent thread.*/private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table;int len = parentTable.length;setThreshold(len);table = new Entry[len];for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {Entry e = parentTable[j];if (e != null) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")ThreadLocal<Object> key = (ThreadLocal<Object>) e.get();if (key != null) {Object value = key.childValue(e.value);Entry c = new Entry(key, value);int h = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);while (table[h] != null)h = nextIndex(h, len);table[h] = c;size++;}}}}/*** Get the entry associated with key. This method* itself handles only the fast path: a direct hit of existing* key. It otherwise relays to getEntryAfterMiss. This is* designed to maximize performance for direct hits, in part* by making this method readily inlinable.** @param key the thread local object* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such*/private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);Entry e = table[i];if (e != null && e.get() == key)return e;elsereturn getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);}/*** Version of getEntry method for use when key is not found in* its direct hash slot.** @param key the thread local object* @param i the table index for key's hash code* @param e the entry at table[i]* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such*/private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;while (e != null) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == key)return e;if (k == null)expungeStaleEntry(i);elsei = nextIndex(i, len);e = tab[i];}return null;}/*** Set the value associated with key.** @param key the thread local object* @param value the value to be set*/private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at// least as common to use set() to create new entries as// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast// path would fail more often than not.Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);for (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == key) {e.value = value;return;}if (k == null) {replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);return;}}tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);int sz = ++size;if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)rehash();}/*** Remove the entry for key.*/private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);for (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {if (e.get() == key) {e.clear();expungeStaleEntry(i);return;}}}/*** Replace a stale entry encountered during a set operation* with an entry for the specified key. The value passed in* the value parameter is stored in the entry, whether or not* an entry already exists for the specified key.** As a side effect, this method expunges all stale entries in the* "run" containing the stale entry. (A run is a sequence of entries* between two null slots.)** @param key the key* @param value the value to be associated with key* @param staleSlot index of the first stale entry encountered while* searching for key.*/private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value,int staleSlot) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;Entry e;// Back up to check for prior stale entry in current run.// We clean out whole runs at a time to avoid continual// incremental rehashing due to garbage collector freeing// up refs in bunches (i.e., whenever the collector runs).int slotToExpunge = staleSlot;for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = prevIndex(i, len))if (e.get() == null)slotToExpunge = i;// Find either the key or trailing null slot of run, whichever// occurs firstfor (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = nextIndex(i, len)) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();// If we find key, then we need to swap it// with the stale entry to maintain hash table order.// The newly stale slot, or any other stale slot// encountered above it, can then be sent to expungeStaleEntry// to remove or rehash all of the other entries in run.if (k == key) {e.value = value;tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];tab[staleSlot] = e;// Start expunge at preceding stale entry if it existsif (slotToExpunge == staleSlot)slotToExpunge = i;cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);return;}// If we didn't find stale entry on backward scan, the// first stale entry seen while scanning for key is the// first still present in the run.if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot)slotToExpunge = i;}// If key not found, put new entry in stale slottab[staleSlot].value = null;tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);// If there are any other stale entries in run, expunge themif (slotToExpunge != staleSlot)cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);}/*** Expunge a stale entry by rehashing any possibly colliding entries* lying between staleSlot and the next null slot. This also expunges* any other stale entries encountered before the trailing null. See* Knuth, Section 6.4** @param staleSlot index of slot known to have null key* @return the index of the next null slot after staleSlot* (all between staleSlot and this slot will have been checked* for expunging).*/private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;// expunge entry at staleSlottab[staleSlot].value = null;tab[staleSlot] = null;size--;// Rehash until we encounter nullEntry e;int i;for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = nextIndex(i, len)) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == null) {e.value = null;tab[i] = null;size--;} else {int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);if (h != i) {tab[i] = null;// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until// null because multiple entries could have been stale.while (tab[h] != null)h = nextIndex(h, len);tab[h] = e;}}}return i;}/*** Heuristically scan some cells looking for stale entries.* This is invoked when either a new element is added, or* another stale one has been expunged. It performs a* logarithmic number of scans, as a balance between no* scanning (fast but retains garbage) and a number of scans* proportional to number of elements, that would find all* garbage but would cause some insertions to take O(n) time.** @param i a position known NOT to hold a stale entry. The* scan starts at the element after i.** @param n scan control: {@code log2(n)} cells are scanned,* unless a stale entry is found, in which case* {@code log2(table.length)-1} additional cells are scanned.* When called from insertions, this parameter is the number* of elements, but when from replaceStaleEntry, it is the* table length. (Note: all this could be changed to be either* more or less aggressive by weighting n instead of just* using straight log n. But this version is simple, fast, and* seems to work well.)** @return true if any stale entries have been removed.*/private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {boolean removed = false;Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;do {i = nextIndex(i, len);Entry e = tab[i];if (e != null && e.get() == null) {n = len;removed = true;i = expungeStaleEntry(i);}} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);return removed;}/*** Re-pack and/or re-size the table. First scan the entire* table removing stale entries. If this doesn't sufficiently* shrink the size of the table, double the table size.*/private void rehash() {expungeStaleEntries();// Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresisif (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)resize();}/*** Double the capacity of the table.*/private void resize() {Entry[] oldTab = table;int oldLen = oldTab.length;int newLen = oldLen * 2;Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];int count = 0;for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {Entry e = oldTab[j];if (e != null) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == null) {e.value = null; // Help the GC} else {int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);while (newTab[h] != null)h = nextIndex(h, newLen);newTab[h] = e;count++;}}}setThreshold(newLen);size = count;table = newTab;}/*** Expunge all stale entries in the table.*/private void expungeStaleEntries() {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {Entry e = tab[j];if (e != null && e.get() == null)expungeStaleEntry(j);}}}ThreadLocal的其他的常规代码
/** Copyright (c) 1997, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS FILE HEADER.** This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 only, as* published by the Free Software Foundation. Oracle designates this* particular file as subject to the "Classpath" exception as provided* by Oracle in the LICENSE file that accompanied this code.** This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License* version 2 for more details (a copy is included in the LICENSE file that* accompanied this code).** You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License version* 2 along with this work; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,* Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.** Please contact Oracle, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065 USA* or visit www.oracle.com if you need additional information or have any* questions.*/package java.lang;
import jdk.internal.misc.TerminatingThreadLocal;import java.lang.ref.*;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.function.Supplier;/*** This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from* their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its* {@code get} or {@code set} method) has its own, independently initialized* copy of the variable. {@code ThreadLocal} instances are typically private* static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g.,* a user ID or Transaction ID).** <p>For example, the class below generates unique identifiers local to each* thread.* A thread's id is assigned the first time it invokes {@code ThreadId.get()}* and remains unchanged on subsequent calls.* <pre>* import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;** public class ThreadId {* // Atomic integer containing the next thread ID to be assigned* private static final AtomicInteger nextId = new AtomicInteger(0);** // Thread local variable containing each thread's ID* private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadId =* new ThreadLocal<Integer>() {* @Override protected Integer initialValue() {* return nextId.getAndIncrement();* }* };** // Returns the current thread's unique ID, assigning it if necessary* public static int get() {* return threadId.get();* }* }* </pre>* <p>Each thread holds an implicit reference to its copy of a thread-local* variable as long as the thread is alive and the {@code ThreadLocal}* instance is accessible; after a thread goes away, all of its copies of* thread-local instances are subject to garbage collection (unless other* references to these copies exist).** @author Josh Bloch and Doug Lea* @since 1.2*/
public class ThreadLocal<T> {/*** ThreadLocals rely on per-thread linear-probe hash maps attached* to each thread (Thread.threadLocals and* inheritableThreadLocals). The ThreadLocal objects act as keys,* searched via threadLocalHashCode. This is a custom hash code* (useful only within ThreadLocalMaps) that eliminates collisions* in the common case where consecutively constructed ThreadLocals* are used by the same threads, while remaining well-behaved in* less common cases.*/private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();/*** The next hash code to be given out. Updated atomically. Starts at* zero.*/private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode =new AtomicInteger();/*** The difference between successively generated hash codes - turns* implicit sequential thread-local IDs into near-optimally spread* multiplicative hash values for power-of-two-sized tables.*/private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;/*** Returns the next hash code.*/private static int nextHashCode() {return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);}/*** Returns the current thread's "initial value" for this* thread-local variable. This method will be invoked the first* time a thread accesses the variable with the {@link #get}* method, unless the thread previously invoked the {@link #set}* method, in which case the {@code initialValue} method will not* be invoked for the thread. Normally, this method is invoked at* most once per thread, but it may be invoked again in case of* subsequent invocations of {@link #remove} followed by {@link #get}.** <p>This implementation simply returns {@code null}; if the* programmer desires thread-local variables to have an initial* value other than {@code null}, {@code ThreadLocal} must be* subclassed, and this method overridden. Typically, an* anonymous inner class will be used.** @return the initial value for this thread-local* 这个就是返回一个null,不知道这么写目的何在*/protected T initialValue() {return null;}/*** Creates a thread local variable. The initial value of the variable is* determined by invoking the {@code get} method on the {@code Supplier}.** @param <S> the type of the thread local's value* @param supplier the supplier to be used to determine the initial value* @return a new thread local variable* @throws NullPointerException if the specified supplier is null* @since 1.8*/public static <S> ThreadLocal<S> withInitial(Supplier<? extends S> supplier) {return new SuppliedThreadLocal<>(supplier);}/*** Creates a thread local variable.* @see #withInitial(java.util.function.Supplier)*/public ThreadLocal() {}/*** Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.** @return the current thread's value of this thread-local根据当前线程拿到ThreadLocalMap(就是返回当前线程的ThreadLocals(Thread类型的t里的ThreadLocalMap)),如果不为空,直接设置到那个ThreadLocalMap里(key是当前的ThreadLocal对象,value是当前我们传入的value)*/public T get() {Thread t = Thread.currentThread();ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);if (map != null) {/**根据当前ThreadLocal的引用从map里拿到对应的Entry*/ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);if (e != null) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")/**如果拿到Entry就返回entry的value*/T result = (T)e.value;return result;}}return setInitialValue();}/*** Returns {@code true} if there is a value in the current thread's copy of* this thread-local variable, even if that values is {@code null}.** @return {@code true} if current thread has associated value in this* thread-local variable; {@code false} if not*/boolean isPresent() {Thread t = Thread.currentThread();ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);return map != null && map.getEntry(this) != null;}/*** Variant of set() to establish initialValue. Used instead* of set() in case user has overridden the set() method.** @return the initial value*/private T setInitialValue() {/**拿到初始值,其实就是null*/T value = initialValue();/**拿到当前线程*/Thread t = Thread.currentThread();/**拿到线程的ThreadLocalMap*/ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);/**如果map不为null设置为上面拿到的初始值*/if (map != null) {map.set(this, value);} else {/**如果map没有初始化,初始化map*/createMap(t, value);}if (this instanceof TerminatingThreadLocal) {TerminatingThreadLocal.register((TerminatingThreadLocal<?>) this);}return value;}/*** Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}* method to set the values of thread-locals.** @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of* this thread-local.*/public void set(T value) {/**先拿到当前的线程*/Thread t = Thread.currentThread();/**拿到当前线程对应的ThreadLocalMap*/ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);/**如果之前已经初始化过map了,直接设置值*/if (map != null) {map.set(this, value);} else {/**如果map没有初始化,初始化map并把当前ThreadLocal作为key,value作为值放入map*/createMap(t, value);}}/*** Removes the current thread's value for this thread-local* variable. If this thread-local variable is subsequently* {@linkplain #get read} by the current thread, its value will be* reinitialized by invoking its {@link #initialValue} method,* unless its value is {@linkplain #set set} by the current thread* in the interim. This may result in multiple invocations of the* {@code initialValue} method in the current thread.** @since 1.5*/public void remove() {ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());if (m != null) {m.remove(this);}}/*** Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in* InheritableThreadLocal.** @param t the current thread* @return the map*/ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {return t.threadLocals;}/*** Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in* InheritableThreadLocal.** @param t the current thread* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map*/void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);}/*** Factory method to create map of inherited thread locals.* Designed to be called only from Thread constructor.** @param parentMap the map associated with parent thread* @return a map containing the parent's inheritable bindings*/static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap);}/*** Method childValue is visibly defined in subclass* InheritableThreadLocal, but is internally defined here for the* sake of providing createInheritedMap factory method without* needing to subclass the map class in InheritableThreadLocal.* This technique is preferable to the alternative of embedding* instanceof tests in methods.*/T childValue(T parentValue) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}/*** An extension of ThreadLocal that obtains its initial value from* the specified {@code Supplier}.*/static final class SuppliedThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> {private final Supplier<? extends T> supplier;SuppliedThreadLocal(Supplier<? extends T> supplier) {this.supplier = Objects.requireNonNull(supplier);}@Overrideprotected T initialValue() {return supplier.get();}}
}为什么要这么设计以及内存泄漏问题
为什么Entry要使用弱引用:
如果是强引用,即使程序中把tl设置为null,但是当前情况是两个强引用指向ThreadLocal这块内存,把tl设置为null只是去掉了一个强引用,还剩下一个强引用,所以依然无法回收这块内存(除非线程结束),但是从程序看这块内存应该是被回收掉了,会有内存泄漏(想处理只有线程被销毁才行,但是线程可能都是7*24小时运行的,所以可能会内存泄漏越来越多导致OOM),而使用弱引用,当tl变为null之后,指向ThreadLocal这块内存的只有key一个弱引用,一旦发生垃圾收集,就会被回收(弱引用的特性,只要垃圾回收期回收,弱引用就会被干掉),也就不存在内存泄漏。
这里需要注意的是,ThreadLocal被回收之后,key的值由原来的ThreadLocal变成了null,我们无法通过null值访问value指向的10M的空间,但是引用会一直存在,也是另外一种内存泄漏。所以我们每次使用完ThreadLocal之后一定要remove。(虽然执行get或者set的时候,会把entry里所有key为null的都清理掉,但是如果长时间没有get和set执行,这块泄漏就一直存在)
如果用的是线程池,用完线程之后要清理ThreadLocals,否则逻辑中如果有可以拿到threadlocal里的值就用原来的,可能会出现问题