提示:DDU,供自己复习使用。欢迎大家前来讨论~
文章目录
- 题目一:99. 岛屿数量
- 思路
- 深度优先搜索DFS
- 广度优先搜索BFS
- 题目二:100. 岛屿的最大面积
- DFS
- BFS
- 总结
题目一:99. 岛屿数量
99. 岛屿数量 (kamacoder.com)
思路
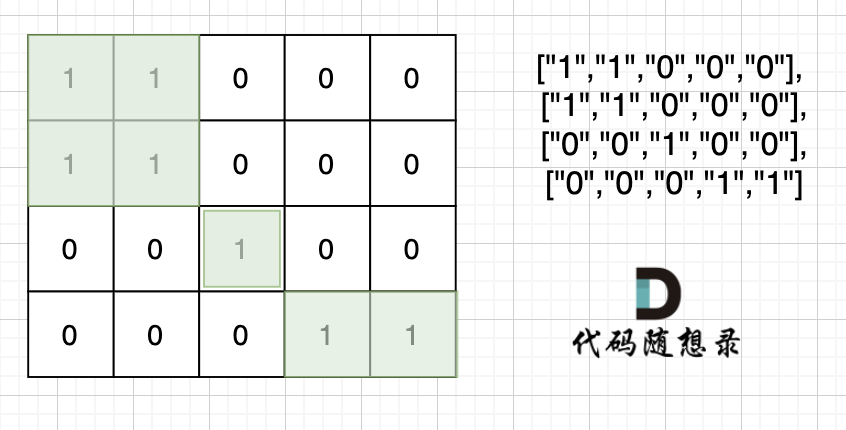
注意题目中每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
也就是说对角线上是不算的, 例如示例二,是三个岛屿,如图:
这道题题目是 DFS,BFS,并查集,基础题目。
本题思路,是用遇到一个没有遍历过的节点陆地,计数器就加一,然后把该节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上。
在遇到标记过的陆地节点和海洋节点的时候直接跳过。 这样计数器就是最终岛屿的数量。
那么如何把节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上呢,就可以使用 DFS,BFS或者并查集。
深度优先搜索DFS
思路:
- 初始化:创建一个变量
result来存储岛屿的数量,初始值为0。 - 检查边界条件:如果网格为空或没有行,直接返回0。
- 双层循环:使用两个嵌套循环遍历网格的每一行和每一列。
- 找到陆地:在内层循环中,检查每个单元格是否为’1’。如果是,增加
result的值,并对该单元格进行DFS。 - DFS函数:DFS函数将遍历当前单元格的所有四个方向(上、下、左、右),如果相邻单元格是陆地(值为’1’)并且没有越界,则递归调用DFS,并标记该单元格为已访问。
- 结束条件:当所有单元格都被检查过,返回
result作为最终的岛屿数量。
注意:
- 递归:DFS是递归实现的,每次递归调用都会检查一个方向的相邻单元格。
- 边界检查:在DFS中,每次移动前都要检查是否会越界,以避免访问数组之外的内存。
- 标记已访问:在DFS中,一旦访问了一个陆地单元格,就将其标记为已访问(通常是将’1’改为’0’),以避免重复计数。
下面给出两种版本的代码:
- 版本一的写法:
- 在调用DFS之前,先对节点进行合法性检查。
- 只有当节点是合法的(即在网格范围内且是陆地)时,才调用DFS函数。
- 这样做可以减少不必要的递归调用,从而提高效率。
- 版本二的写法:
- 不管节点是否合法,都先调用DFS函数。
- 在DFS函数内部,通过终止条件来判断节点是否合法。
- 如果节点不合法(例如,是水或者越界),则直接返回,不进行进一步的递归。
- 这种写法可能在理解上更直观,因为所有的递归逻辑都封装在DFS函数内部。
两种写法的主要区别在于何时进行合法性检查。版本一在调用DFS之前进行检查,而版本二在DFS函数内部进行检查。理论上,版本一的效率可能更高,因为它避免了对不合法节点的递归调用。然而,从代码的可读性角度来看,版本二可能更清晰,因为它将所有的递归逻辑集中在一起。
完整C++代码如下:
// 版本一
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void dfs(const vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextx = x + dir[i][0];int nexty = y + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) { // 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的visited[nextx][nexty] = true;dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);}}
}int main() {int n, m;cin >> n >> m;vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(m, 0));for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {cin >> grid[i][j];}}vector<vector<bool>> visited(n, vector<bool>(m, false));int result = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {visited[i][j] = true;result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true}}}cout << result << endl;
}
为什么 以上代码中的dfs函数,没有终止条件呢? 感觉递归没有终止很危险。
其实终止条件 就写在了 调用dfs的地方,如果遇到不合法的方向,直接不会去调用dfs。
当然也可以这么写:
// 版本二
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void dfs(const vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // 终止条件:访问过的节点 或者 遇到海水visited[x][y] = true; // 标记访问过for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextx = x + dir[i][0];int nexty = y + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);}
}int main() {int n, m;cin >> n >> m;vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(m, 0));for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {cin >> grid[i][j];}}vector<vector<bool>> visited(n, vector<bool>(m, false));int result = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true}}}cout << result << endl;
}
最后是另一个更清晰简单的思路的C++代码:
#include <vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {
public:int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {if (grid.empty() || grid[0].empty()) {return 0;}int result = 0;int row = grid.size();int col = grid[0].size();for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {if (grid[i][j] == '1') {result++;dfs(grid, i, j, row, col);}}}return result;}private:void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, int x, int y, int row, int col) {if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= row || y >= col || grid[x][y] == '0') {return;}grid[x][y] = '0'; // 标记为已访问dfs(grid, x - 1, y, row, col); // 向上dfs(grid, x + 1, y, row, col); // 向下dfs(grid, x, y - 1, row, col); // 向左dfs(grid, x, y + 1, row, col); // 向右}
};
广度优先搜索BFS
BFS和队列数据结构是相辅相成的
本题完整广搜代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void bfs(const vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {queue<pair<int, int>> que;que.push({x, y});visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记while(!que.empty()) {pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();int curx = cur.first;int cury = cur.second;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) {que.push({nextx, nexty});visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记}}}
}int main() {int n, m;cin >> n >> m;vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(m, 0));for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {cin >> grid[i][j];}}vector<vector<bool>> visited(n, vector<bool>(m, false));int result = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1bfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true}}}cout << result << endl;
}
另一种解法:
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Solution {
public:int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {if (grid.empty() || grid[0].empty()) {return 0;}int result = 0;int row = grid.size();int col = grid[0].size();queue<pair<int, int>> q;for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {if (grid[i][j] == '1') {result++;q.push({i, j});grid[i][j] = '0'; // Mark as visitedwhile (!q.empty()) {auto cur = q.front();q.pop();int x = cur.first;int y = cur.second;// Check and mark neighborsif (x - 1 >= 0 && grid[x - 1][y] == '1') {q.push({x - 1, y});grid[x - 1][y] = '0';}if (y - 1 >= 0 && grid[x][y - 1] == '1') {q.push({x, y - 1});grid[x][y - 1] = '0';}if (x + 1 < row && grid[x + 1][y] == '1') {q.push({x + 1, y});grid[x + 1][y] = '0';}if (y + 1 < col && grid[x][y + 1] == '1') {q.push({x, y + 1});grid[x][y + 1] = '0';}}}}}return result;}
};int main() {Solution solution;vector<vector<char>> grid = {{'1', '1', '0', '0', '0'},{'0', '1', '1', '0', '0'},{'0', '0', '0', '1', '1'},{'1', '0', '0', '0', '1'},{'0', '1', '1', '0', '0'}};cout << "Number of islands: " << solution.numIslands(grid) << endl;return 0;
}
题目二:100. 岛屿的最大面积
100. 岛屿的最大面积 (kamacoder.com)
DFS
在编写DFS(深度优先搜索)函数时,存在两种常见写法:一种是在DFS函数外部进行合法性检查后再调用DFS,另一种是在DFS函数内部通过终止条件进行判断。
写法一,dfs只处理下一个节点,即在主函数遇到岛屿就计数为1,dfs处理接下来的相邻陆地
// 版本一
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int count;
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextx = x + dir[i][0];int nexty = y + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) { // 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的visited[nextx][nexty] = true;count++;dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);}}
}int main() {int n, m;cin >> n >> m;vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(m, 0));for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {cin >> grid[i][j];}}vector<vector<bool>> visited(n, vector<bool>(m, false));int result = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {count = 1; // 因为dfs处理下一个节点,所以这里遇到陆地了就先计数,dfs处理接下来的相邻陆地visited[i][j] = true;dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 trueresult = max(result, count);}}}cout << result << endl;}
写法二,dfs处理当前节点,即在主函数遇到岛屿就计数为0,dfs处理接下来的全部陆地
dfs
// 版本二
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int count;
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // 终止条件:访问过的节点 或者 遇到海水visited[x][y] = true; // 标记访问过count++;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextx = x + dir[i][0];int nexty = y + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);}
}int main() {int n, m;cin >> n >> m;vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(m, 0));for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {cin >> grid[i][j];}}vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));int result = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {count = 0; // 因为dfs处理当前节点,所以遇到陆地计数为0,进dfs之后在开始从1计数dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 trueresult = max(result, count);}}}cout << result << endl;
}
两种DFS写法的差异主要在于何时进行岛屿计数:一种是在主函数中遇到新陆地即计数,另一种是将计数完全放在DFS函数内部处理。这种差异导致了不同的代码风格和逻辑结构,也是造成DFS实现方式多样性的根本原因。
BFS
本题BFS代码如下:
class Solution {
private:int count;int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向void bfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {queue<int> que;que.push(x);que.push(y);visited[x][y] = true; // 加入队列就意味节点是陆地可到达的点count++;while(!que.empty()) {int xx = que.front();que.pop();int yy = que.front();que.pop();for (int i = 0 ;i < 4; i++) {int nextx = xx + dir[i][0];int nexty = yy + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) { // 节点没有被访问过且是陆地visited[nextx][nexty] = true;count++;que.push(nextx);que.push(nexty);}}}}public:int maxAreaOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));int result = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {count = 0;bfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 trueresult = max(result, count);}}}return result;}
};
总结
BFS、DFS、并查集解决岛屿问题
- 算法选择:
- BFS:适用于层级遍历,可以找到最短路径,适合于岛屿问题因为它可以逐层扩展,直到所有相连的陆地都被访问。
- DFS:适用于深度遍历,可以探索所有可能的路径,适合于岛屿问题因为它可以深入探索每个岛屿直到尽头。
- 并查集:适用于处理动态连通性问题,通过合并操作来识别和跟踪连通的组件,适合于岛屿问题因为它可以快速判断和合并相连的陆地。
- 实现方式:
- BFS:使用队列存储待访问的节点,逐层访问,每访问一个陆地节点,就将其所有未访问的相邻陆地节点加入队列。
- DFS:使用递归或栈存储待访问的节点,深入访问,每访问一个陆地节点,就递归地访问其所有未访问的相邻陆地节点。
- 并查集:使用集合数据结构,每个陆地节点初始时属于自己的集合,当访问到相邻陆地时,通过并查集的合并操作将它们归为同一集合。
- 效率和适用性:
- BFS:在某些情况下可能比DFS更高效,因为它按层次访问,可以更快地找到所有相邻的陆地,但空间复杂度较高。
- DFS:在递归深度不大的情况下非常高效,但可能会导致栈溢出,特别是在深度很大的网格中。
- 并查集:在处理大规模数据时通常更高效,因为它减少了重复访问和递归调用,但需要额外的空间来维护集合信息。