线程创建方式
- 继承Thread类
- 实现Runnable接口
- 实现Callable接口
LockSupport的使用
LockSupport.park()/LockSupport.unpark()
LockSupport是一个工具类,提供了基本的线程阻塞和唤醒功能,它是创建锁和其他同步组件的基础工具,内部是使用sun.misc.Unsafe类实现的,LockSupport和使用它的线程都会关联一个许可,park方法表示消耗一个许可,调用park方法时,如果许可可用则park方法返回,如果没有许可则一直阻塞直到许可可用。unpark方法表示增加一个许可,多次调用并不会积累许可,因为许可数最大值为1。
sychronized的notify和notifyAll可以实现线程的阻塞和唤醒,但是只能唤醒一个和全部唤醒,无法指定唤醒某一个线程,并且必须和sychronized配合使用。
public class T1 {public void printA(Thread thread){try {Thread.sleep(20L);System.out.println("A");LockSupport.park(thread);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}public void printB(Thread thread){try {Thread.sleep(20L);System.out.println("B");LockSupport.park(thread);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}public void printC(){try {Thread.sleep(20L);System.out.println("C");} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}public static void main(String[] args) {T1 t = new T1();Thread threadC = new Thread(t::printC);Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> t.printB(threadC));Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> t.printA(threadB));threadA.start();threadB.start();threadC.start();}}
ReentrantLock的简单使用
Lock在默认情况下实现的是独占的,不可响应中断的锁。
obj.lock/obj.unlock()
public class T2 {private volatile int num;private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();private int getNum(){return num;}private void addNum(){lock.lock();try {Thread.sleep(5L);System.out.println(num);num++;} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}finally {lock.unlock();}}public static void main(String[] args) {T2 t2 = new T2();for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {new Thread(t2::addNum).start();}}
}
// 默认调用非公平锁
public ReentrantLock() {sync = new NonfairSync();
}
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
一个框架:构建锁,构建同步器
eg:ReentrantLock,Semaphore,ReentrantReadWriteLock,SynchronousQueue,FutureTask。也可以自定义同步器。
核心思想
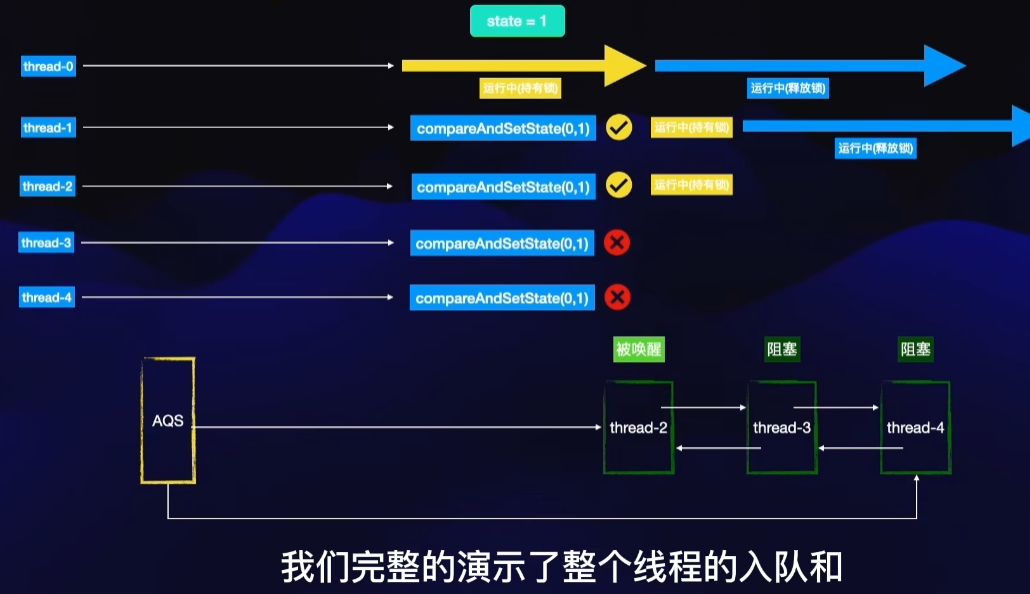
AQS核心思想是,如果被请求的共享资源空闲,则将当前请求资源的线程设置为有效的工作线程,并且将共享资源设置为锁定状态。如果被请求的共享资源被占用,那么就需要一套线程阻塞等待以及被唤醒时锁分配的机制,这个机制AQS是用CLH队列锁实现的,即将暂时获取不到锁的线程加入到队列中。
if(共享资源空闲){将当前请求资源的线程设置为有效的工作线程;共享资源加锁;
}else(共享资源占用){线程阻塞等待&唤醒时锁分配机制;//AQS是用CLH队列锁实现,暂时获取不到锁的线程加入到队列中。
}
CLH
CLH(Craig,Landin,and Hagersten)队列是一个虚拟的双向队列(虚拟的双向队列即不存在队列实例,仅存在结点之间的关联关系)。AQS是将每条请求共享资源的线程封装成一个CLH锁队列的一个结点(Node)来实现锁的分配。
内部实现
- AQS用int成员变量来表示同步状态,用FIFO队列完成获取资源线程的排队。AQS使用CAS对该同步状态进行原子操作实现对其值的修改。
private volatile int state;//共享变量,使用volatile修饰保证线程可见性
- 对state的操作
state的值决定了哪些线程可以拿到锁,获取不到锁的线程打包到node结点
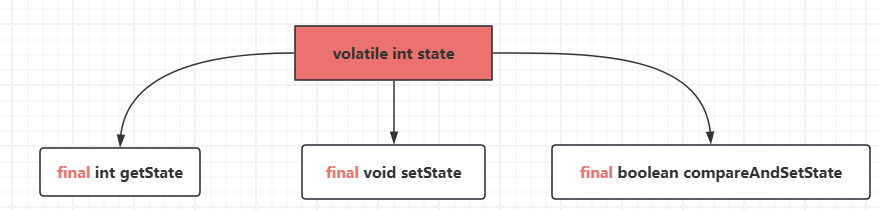
/*** The synchronization state.*/private volatile int state;/*** Returns the current value of synchronization state.* This operation has memory semantics of a {@code volatile} read.* @return current state value*///返回同步状态的当前值protected final int getState() {return state;}/*** Sets the value of synchronization state.* This operation has memory semantics of a {@code volatile} write.* @param newState the new state value*/// 设置同步状态的值protected final void setState(int newState) {state = newState;}/*** Atomically sets synchronization state to the given updated* value if the current state value equals the expected value.* This operation has memory semantics of a {@code volatile} read* and write.** @param expect the expected value* @param update the new value* @return {@code true} if successful. False return indicates that the actual* value was not equal to the expected value.*///原子地(CAS操作)将同步状态值设置为给定值update如果当前同步状态的值等于expect(期望值)protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {return U.compareAndSetInt(this, STATE, expect, update);}

资源共享
| Exclusive(独占) | 公平锁:先到先得 | ReentrantLock可选择是否公平 |
|---|---|---|
| 非公平锁:无视队列顺序,抢占式 | sycronized非公平 饥饿问题 | |
| Share(共享) | 多线程可同时执行 | Semaphore/CountDownLatch。Semaphore、CountDownLatCh、 CyclicBarrier、ReadWriteLock |
不同的自定义同步器争用共享资源的方式也不同。自定义同步器在实现时只需要实现共享资源 state 的获取与释放方式即可,至于具体线程等待队列的维护(如获取资源失败入队/唤醒出队等),AQS已经在上层已经帮我们实现好了。
AQS底层使用了模板方法模式
自定义同步器
使用者继承AbstractQueuedSynchronizer并重写指定的方法。(这些重写方法很简单,无非是对于共享资源state的获取和释放) 将AQS组合在自定义同步组件的实现中,并调用其模板方法,而这些模板方法会调用使用者重写的方法。
isHeldExclusively()//该线程是否正在独占资源。只有用到condition才需要去实现它。
tryAcquire(int)//独占方式。尝试获取资源,成功则返回true,失败则返回false。
tryRelease(int)//独占方式。尝试释放资源,成功则返回true,失败则返回false。
tryAcquireShared(int)//共享方式。尝试获取资源。负数表示失败;0表示成功,但没有剩余可用资源;正数表示成功,且有剩余资源。
tryReleaseShared(int)//共享方式。尝试释放资源,成功则返回true,失败则返回false。
要求:
- 方法内部线程安全
- 简短而不是阻塞
- 其他方法是final,无法被其他类使用
eg****:
以ReentrantLock为例,state初始化为0,表示未锁定状态。A线程lock()时,会调用tryAcquire()独占该锁并将state+1。此后,其他线程再tryAcquire()时就会失败,直到A线程unlock()到state=0(即释放锁)为止,其它线程才有机会获取该锁。当然,释放锁之前,A线程自己是可以重复获取此锁的(state会累加),这就是可重入的概念。但要注意,获取多少次就要释放多少次,这样才能保证state是能回到零态的。
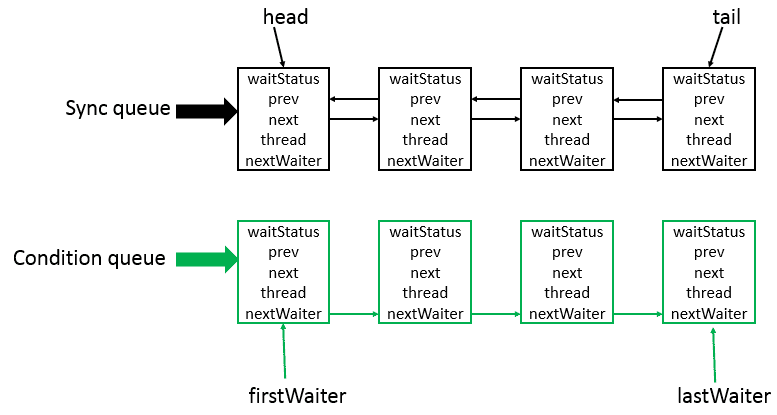
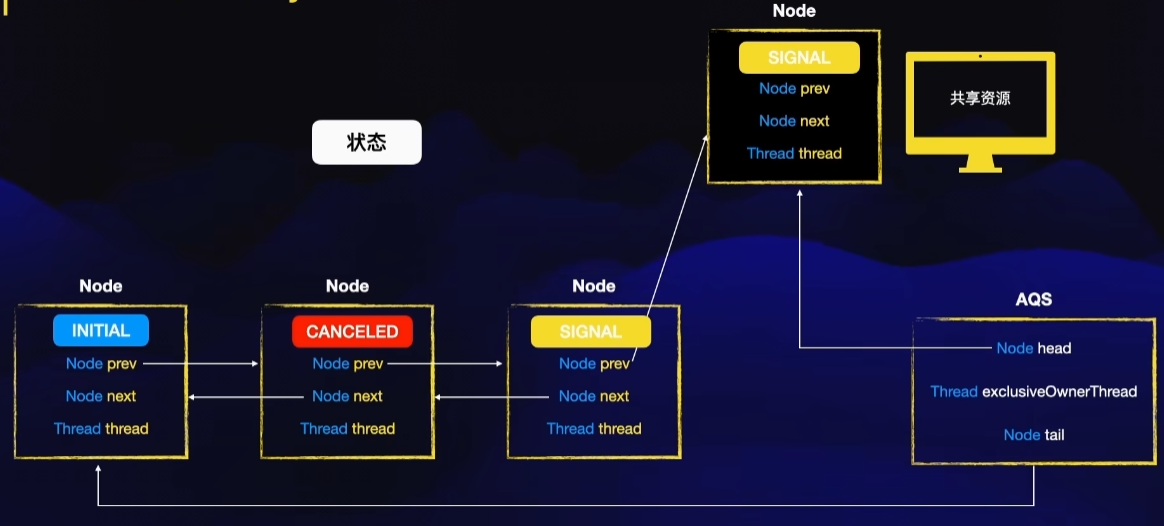
AQS数据结构
CLH队列,虚拟的双向队列。
Sync queue,即同步队列,是双向链表,包括head结点和tail结点,head结点主要用作后续的调度。
Condition queue不是必须的,其是一个单向链表,只有当使用Condition时,才会存在此单向链表。并且可能会有多个Condition queue。
AQS源码
private Node enq(final Node node) {for (;;) {Node t = tail;if (t == null) { // Must initializeif (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))tail = head;} else {node.prev = t;if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {t.next = node;return t;}}}
}
该方法的关键在于使用CAS的方式修改头尾节点,防止了多线程下出现的问题。
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {int ws = pred.waitStatus;if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)/** This node has already set status asking a release* to signal it, so it can safely park.*/return true;if (ws > 0) {/** Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and* indicate retry.*/do {node.prev = pred = pred.prev;} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);pred.next = node;} else {/** waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.*/compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);}return false;
}
真正实现阻塞的方法
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {LockSupport.park(this);return Thread.interrupted();
}
Lock的流程
加锁

unlock的流程
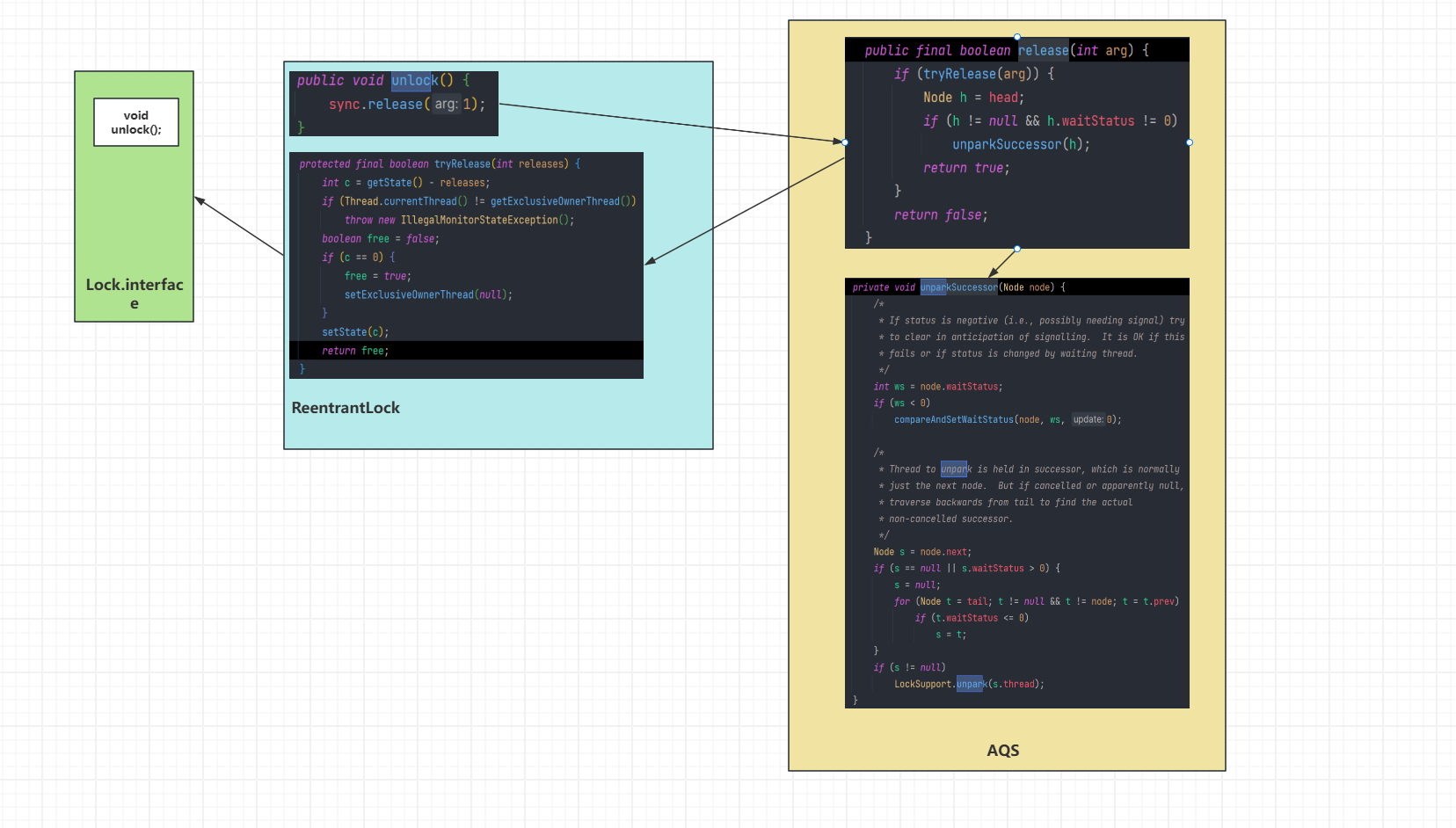
- 释放锁的步骤
- 解锁
- 唤醒下一个结点
- 唤醒下一个节点的条件
- 头节点不为空&&头节点等待状态不为0
transient关键字
transient 关键字用于表示某个字段不应该被序列化。当一个对象被序列化时,使用 transient 修饰的变量不会被保存到持久化存储中,例如文件或网络流中。
使用场景:
- 序列化中的敏感数据(密码)
- 非必要数据(缓存、计算结果)
注意:
transient只能用于对象的实例字段,不能用于静态字段(static),因为静态字段本来就不属于某个具体对象,而是属于类。- 在使用
transient时,如果字段的数据在反序列化后需要被重新初始化,通常需要自定义反序列化逻辑(例如通过实现readObject方法)。
transient 关键字可以提高安全性和性能,尤其是在处理敏感数据或无关紧要的临时数据时。
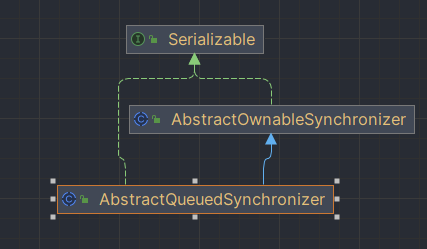
类结构
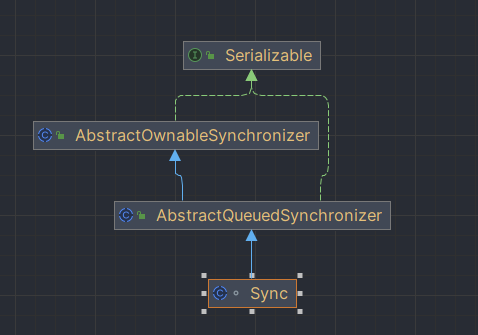
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer继承自AbstractOwnableSynchronizer抽象类,并且实现了Serializable接口,可以进行序列化。
public abstract class AbstractOwnableSynchronizer implements java.io.Serializable {// 版本序列号private static final long serialVersionUID = 3737899427754241961L;// 构造方法protected AbstractOwnableSynchronizer() { }// 独占模式下的线程private transient Thread exclusiveOwnerThread;// 设置独占线程 protected final void setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread thread) {exclusiveOwnerThread = thread;}// 获取独占线程 protected final Thread getExclusiveOwnerThread() {return exclusiveOwnerThread;}
}
内部类Node
static final class Node {// 模式,分为共享与独占// 共享模式static final Node SHARED = new Node();// 独占模式static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null; // 结点状态// CANCELLED,值为1,表示当前的线程被取消// SIGNAL,值为-1,表示当前节点的后继节点包含的线程需要运行,也就是unpark// CONDITION,值为-2,表示当前节点在等待condition,也就是在condition队列中// PROPAGATE,值为-3,表示当前场景下后续的acquireShared能够得以执行// 值为0,表示当前节点在sync队列中,等待着获取锁static final int CANCELLED = 1;static final int SIGNAL = -1;static final int CONDITION = -2;static final int PROPAGATE = -3; // 结点状态volatile int waitStatus; // 前驱结点volatile Node prev; // 后继结点volatile Node next; // 结点所对应的线程volatile Thread thread; // 下一个等待者Node nextWaiter;// 结点是否在共享模式下等待final boolean isShared() {return nextWaiter == SHARED;}// 获取前驱结点,若前驱结点为空,抛出异常final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {// 保存前驱结点Node p = prev; if (p == null) // 前驱结点为空,抛出异常throw new NullPointerException();else // 前驱结点不为空,返回return p;}// 无参构造方法Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker}// 构造方法Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiterthis.nextWaiter = mode;this.thread = thread;}// 构造方法Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Conditionthis.waitStatus = waitStatus;this.thread = thread;}
}

内部类ConditionObject
public class ConditionObject implements Condition, java.io.Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1173984872572414699L;/** First node of condition queue. */private transient ConditionNode firstWaiter;/** Last node of condition queue. */private transient ConditionNode lastWaiter;/*** Creates a new {@code ConditionObject} instance.*/// 构造方法public ConditionObject() { }// Signalling methods/*** Removes and transfers one or all waiters to sync queue.*/// 删除并转移一个或所有 Waiter 到同步队列。private void doSignal(ConditionNode first, boolean all) {while (first != null) {ConditionNode next = first.nextWaiter;if ((firstWaiter = next) == null)lastWaiter = null;if ((first.getAndUnsetStatus(COND) & COND) != 0) {enqueue(first);if (!all)break;}first = next;}}/*** Moves the longest-waiting thread, if one exists, from the* wait queue for this condition to the wait queue for the* owning lock.** @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if {@link #isHeldExclusively}* returns {@code false}*///将等待时间最长的线程(如果存在)从此条件的等待队列移动到拥有锁的等待队列。public final void signal() {ConditionNode first = firstWaiter;if (!isHeldExclusively())throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();if (first != null)doSignal(first, false);}/*** Moves all threads from the wait queue for this condition to* the wait queue for the owning lock.** @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if {@link #isHeldExclusively}* returns {@code false}*/// 将所有线程从此条件的等待队列移动到拥有锁的等待队列。public final void signalAll() {ConditionNode first = firstWaiter;if (!isHeldExclusively())throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();if (first != null)doSignal(first, true);}// Waiting methods/*** Adds node to condition list and releases lock.** @param node the node* @return savedState to reacquire after wait*/// 将节点添加到条件列表并释放锁private int enableWait(ConditionNode node) {if (isHeldExclusively()) {node.waiter = Thread.currentThread();node.setStatusRelaxed(COND | WAITING);ConditionNode last = lastWaiter;if (last == null)firstWaiter = node;elselast.nextWaiter = node;lastWaiter = node;int savedState = getState();if (release(savedState))return savedState;}node.status = CANCELLED; // lock not held or inconsistentthrow new IllegalMonitorStateException();}/*** Returns true if a node that was initially placed on a condition* queue is now ready to reacquire on sync queue.* @param node the node* @return true if is reacquiring*/// 如果最初放置在条件队列上的节点现在已准备好在同步队列上重新获取,则返回 true。private boolean canReacquire(ConditionNode node) {// check links, not status to avoid enqueue racereturn node != null && node.prev != null && isEnqueued(node);}/*** Unlinks the given node and other non-waiting nodes from* condition queue unless already unlinked.*/// 从condition队列中清除状态为CANCEL的结点private void unlinkCancelledWaiters(ConditionNode node) {if (node == null || node.nextWaiter != null || node == lastWaiter) {ConditionNode w = firstWaiter, trail = null;while (w != null) {ConditionNode next = w.nextWaiter;if ((w.status & COND) == 0) {w.nextWaiter = null;if (trail == null)firstWaiter = next;elsetrail.nextWaiter = next;if (next == null)lastWaiter = trail;} elsetrail = w;w = next;}}}/*** Implements uninterruptible condition wait.* <ol>* <li>Save lock state returned by {@link #getState}.* <li>Invoke {@link #release} with saved state as argument,* throwing IllegalMonitorStateException if it fails.* <li>Block until signalled.* <li>Reacquire by invoking specialized version of* {@link #acquire} with saved state as argument.* </ol>*/// 等待,当前线程在接到信号之前一直处于等待状态,不响应中断public final void awaitUninterruptibly() {ConditionNode node = new ConditionNode();int savedState = enableWait(node);LockSupport.setCurrentBlocker(this); // for back-compatibilityboolean interrupted = false, rejected = false;while (!canReacquire(node)) {if (Thread.interrupted())interrupted = true;else if ((node.status & COND) != 0) {try {if (rejected)node.block();elseForkJoinPool.managedBlock(node);} catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {rejected = true;} catch (InterruptedException ie) {interrupted = true;}} elseThread.onSpinWait(); // awoke while enqueuing}LockSupport.setCurrentBlocker(null);node.clearStatus();acquire(node, savedState, false, false, false, 0L);if (interrupted)Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}/*** Implements interruptible condition wait.* <ol>* <li>If current thread is interrupted, throw InterruptedException.* <li>Save lock state returned by {@link #getState}.* <li>Invoke {@link #release} with saved state as argument,* throwing IllegalMonitorStateException if it fails.* <li>Block until signalled or interrupted.* <li>Reacquire by invoking specialized version of* {@link #acquire} with saved state as argument.* <li>If interrupted while blocked in step 4, throw InterruptedException.* </ol>*/// 等待,当前线程在接到信号或被中断之前一直处于等待状态public final void await() throws InterruptedException {if (Thread.interrupted())throw new InterruptedException();ConditionNode node = new ConditionNode();int savedState = enableWait(node);LockSupport.setCurrentBlocker(this); // for back-compatibilityboolean interrupted = false, cancelled = false, rejected = false;while (!canReacquire(node)) {if (interrupted |= Thread.interrupted()) {if (cancelled = (node.getAndUnsetStatus(COND) & COND) != 0)break; // else interrupted after signal} else if ((node.status & COND) != 0) {try {if (rejected)node.block();elseForkJoinPool.managedBlock(node);} catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {rejected = true;} catch (InterruptedException ie) {interrupted = true;}} elseThread.onSpinWait(); // awoke while enqueuing}LockSupport.setCurrentBlocker(null);node.clearStatus();acquire(node, savedState, false, false, false, 0L);if (interrupted) {if (cancelled) {unlinkCancelledWaiters(node);throw new InterruptedException();}Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}}/*** Implements timed condition wait.* <ol>* <li>If current thread is interrupted, throw InterruptedException.* <li>Save lock state returned by {@link #getState}.* <li>Invoke {@link #release} with saved state as argument,* throwing IllegalMonitorStateException if it fails.* <li>Block until signalled, interrupted, or timed out.* <li>Reacquire by invoking specialized version of* {@link #acquire} with saved state as argument.* <li>If interrupted while blocked in step 4, throw InterruptedException.* </ol>*/// 等待,当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定等待时间之前一直处于等待状态 public final long awaitNanos(long nanosTimeout)throws InterruptedException {if (Thread.interrupted())throw new InterruptedException();ConditionNode node = new ConditionNode();int savedState = enableWait(node);long nanos = (nanosTimeout < 0L) ? 0L : nanosTimeout;long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanos;boolean cancelled = false, interrupted = false;while (!canReacquire(node)) {if ((interrupted |= Thread.interrupted()) ||(nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime()) <= 0L) {if (cancelled = (node.getAndUnsetStatus(COND) & COND) != 0)break;} elseLockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);}node.clearStatus();acquire(node, savedState, false, false, false, 0L);if (cancelled) {unlinkCancelledWaiters(node);if (interrupted)throw new InterruptedException();} else if (interrupted)Thread.currentThread().interrupt();long remaining = deadline - System.nanoTime(); // avoid overflowreturn (remaining <= nanosTimeout) ? remaining : Long.MIN_VALUE;}/*** Implements absolute timed condition wait.* <ol>* <li>If current thread is interrupted, throw InterruptedException.* <li>Save lock state returned by {@link #getState}.* <li>Invoke {@link #release} with saved state as argument,* throwing IllegalMonitorStateException if it fails.* <li>Block until signalled, interrupted, or timed out.* <li>Reacquire by invoking specialized version of* {@link #acquire} with saved state as argument.* <li>If interrupted while blocked in step 4, throw InterruptedException.* <li>If timed out while blocked in step 4, return false, else true.* </ol>*/// 等待,当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定最后期限之前一直处于等待状态public final boolean awaitUntil(Date deadline)throws InterruptedException {long abstime = deadline.getTime();if (Thread.interrupted())throw new InterruptedException();ConditionNode node = new ConditionNode();int savedState = enableWait(node);boolean cancelled = false, interrupted = false;while (!canReacquire(node)) {if ((interrupted |= Thread.interrupted()) ||System.currentTimeMillis() >= abstime) {if (cancelled = (node.getAndUnsetStatus(COND) & COND) != 0)break;} elseLockSupport.parkUntil(this, abstime);}node.clearStatus();acquire(node, savedState, false, false, false, 0L);if (cancelled) {unlinkCancelledWaiters(node);if (interrupted)throw new InterruptedException();} else if (interrupted)Thread.currentThread().interrupt();return !cancelled;}/*** Implements timed condition wait.* <ol>* <li>If current thread is interrupted, throw InterruptedException.* <li>Save lock state returned by {@link #getState}.* <li>Invoke {@link #release} with saved state as argument,* throwing IllegalMonitorStateException if it fails.* <li>Block until signalled, interrupted, or timed out.* <li>Reacquire by invoking specialized version of* {@link #acquire} with saved state as argument.* <li>If interrupted while blocked in step 4, throw InterruptedException.* <li>If timed out while blocked in step 4, return false, else true.* </ol>*/// 等待,当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定等待时间之前一直处于等待状态。此方法在行为上等效于: awaitNanos(unit.toNanos(time)) > 0public final boolean await(long time, TimeUnit unit)throws InterruptedException {long nanosTimeout = unit.toNanos(time);if (Thread.interrupted())throw new InterruptedException();ConditionNode node = new ConditionNode();int savedState = enableWait(node);long nanos = (nanosTimeout < 0L) ? 0L : nanosTimeout;long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanos;boolean cancelled = false, interrupted = false;while (!canReacquire(node)) {if ((interrupted |= Thread.interrupted()) ||(nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime()) <= 0L) {if (cancelled = (node.getAndUnsetStatus(COND) & COND) != 0)break;} elseLockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);}node.clearStatus();acquire(node, savedState, false, false, false, 0L);if (cancelled) {unlinkCancelledWaiters(node);if (interrupted)throw new InterruptedException();} else if (interrupted)Thread.currentThread().interrupt();return !cancelled;}// support for instrumentation/*** Returns true if this condition was created by the given* synchronization object.** @return {@code true} if owned*/final boolean isOwnedBy(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer sync) {return sync == AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.this;}/*** Queries whether any threads are waiting on this condition.* Implements {@link AbstractQueuedSynchronizer#hasWaiters(ConditionObject)}.** @return {@code true} if there are any waiting threads* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if {@link #isHeldExclusively}* returns {@code false}*/// 查询是否有正在等待此条件的任何线程protected final boolean hasWaiters() {if (!isHeldExclusively())throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();for (ConditionNode w = firstWaiter; w != null; w = w.nextWaiter) {if ((w.status & COND) != 0)return true;}return false;}/*** Returns an estimate of the number of threads waiting on* this condition.* Implements {@link AbstractQueuedSynchronizer#getWaitQueueLength(ConditionObject)}.** @return the estimated number of waiting threads* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if {@link #isHeldExclusively}* returns {@code false}*/// 返回正在等待此条件的线程数估计值protected final int getWaitQueueLength() {if (!isHeldExclusively())throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();int n = 0;for (ConditionNode w = firstWaiter; w != null; w = w.nextWaiter) {if ((w.status & COND) != 0)++n;}return n;}/*** Returns a collection containing those threads that may be* waiting on this Condition.* Implements {@link AbstractQueuedSynchronizer#getWaitingThreads(ConditionObject)}.** @return the collection of threads* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if {@link #isHeldExclusively}* returns {@code false}*/// 返回包含那些可能正在等待此条件的线程集合protected final Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads() {if (!isHeldExclusively())throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<>();for (ConditionNode w = firstWaiter; w != null; w = w.nextWaiter) {if ((w.status & COND) != 0) {Thread t = w.waiter;if (t != null)list.add(t);}}return list;}
}
public interface Condition {// 等待,当前线程在接到信号或被中断之前一直处于等待状态void await() throws InterruptedException;// 等待,当前线程在接到信号之前一直处于等待状态,不响应中断void awaitUninterruptibly();//等待,当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定等待时间之前一直处于等待状态 long awaitNanos(long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException;// 等待,当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定等待时间之前一直处于等待状态。此方法在行为上等效于: awaitNanos(unit.toNanos(time)) > 0boolean await(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;// 等待,当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定最后期限之前一直处于等待状态boolean awaitUntil(Date deadline) throws InterruptedException;// 唤醒一个等待线程。如果所有的线程都在等待此条件,则选择其中的一个唤醒。在从 await 返回之前,该线程必须重新获取锁。void signal();// 唤醒所有等待线程。如果所有的线程都在等待此条件,则唤醒所有线程。在从 await 返回之前,每个线程都必须重新获取锁。void signalAll();
}
类的属性
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984972572414691L;// Node status bits, also used as argument and return valuesstatic final int WAITING = 1; // must be 1static final int CANCELLED = 0x80000000; // must be negativestatic final int COND = 2; // in a condition wait/*** Head of the wait queue, lazily initialized.*/private transient volatile Node head;/*** Tail of the wait queue. After initialization, modified only via casTail.*/private transient volatile Node tail;/*** The synchronization state.*/private volatile int state;private static final Unsafe U = Unsafe.getUnsafe();private static final long STATE= U.objectFieldOffset(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class, "state");private static final long HEAD= U.objectFieldOffset(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class, "head");private static final long TAIL= U.objectFieldOffset(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class, "tail");static {Class<?> ensureLoaded = LockSupport.class;}
}
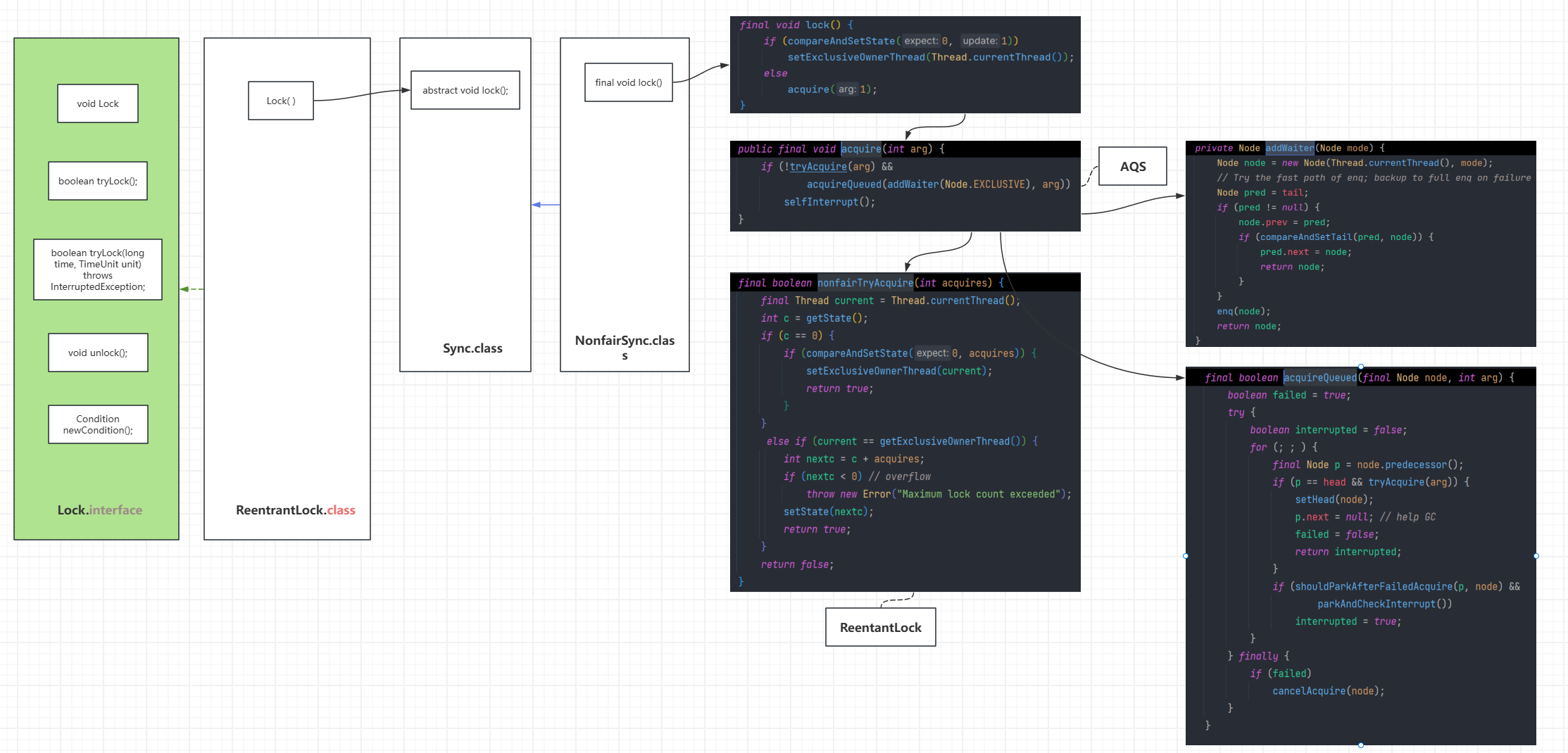
核心方法-acquire
该方法以独占模式获取(资源),忽略中断,即线程在aquire过程中,中断此线程是无效的。
/*** Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented* by invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquire},* returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly* repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link* #tryAcquire} until success. This method can be used* to implement method {@link Lock#lock}.** @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to* {@link #tryAcquire} but is otherwise uninterpreted and* can represent anything you like.*/
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg))acquire(null, arg, false, false, false, 0L);
}
- 首先调用tryAcquire方法,调用此方法的线程会试图在独占模式下获取对象状态。此方法应该查询是否允许它在独占模式下获取对象状态,如果允许,则获取它。在AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码中默认会抛出一个异常,即需要子类去重写此方法完成自己的逻辑。之后会进行分析。
- 调用acquireQueued方法
- 由于tryAcquire默认实现是抛出异常,所以此时,不进行分析,之后会结合一个例子进行分析。
final int acquire(Node node, int arg, boolean shared,boolean interruptible, boolean timed, long time) {Thread current = Thread.currentThread();byte spins = 0, postSpins = 0; // retries upon unpark of first threadboolean interrupted = false, first = false;Node pred = null; // predecessor of node when enqueued/** Repeatedly:* Check if node now first* if so, ensure head stable, else ensure valid predecessor* if node is first or not yet enqueued, try acquiring* else if node not yet created, create it* else if not yet enqueued, try once to enqueue* else if woken from park, retry (up to postSpins times)* else if WAITING status not set, set and retry* else park and clear WAITING status, and check cancellation*/for (;;) {if (!first && (pred = (node == null) ? null : node.prev) != null &&!(first = (head == pred))) {if (pred.status < 0) {cleanQueue(); // predecessor cancelledcontinue;} else if (pred.prev == null) {Thread.onSpinWait(); // ensure serializationcontinue;}}if (first || pred == null) {boolean acquired;try {if (shared)acquired = (tryAcquireShared(arg) >= 0);elseacquired = tryAcquire(arg);} catch (Throwable ex) {cancelAcquire(node, interrupted, false);throw ex;}if (acquired) {if (first) {node.prev = null;head = node;pred.next = null;node.waiter = null;if (shared)signalNextIfShared(node);if (interrupted)current.interrupt();}return 1;}}if (node == null) { // allocate; retry before enqueueif (shared)node = new SharedNode();elsenode = new ExclusiveNode();} else if (pred == null) { // try to enqueuenode.waiter = current;Node t = tail;node.setPrevRelaxed(t); // avoid unnecessary fenceif (t == null)tryInitializeHead();else if (!casTail(t, node))node.setPrevRelaxed(null); // back outelset.next = node;} else if (first && spins != 0) {--spins; // reduce unfairness on rewaitsThread.onSpinWait();} else if (node.status == 0) {node.status = WAITING; // enable signal and recheck} else {long nanos;spins = postSpins = (byte)((postSpins << 1) | 1);if (!timed)LockSupport.park(this);else if ((nanos = time - System.nanoTime()) > 0L)LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);elsebreak;node.clearStatus();if ((interrupted |= Thread.interrupted()) && interruptible)break;}}return cancelAcquire(node, interrupted, interruptible);
}
- 该方法实现了线程的锁获取逻辑,支持独占锁和共享锁模式。
- 线程在循环中不断尝试获取锁,必要时自旋等待或休眠,并处理各种边界情况如超时、中断和取消。
- 如果锁成功获取,当前线程将成为队列头节点,并清理队列结构。
共享锁
CoutDownLatch

- 一个线程等待多个线程
- 多个线程等待一个线程
- 多个线程等待多个线程
几个小问题
Q1:AQS中没有抽象方法为什么要定义为抽象类
目的:为其他同步组件完成功能的框架,不希望其他对象直接拿来使用,不能通过new对象的方式来使用。
- 限制直接实例化
- 模板方法模式
- 提供默认实现并允许扩展
- 强调子类的职责
Q2:AQS为一个抽象类为什么其子类实现的方法没有定义为抽象方法
目的:为了使用通用模板; 抽象类的主要目的是提供一种结构,使子类可以通过继承实现不同的功能,而不必重新实现公共功能。
Java中的中断
在 Java 中,线程的中断机制是多线程编程中的一个重要概念。中断是线程协作的一种方式,主要用于通知线程停止当前操作或结束运行。Java 提供了三种常见的方式来处理中断,它们包括以下几种操作:
1. Thread.interrupt():发送中断请求
Thread.interrupt() 方法用于向某个线程发送一个中断请求。调用这个方法不会直接终止线程,而是设置线程的中断状态,由线程自己决定如何响应中断。
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {// 执行任务}
});
thread.start();
thread.interrupt(); // 向线程发送中断请求
interrupt()仅仅是通知线程它应该终止,但线程是否终止取决于它自身的逻辑。- 当线程处于阻塞状态(例如通过
sleep()、wait()或join()方法),它会抛出InterruptedException并清除中断状态。
2. Thread.isInterrupted():检查中断状态
Thread.isInterrupted() 用于检查当前线程的中断状态。这个方法不会清除中断状态。
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {// 检查中断状态,执行任务System.out.println("Thread is running...");}
});
thread.start();
thread.interrupt(); // 发送中断请求
- 如果返回
true,表示线程已经被中断。 - 这个方法可以在任务循环中用于检查线程是否收到中断信号,从而决定是否继续执行任务。
3. Thread.interrupted():检查并清除中断状态
Thread.interrupted() 方法不仅会检查当前线程的中断状态,还会清除中断标志,如果中断标志被设置为 true,该方法会返回 true,同时将中断标志复位为 false。
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {while (true) {if (Thread.interrupted()) {System.out.println("Thread was interrupted.");break;}}
});
thread.start();
thread.interrupt(); // 发送中断请求
- 如果中断状态为
true,调用Thread.interrupted()会返回true,并且清除中断状态,下次再调用时会返回false。 - 通常在需要多次检查中断状态的情况下,
Thread.interrupted()用于一次性检测和清除中断状态。
中断的实际应用场景:
- 阻塞状态下的中断:如果线程调用了阻塞方法(如
Thread.sleep()、Object.wait()、Thread.join()等),线程被中断时会抛出InterruptedException。此时需要捕获异常并决定如何处理中断。
try {Thread.sleep(10000); // 阻塞操作
} catch (InterruptedException e) {// 捕获中断异常并处理Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // 重新设置中断状态
}
- 循环任务的中断:如果线程在一个长时间运行的任务中,如循环操作,可以使用
isInterrupted()或interrupted()来定期检查线程是否已被中断。
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {// 执行任务
}
总结
interrupt():向线程发送中断请求,设置中断标志。isInterrupted():检查线程的中断状态,但不清除中断标志。interrupted():检查并清除中断标志。
这三个方法共同构成了 Java 中的中断机制,用于线程协作和任务终止的场景。
参考
AQS详解
模板方法
b站视频

![【大模型技术教程】FastGPT一站式解决方案[1-部署篇]:轻松实现RAG-智能问答系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/de6bd4e8e37c4e61a79c37b2551d466e.png)