前言
在Flink的各个服务组件中,ResourceManager、JobMaster、TaskExecutor三者之间存在相互检测的心跳机制:ResourceManager会主动发送心跳请求探测JobMaster、TaskExecutor是否存活;JobMaster也会主动发送心跳请求探测TaskExecutor是否存活,以便进行任务重启或者失败处理。
核心组件
HeartbeatMonitor
接口,定义心跳状态信息相关的接口,管理需要心跳通信相关组件的心跳状态
HeartbeatTarget
作用
1.发起心跳的请求
2.接收心跳并进行响应
3.心跳信息中的负载可以添加额外的信息
4.维护ResourceId和HeartBeatMonitor的Map集合映射
UML
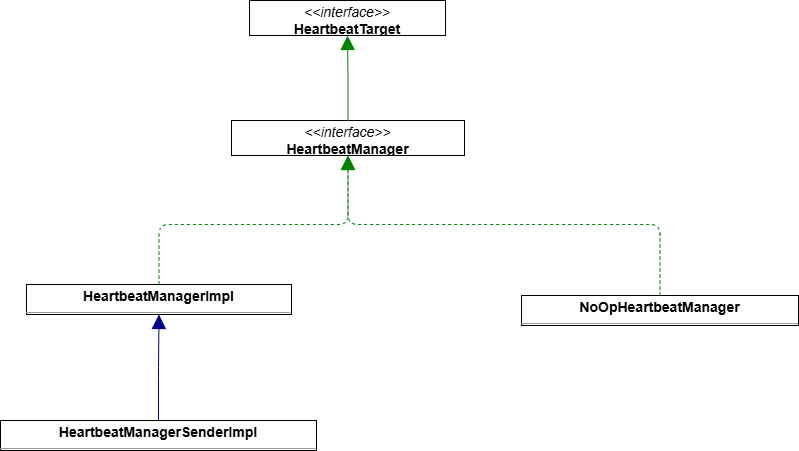
HeartbeatManager
接口,能够停止/启动 心跳的监听,并且能够在心跳超时进行上报
HeartbeatManagerImpl
HeartbeatManager的实现类,提供了组件监听的方法,心跳目标对象注册后会将监控对象信息方法Map中
HeartbeatManagerSenderImpl
继承了HeartbeatManagerImpl,实现了Runnable接口,能够周期性的调度进行心跳的检测
初始化
HeartbeatManagerSenderImpl(long heartbeatPeriod,long heartbeatTimeout,int failedRpcRequestsUntilUnreachable,ResourceID ownResourceID,HeartbeatListener<I, O> heartbeatListener,ScheduledExecutor mainThreadExecutor,Logger log,HeartbeatMonitor.Factory<O> heartbeatMonitorFactory) {super(heartbeatTimeout,failedRpcRequestsUntilUnreachable,ownResourceID,heartbeatListener,mainThreadExecutor,log,heartbeatMonitorFactory);this.heartbeatPeriod = heartbeatPeriod;mainThreadExecutor.schedule(this, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);}在初始化的时候会被线程池提交一个立刻执行的任务,从而进入到run方法
@Overridepublic void run() {if (!stopped) {log.debug("Trigger heartbeat request.");for (HeartbeatMonitor<O> heartbeatMonitor : getHeartbeatTargets().values()) {requestHeartbeat(heartbeatMonitor);}getMainThreadExecutor().schedule(this, heartbeatPeriod, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);}}作用
1.进行状态判断
2.遍历心跳请求目标
3.发起心跳请求
4.以固定心跳周期的定时任务进行调度
HeartbeatServices
ClusterEntrypoint是集群启动的入口,启动的过程中initializeServices进行了服务的初始化,也包含心跳服务HeartbeatServices的初始化。
初始化HeartbeatServices调用方法栈如下:
ClusterEntrypoint#runCluster->ClusterEntrypoint#initializeServices->ClusterEntrypoint#createHaServices->HeartbeatServices#fromConfiguration作用
负责创建HeartbeatManagerSenderImpl对象
@Overridepublic <I, O> HeartbeatManager<I, O> createHeartbeatManagerSender(ResourceID resourceId,HeartbeatListener<I, O> heartbeatListener,ScheduledExecutor mainThreadExecutor,Logger log) {return new HeartbeatManagerSenderImpl<>(heartbeatInterval,heartbeatTimeout,failedRpcRequestsUntilUnreachable,resourceId,heartbeatListener,mainThreadExecutor,log);}组件心跳服务启动
之前分析Flink Rpc底层原理,Flink的组件都继承自EndPoint,组件初始化后会执行start方法,给组件本身发送Start 控制类消息,从而进入到onStart方法,组件的心跳服务一般都在onStart方法进行启动
ResourceManager
onStart方法
组件启动进入到onStart方法,该方法中对ResourceManager的服务进行初始化
@Overridepublic final void onStart() throws Exception {try {log.info("Starting the resource manager.");//初始化ResourceManager的服务startResourceManagerServices();startedFuture.complete(null);} catch (Throwable t) {final ResourceManagerException exception =new ResourceManagerException(String.format("Could not start the ResourceManager %s", getAddress()),t);onFatalError(exception);throw exception;}}
startResourceManagerServices 启动心跳服务
private void startResourceManagerServices() throws Exception {try {jobLeaderIdService.start(new JobLeaderIdActionsImpl());registerMetrics();startHeartbeatServices();slotManager.start(getFencingToken(),getMainThreadExecutor(),resourceAllocator,new ResourceEventListenerImpl(),blocklistHandler::isBlockedTaskManager);delegationTokenManager.start(this);initialize();} catch (Exception e) {handleStartResourceManagerServicesException(e);}}ResourceManager负责计算资源的分配,JobMaster解析作业后会向ResouceManager申请资源,ReouceManger收到申请后会分配TaskManager Slot资源给用于运行任务,所以ReouceManager和这两个组件需要维持心跳,startHeartbeatServices方法内就进行了心跳管理对象的初始化
private void startHeartbeatServices() {//taskmanager 心跳管理对象 底层使用map进行存储taskManagerHeartbeatManager =heartbeatServices.createHeartbeatManagerSender(resourceId,new TaskManagerHeartbeatListener(),getMainThreadExecutor(),log);//jobMaster 心跳管理对象 底层使用map进行存储jobManagerHeartbeatManager =heartbeatServices.createHeartbeatManagerSender(resourceId,new JobManagerHeartbeatListener(),getMainThreadExecutor(),log);}heartbeatServices创建HeartbeatManagerSender内部就启动一个定时任务调度,遍历这两个对象的Map集合,因为ResourceManager初始化后还没组件进行心跳注册,此时为空跑。
JobMaster
onStart方法
@Override
protected void onStart() throws JobMasterException {try {startJobExecution();} catch (Exception e) {final JobMasterException jobMasterException =new JobMasterException("Could not start the JobMaster.", e);handleJobMasterError(jobMasterException);throw jobMasterException;}
}心跳服务初始化,方法调用栈如下
startJobExecution->startJobMasterServices->this.taskManagerHeartbeatManager = createTaskManagerHeartbeatManager(heartbeatServices);this.resourceManagerHeartbeatManager =createResourceManagerHeartbeatManager(heartbeatServices); private void startJobMasterServices() throws Exception {try {this.taskManagerHeartbeatManager = createTaskManagerHeartbeatManager(heartbeatServices);this.resourceManagerHeartbeatManager =createResourceManagerHeartbeatManager(heartbeatServices);// start the slot pool make sure the slot pool now accepts messages for this leaderslotPoolService.start(getFencingToken(), getAddress(), getMainThreadExecutor());// job is ready to go, try to establish connection with resource manager// - activate leader retrieval for the resource manager// - on notification of the leader, the connection will be established and// the slot pool will start requesting slots//选举ResourceManager的leaderresourceManagerLeaderRetriever.start(new ResourceManagerLeaderListener());} catch (Exception e) {handleStartJobMasterServicesError(e);}}初始化了TaskManager和ResourceManager的心跳管理服务
resourceManagerLeaderRetriever.start 获取ResourceManager的Leader对象,获取成功后监听器进行回调
@Overridepublic void start(LeaderRetrievalListener listener) {checkNotNull(listener, "Listener must not be null.");synchronized (startStopLock) {checkState(!started, "StandaloneLeaderRetrievalService can only be started once.");started = true;// directly notify the listener, because we already know the leading JobManager's// addresslistener.notifyLeaderAddress(leaderAddress, leaderId);}}监听器回调方法对状态进行校验,然后会进入到rpc连接的方法
private void openRpcConnectionTo(String leaderAddress, JobMasterId jobMasterId) {Preconditions.checkState(currentJobMasterId == null && rpcConnection == null,"Cannot open a new rpc connection if the previous connection has not been closed.");currentJobMasterId = jobMasterId;//封装rpc连接信息rpcConnection =new JobManagerRegisteredRpcConnection(LOG, leaderAddress, jobMasterId, rpcService.getScheduledExecutor());LOG.info("Try to register at job manager {} with leader id {}.",leaderAddress,jobMasterId.toUUID());//开始和ResourceManager建立Rpc连接rpcConnection.start();}RegisteredRpcConnection#start方法开始对rpc连接进行注册
public void start() {//连接状态校验checkState(!closed, "The RPC connection is already closed");checkState(!isConnected() && pendingRegistration == null,"The RPC connection is already started");//创建新的注册对象,这一步生成注册信息final RetryingRegistration<F, G, S, R> newRegistration = createNewRegistration();if (REGISTRATION_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, null, newRegistration)) {newRegistration.startRegistration();} else {// concurrent start operationnewRegistration.cancel();}}createNewRegistration方法如下,
private RetryingRegistration<F, G, S, R> createNewRegistration() {//初始化注册信息RetryingRegistration<F, G, S, R> newRegistration = checkNotNull(generateRegistration());CompletableFuture<RetryingRegistration.RetryingRegistrationResult<G, S, R>> future =newRegistration.getFuture();//回调方法future.whenCompleteAsync(//代码省略);return newRegistration;}
}generateRegistration会创建RetryingRegistration,并定义了注册的方法
protected RetryingRegistration<ResourceManagerId,ResourceManagerGateway,JobMasterRegistrationSuccess,RegistrationResponse.Rejection>generateRegistration() {return new RetryingRegistration<ResourceManagerId,ResourceManagerGateway,JobMasterRegistrationSuccess,RegistrationResponse.Rejection>(log,getRpcService(),"ResourceManager",ResourceManagerGateway.class,getTargetAddress(),getTargetLeaderId(),jobMasterConfiguration.getRetryingRegistrationConfiguration()) {//定义了异步方法@Overrideprotected CompletableFuture<RegistrationResponse> invokeRegistration(ResourceManagerGateway gateway,ResourceManagerId fencingToken,long timeoutMillis) {Time timeout = Time.milliseconds(timeoutMillis);return gateway.registerJobMaster(jobMasterId,jobManagerResourceID,jobManagerRpcAddress,jobID,timeout);}};}ResourceManagerGateway是ResourceManager的动态代理对象,执行gateway.registerJobMaster这个方法会远程调用ResourceManager的registerJobMaster方法,ResourceManager#registerJobMaster如下,
public CompletableFuture<RegistrationResponse> registerJobMaster(final JobMasterId jobMasterId,final ResourceID jobManagerResourceId,final String jobManagerAddress,final JobID jobId,final Time timeout) {CompletableFuture<JobMasterGateway> jobMasterGatewayFuture =getRpcService().connect(jobManagerAddress, jobMasterId, JobMasterGateway.class);CompletableFuture<RegistrationResponse> registrationResponseFuture =jobMasterGatewayFuture.thenCombineAsync(jobMasterIdFuture,(JobMasterGateway jobMasterGateway, JobMasterId leadingJobMasterId) -> {if (Objects.equals(leadingJobMasterId, jobMasterId)) {return registerJobMasterInternal(jobMasterGateway,jobId,jobManagerAddress,jobManagerResourceId);} else {final String declineMessage =String.format("The leading JobMaster id %s did not match the received JobMaster id %s. "+ "This indicates that a JobMaster leader change has happened.",leadingJobMasterId, jobMasterId);log.debug(declineMessage);return new RegistrationResponse.Failure(new FlinkException(declineMessage));}},getMainThreadExecutor());}会走到registerJobMasterInternal这个方法
private RegistrationResponse registerJobMasterInternal(final JobMasterGateway jobMasterGateway,JobID jobId,String jobManagerAddress,ResourceID jobManagerResourceId) {//代码省略// jobmastet 作为监听对象存入map中jobManagerHeartbeatManager.monitorTarget(jobManagerResourceId, new JobMasterHeartbeatSender(jobMasterGateway));return new JobMasterRegistrationSuccess(getFencingToken(), resourceId);}jobManagerHeartbeatManager.monitorTarget 最终ResouceManager会把JobMaster作为监控对象存在Map中,后续调度遍历map发送心跳请求