图像相似性搜索的核心在于一个简单的想法:图像可以表示为高维空间中的向量。当两个图像相似时,它们的向量应该在这个空间中占据相似的位置。我们可以通过测量角度(或余弦相似度)来确定这些向量的相似程度。如果角度小,图像就接近(相似)。如果角度大(不同),图像就会相距很远。这就像在公寓大楼里寻找邻居一样,但方式要抽象得多。使用不同的 AI 模型,例如 ViT、CLIP、BLIP、EfficientNet、DINO-v2 和 VGG16比较图像并查看它们的相似之处。

模型介绍
关于图像相似度计算的几种深度学习方法,以下是对几个模型的介绍,包括它们的优缺点:
1. ViT(Vision Transformer)
ViT是Google在2020年提出的模型,将Transformer架构应用于图像分类任务。ViT通过将图像分割成多个小块(patches),然后将这些小块线性映射到低维空间,并添加位置编码后输入到Transformer Encoder中进行处理。
优点:
- 全局感受野:ViT能够捕获图像的全局特征,这在CNN中较难实现。
- 可扩展性:模型的效果随着模型大小的增加而提升,表现出很好的可扩展性。
- 较少的训练资源:在大规模数据集上预训练后,ViT在多个中小型图像识别基准上的表现优于SOTA的CNN,同时需要的训练资源更少。
缺点:
- 缺乏归纳偏置:ViT不具有CNN的归纳偏置,如平移不变性和局部感受野,这可能需要额外的技术来补偿。
- 对数据量要求高:ViT在小数据集上的表现可能不如CNN,需要大量数据进行预训练才能发挥其优势。
2. CLIP(Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training)
CLIP是OpenAI在2021年发布的多模态预训练神经网络,通过对比学习的方式,将图像和文本映射到共享的向量空间中,实现图像和文本之间的语义关联。
优点:
- 零样本学习:CLIP在零样本学习任务中表现出色,不需要看到新的图像或文本的训练示例就能进行预测。
- 简洁有效的架构:模型架构简洁,效果好,适用于多种视觉和语言任务。
缺点:
- 对标注数据的依赖:尽管CLIP在预训练阶段不需要大量标注数据,但在某些任务中,如图像分类,可能需要额外的标注数据来微调模型。
3. BLIP(Bootstrapped Language-Image Pretraining)
BLIP是Salesforce提出的多模态Transformer模型,旨在统一视觉理解任务和生成任务。BLIP通过引入Captioner和Filter模块来提高数据质量和数量,从而提升模型性能。
优点:
- 理解和生成能力:BLIP兼具图文多模态的理解和生成能力,适用于多种视觉语言任务。
- 数据质量提升:通过Captioner和Filter模块,BLIP能够去除网络资源中的文本噪声,提高模型性能。
缺点:
- 训练成本:BLIP的训练需要较大的网络架构和数据集,导致较大的训练代价。
4. EfficientNet
EfficientNet是Google提出的模型,通过复合缩放方法(同时考虑网络深度、宽度和图像分辨率)来提高模型的效率和准确性。
优点:
- 高效率:EfficientNet在保持高准确率的同时,模型更小、更快,提高了网络的实用性和工业落地可能。
- 系统性模型缩放:EfficientNet提出了一种系统性的方法来缩放模型,而不是随意增加网络的深度或宽度。
缺点:
- 对资源的需求:尽管EfficientNet在效率上有显著提升,但在某些情况下,可能仍然需要较多的计算资源。
5. DINO-v2
DINO-v2是Meta AI发布的自监督学习模型,能够抽取强大的图像特征,且在下游任务上不需要微调。
优点:
- 无需微调:DINO-v2可以直接用作多种计算机视觉任务的骨干网络,无需微调。
- 自监督学习:DINO-v2使用自监督学习,可以从任何图像集合中学习,不依赖于大量的标记数据。
缺点:
- 对数据集的依赖:虽然DINO-v2可以从任何图像集合中学习,但其性能可能依赖于数据集的质量和多样性。
步骤1:数据准备
从维基百科抓取了国旗图像,将世界各地国家的国旗变成了一个数据集。
图像相似性搜索的核心在于一个简单的想法:图像可以表示为高维空间中的向量。当两个图像相似时,它们的向量应该在这个空间中占据相似的位置。我们可以通过测量角度(或余弦相似度)来确定这些向量的相似程度。如果角度小,图像就接近(相似)。如果角度大(不同),图像就会相距很远。这就像在公寓大楼里寻找邻居一样,但方式要抽象得多。
import pandas as pd
flags_df = pd.read_csv('national_flags.csv')
print(flags_df)

步骤2:特征提取
提取特征,将每个模型获取标志的图像并将其转换为特征向量,并将其特征转换为数字列表。在本实验中,将使用 Huggingface 的特征转换器库来进行特征提取。
- EfficientNet: 通过平均最后一个隐藏层输出的空间维度来提取标志特征,重点关注细粒度模式。
image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("google/efficientnet-b7")
model = EfficientNetModel.from_pretrained("google/efficientnet-b7")# prepare input image
inputs = image_processor(img, return_tensors='pt')with torch.no_grad():outputs = model(**inputs, output_hidden_states=True)embedding = outputs.hidden_states[-1]
embedding = torch.mean(embedding, dim=[2,3])
- ViT: 使用其转换器架构中第一个标记的最后隐藏状态,捕获局部和全局视觉特征。
image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("google/vit-large-patch16-224-in21k")
model = ViTModel.from_pretrained("google/vit-large-patch16-224-in21k")# prepare input image
inputs = image_processor(img, return_tensors='pt')with torch.no_grad():outputs = model(**inputs)
embedding = outputs.last_hidden_state
embedding = embedding[:, 0, :].squeeze(1)
- DINO-v2: 通过专注于自我监督学习来生成嵌入,利用第一个标记来捕获以对象为中心的细节。
image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained('facebook/dinov2-base')
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained('facebook/dinov2-base')# prepare input image
inputs = image_processor(img, return_tensors='pt')with torch.no_grad():outputs = model(**inputs)
embedding = outputs.last_hidden_state
embedding = embedding[:, 0, :].squeeze(1)
- CLIP: 结合图像和文本嵌入,使用图像特征来理解视觉概念以及来自配对文本的上下文数据。
image_processor = CLIPProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")# prepare input image
inputs = image_processor(images=img, return_tensors='pt', padding=True)with torch.no_grad():embedding = model.get_image_features(**inputs)
- BLIP-2: 采用视觉语言模型,通过其以查询为中心的转换器 (Q-Former) 提取特征来捕获图像语义和关系。
image_processor = Blip2Processor.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b")
model = Blip2Model.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b", torch_dtype=torch.float16)inputs = image_processor(images=img, return_tensors='pt', padding=True)
print('input shape: ', inputs['pixel_values'].shape)with torch.no_grad():outputs = model.get_qformer_features(**inputs)
embedding = outputs.last_hidden_state
embedding = embedding[:, 0, :].squeeze(1)
- VGG16: 一种 CNN 模型,通过应用一堆卷积层来输出标记嵌入,强调分层图像表示。
model = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
model.eval() # Set the model to evaluation modebatch_t = torch.unsqueeze(img, 0)with torch.no_grad():embedding = model(batch_t)
接着将每个模型提取的图像特征,转换为DataFrame数据,这将作为相似性分析的基础。
步骤 3:使用FAISS余弦相似度
通过上面的方法将图像通过各个模型进行特征提取,并将特征转换成dataframe的形式。利用余弦相似度来计算图像相似程度。余弦相似度比较两个向量的方向,使其能够有效地根据模式而不是大小来识别关系。这种方法在分析数据相似度上特别有用,其中重点是相对形状和像素元素,而不是特征向量的绝对大小。
-
归一化:每个特征向量都归一化为单位长度,因此余弦相似度可以计算为向量的点积。这确保相似性反映了向量之间的角度。
-
用于相似性搜索的 FAISS:利用 FAISS(一个针对高效相似性搜索而优化的库),根据其标准化特征向量,根据测试的数据查找前 K 个最相似的国家/地区。在大型旗帜图像数据集上进行快速且可扩展的比较。
def clean_feature_string(feature_str):cleaned_str = re.sub(r'[\[\]]', '', feature_str) # Remove bracketscleaned_values = np.fromstring(cleaned_str, sep=' ') # Parse values into numpy arrayreturn cleaned_values# Function to get top K similar countries using FAISS
def get_top_k_similar_countries(input_country, df, k=5):countries = df['Country'].valuesfeatures = np.array([clean_feature_string(f) for f in df['features'].values])# Find the index of the input countrytry:input_idx = list(countries).index(input_country)except ValueError:return f"Country '{input_country}' not found in the dataset."input_embedding = features[input_idx].reshape(1, -1)# Normalize the feature vectors for cosine similarityfeatures_normalized = features / np.linalg.norm(features, axis=1, keepdims=True)# Create a FAISS index for similarity searchdim = features.shape[1]index = faiss.IndexFlatIP(dim) # Add all features to the FAISS indexindex.add(features_normalized)# Search for the top K most similar countriesdistances, top_k_idx = index.search(input_embedding, k+1) # k+1 to exclude the country itself# Return top K countries with their similarity scoresreturn [(countries[i], distances[0][j]) for j, i in enumerate(top_k_idx[0]) if i != input_idx]## Display top 5 similar flags
top_5_countries = get_top_k_similar_countries(country, k=5)for idx, (country, score) in enumerate(top_5_countries):# Load the flag image for each country from the local folderimg = load_local_image(country)display(img)
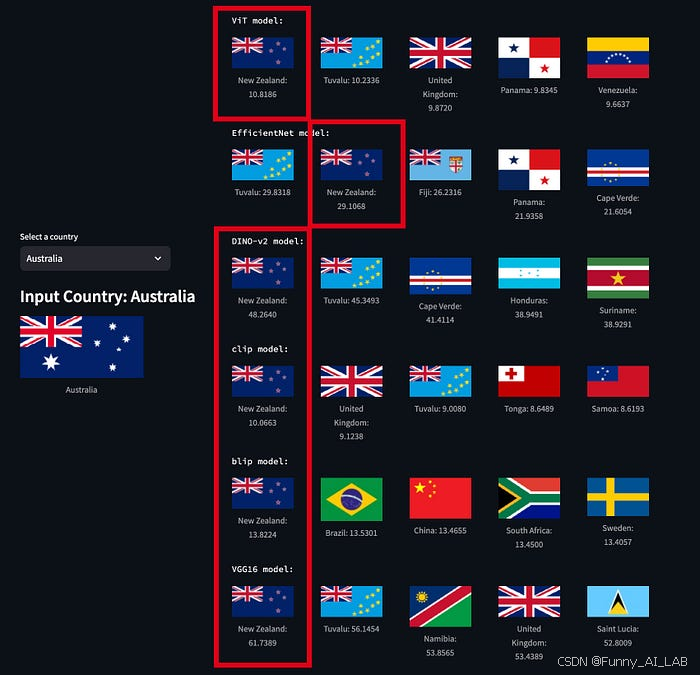
步骤4: 模型测试
测试 1:乍得和罗马尼亚 所有模型都返回“罗马尼亚”作为最佳匹配。

测试 2:澳大利亚和新西兰 所有模型都正确识别了新西兰。
完整版代码如下:
# script to generate embeddings and perform similarity searchesimport pandas as pd
import torch
from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, EfficientNetModel, ViTModel, AutoModel, CLIPProcessor, CLIPModel, Blip2Processor, Blip2Model
from torchvision import models, transforms
import numpy as np
import os
import re
import faiss
flags_df = pd.read_csv('national_flags.csv') # Uncomment if you're loading from a CSV
IMAGE_DIR = "images"
def load_local_image(country_name):# Sanitize the country name to match the local image file naming conventionsanitized_country_name = country_name.replace(" ", "_").replace("[", "").replace("]", "")# Path to the local image fileimage_path = os.path.join(IMAGE_DIR, f"{sanitized_country_name}.png")# Check if the image exists in the folderif os.path.exists(image_path):img = Image.open(image_path)# Convert image to RGB if not already in that modeif img.mode != 'RGB':img = img.convert('RGB')return imgelse:print(f"Image for {country_name} not found.")return None
#ViTdef extract_features_vit(country):image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("google/vit-large-patch16-224-in21k")model = ViTModel.from_pretrained("google/vit-large-patch16-224-in21k")# prepare input imageimg = load_local_image(country)inputs = image_processor(img, return_tensors='pt')with torch.no_grad():outputs = model(**inputs)embedding = outputs.last_hidden_stateembedding = embedding[:, 0, :].squeeze(1)return embedding.numpy()
#EfficientNetdef extract_features_efficientNet(country):# load pre-trained image processor for efficientnet-b7 and model weightimage_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("google/efficientnet-b7")model = EfficientNetModel.from_pretrained("google/efficientnet-b7")# prepare input imageimg = load_local_image(country)inputs = image_processor(img, return_tensors='pt')with torch.no_grad():outputs = model(**inputs, output_hidden_states=True)embedding = outputs.hidden_states[-1]embedding = torch.mean(embedding, dim=[2,3])return embedding.numpy()#DINO-v2def extract_features_DINO_v2(country):# load pre-trained image processor for efficientnet-b7 and model weightimage_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained('facebook/dinov2-base')model = AutoModel.from_pretrained('facebook/dinov2-base')# prepare input imageimg = load_local_image(country)inputs = image_processor(img, return_tensors='pt')with torch.no_grad():outputs = model(**inputs)embedding = outputs.last_hidden_stateembedding = embedding[:, 0, :].squeeze(1)return embedding.numpy()#CLIPdef extract_features_clip(country):# load pre-trained image processor for efficientnet-b7 and model weightimage_processor = CLIPProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")# prepare input imageimg = load_local_image(country)inputs = image_processor(images=img, return_tensors='pt', padding=True)with torch.no_grad():embedding = model.get_image_features(**inputs) return embedding.numpy()#Blip 2def extract_features_blip(country):image_processor = Blip2Processor.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b")model = Blip2Model.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b", torch_dtype=torch.float16)img = load_local_image(country)inputs = image_processor(images=img, return_tensors='pt', padding=True)print('input shape: ', inputs['pixel_values'].shape)with torch.no_grad():outputs = model.get_qformer_features(**inputs)embedding = outputs.last_hidden_stateembedding = embedding[:, 0, :].squeeze(1)return embedding.numpy()#vgg16def extract_features_vgg16(country):model = models.vgg16(pretrained=True) model.eval() # Set the model to evaluation mode# Define the transformation to preprocess the imagepreprocess = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(256),transforms.CenterCrop(224),transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),])img = load_local_image(country)img_t = preprocess(img)batch_t = torch.unsqueeze(img_t, 0)with torch.no_grad():embedding = model(batch_t)return embedding.numpy()# Extract features for all flags
flags_df['features'] = flags_df['Country'].apply(extract_features_vit)
#export embeddings to CSV
flags_df.to_csv('national_flag_embeddings_blip.csv', index=False)
#Cosine similarity with FAISSdf = pd.read_csv('embeddings/national_flag_embeddings_vit.csv')
country = "Australia"def clean_feature_string(feature_str):cleaned_str = re.sub(r'[\[\]]', '', feature_str) # Remove bracketscleaned_values = np.fromstring(cleaned_str, sep=' ') # Parse values into numpy arrayreturn cleaned_values# Function to get top K similar countries using FAISS
def get_top_k_similar_countries(input_country, df, k=5):countries = df['Country'].valuesfeatures = np.array([clean_feature_string(f) for f in df['features'].values])# Find the index of the input countrytry:input_idx = list(countries).index(input_country)except ValueError:return f"Country '{input_country}' not found in the dataset."input_embedding = features[input_idx].reshape(1, -1)# Normalize the feature vectors for cosine similarityfeatures_normalized = features / np.linalg.norm(features, axis=1, keepdims=True)# Create a FAISS index for similarity searchdim = features.shape[1]index = faiss.IndexFlatIP(dim) # Add all features to the FAISS indexindex.add(features_normalized)# Search for the top K most similar countriesdistances, top_k_idx = index.search(input_embedding, k+1) # k+1 to exclude the country itself# Return top K countries with their similarity scoresreturn [(countries[i], distances[0][j]) for j, i in enumerate(top_k_idx[0]) if i != input_idx]# Display top 5 similar flags
top_5_countries = get_top_k_similar_countries(country, k=5)for idx, (country, score) in enumerate(top_5_countries):# Load the flag image for each country from the local folderimg = load_local_image(country)display(img)获取数据代码:
script to scrape flag images from Wikipedia and download images
import pandas as pd
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import os
import pandas as pd
import requests
from PIL import Image
from io import BytesIO
# URL of the Wikipedia page
url = "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_national_flags_of_sovereign_states"# Send a GET request to the URL
response = requests.get(url)# Parse the content of the page with BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.content, 'html.parser')# Find the table with the flags
table = soup.find('table', class_='wikitable')# Initialize lists to store the names and images
names = []
images = []# Iterate through the rows of the table
for row in table.find_all('tr')[1:]: # Skip the header rowflag_cell = row.find('td')name_cell = row.find('th') # Extract the name cell# Check if both cells are foundif flag_cell and name_cell:# Extract the country namename = name_cell.get_text(strip=True)# Extract the flag image URL (from the <img> tag)img_tag = flag_cell.find('img')if img_tag and img_tag.has_attr('src'):# Construct the full image URLimg_url = "https:" + img_tag['src']else:img_url = None# Append the results to the listsnames.append(name)images.append(img_url)# Create a DataFrame with the results
flags_df = pd.DataFrame({'Country': names,'Flag Image': images
})# Display the DataFrame# Optionally, save the DataFrame to a CSV file
flags_df.to_csv('national_flags.csv', index=False)