Android 12 源码分析 —— 应用层 六(StatusBar的UI创建和初始化)
在前面的文章中,我们分别介绍了Layout整体布局,以及StatusBar类的初始化.前者介绍了整体上面的布局,后者介绍了三大窗口的创建的入口处,以及需要做的准备工作.现在我们分别来细化三大窗口的UI创建和初始化,首先从StatusBar窗口开始
前面的文章有:
- “Android 12 源码分析 —— 应用层 四(SystemUI的基本布局设计及其基本概念)http://t.csdn.cn/yYS80”
- “Android 12 源码分析 —— 应用层 五(SystemUI的StatusBar类的启动过程和三个窗口的创建)http://t.csdn.cn/n3gwH”
本篇,将介绍StatusBar窗口的创建和初始化过程,并查看StatusBar中图标出现时的动画.
StatusBar的UI开始处
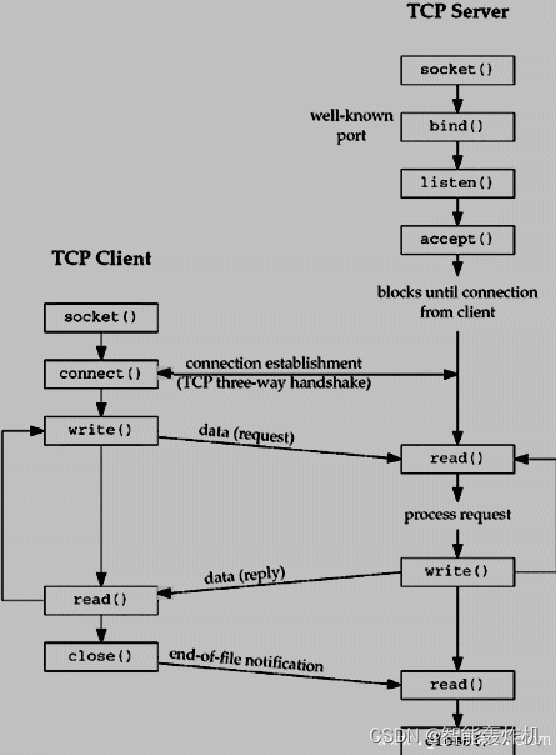
在上一篇文章中(“Android 12 源码分析 —— 应用层 五(SystemUI的StatusBar类的启动过程和三个窗口的创建)http://t.csdn.cn/n3gwH”),我们提及,三大窗口的创建,首先createAndAddWindows()函数开始,然后调用makeStatusBar()函数进行创建,接着调用InflateStatusBarWindow()函数进行View的创建.而在创建View视图的时候,是通过SuperStatusBarViewFactory工厂类来获得对应的View.至此我们就没有再做进一步解释.接下来我们就从此处开始,详细介绍UI的创建和初始化.
先看看SuperStatusBarViewFactory的getStatusBarWindowView()函数,源码如下:
public StatusBarWindowView getStatusBarWindowView() {//如果有缓存View,则直接返回if (mStatusBarWindowView != null) {return mStatusBarWindowView;}//如果没有缓存,则创建View对象,并返回mStatusBarWindowView =(StatusBarWindowView) mInjectionInflationController.injectable(LayoutInflater.from(mContext)).inflate(R.layout.super_status_bar,/* root= */ null);//因为R.layout.super_status_bar文件很是关键,倘若创建不成功则会直接抛出异常if (mStatusBarWindowView == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("R.layout.super_status_bar could not be properly inflated");}return mStatusBarWindowView;
}
上面的函数很简单,即:
- 先调用InjectionInflationController的injectable()函数,它返回一个LayoutInflater对象
- 并调用这个对象的inflate()函数.然后返回相应的View对象,这个对象就是整个StatusBar窗口的顶层View叫做StatusBarWindowView
从名字可以知道,这个类跟注入有关.那么我们来看看InjectionInflationController所要做的工作.
InjectionInflationController
InjectionInflationController的构造函数中,放入了@Inject,因此其创建由Dagger2负责.构造函数如下:
@Inject
public InjectionInflationController(ViewInstanceCreator.Factory viewInstanceCreatorFactory) {mViewInstanceCreatorFactory = viewInstanceCreatorFactory;initInjectionMap();
}private void initInjectionMap() {//获取ViewInstanceCreator的方法for (Method method : ViewInstanceCreator.class.getDeclaredMethods()) {//如果是返回类型是View的子类,且为Public,那么就将其加入一个Map中.//可见,这个InjectionInflationControllerView,缓存了View类的对象的创建方法.if (View.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getReturnType())&& (method.getModifiers() & Modifier.PUBLIC) != 0) {mInjectionMap.put(method.getReturnType().getName(), method);}}
}
在上面的函数中,InjectionInflationController对象,缓存了ViewInstanceCreator的创建View子类的方法.我们看看ViewInstanceCreator.如下:
ViewInstanceCreator
ViewInstanceCreator被定义在InjectionInflationController文件中,源码如下:
//定义为子组件,被放入Dagger2中
@Subcomponent
public interface ViewInstanceCreator {//定义其Factory方法@Subcomponent.Factoryinterface Factory {ViewInstanceCreator build(@BindsInstance @Named(VIEW_CONTEXT) Context context,@BindsInstance AttributeSet attributeSet);}//定义返回NotificationStackScrollLayout的对象//而这个对象是View的子类,这个对象的创建也由Dagger2创建NotificationStackScrollLayout createNotificationStackScrollLayout();
}
现在我们知道了InjectionInflationController的对象在创建的时候,缓存了谁了,即-------NotificationStackScrollLayout对象
现在就需要思考一下,为何只有一个View被这样定义了?难道其他的View就不能被定义吗?
这里涉及到一个历史问题,在早期的版本中还包括,QSPanel,QuickQSPanel,以及KeyguardMessageArea等等View的创建.但是随着SystemUI的复杂度增加,相应的Dagger图也被慢慢扩大,在测试的时候发现,存在于Dagger中的类和接口会以非常简单的形式存在,甚至是空对象.导致带来大量的测试工作无法完成.因此慢慢将这样的方式去掉.
所以,现在正确的做法是,对于View尽可能的不要走Dagger2的创建,而是创建另外一个xxxController对象,在xxxController对象中,通过Dagger2来注入需要的各种依赖.然后将这个View和对应的Controller进行连接(attach)
但是现在依然还存在一个View由Dagger2进行创建,那么我们看看SystemUI是如何实现这个流程的.也就是从InjectinInflationController的injectable函数开始的.
InjectionInflationController的injectable()函数
源码如下:
public LayoutInflater injectable(LayoutInflater inflater) {//首先从克隆一个LayoutInflaterLayoutInflater ret = inflater.cloneInContext(inflater.getContext());//然后为克隆的LayoutInflater设置一个私有的工厂对象//这个对象在创建某个View之前,会触发这个私有的工厂对象,好让这个私有对象实现一些自定义创建ret.setPrivateFactory(mFactory);return ret;
}
函数较简单,见注释即可.
mFactory对象的实现是:InjectionInflationController文件中的InjectionFactory类,如下:
InjectionFactory
源码如下:
private class InjectionFactory implements LayoutInflater.Factory2 {@Overridepublic View onCreateView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {//首先查看当初在构造函数中保存的创建View的方法Method creationMethod = mInjectionMap.get(name);//如果创建方法存在,则调用创建方法来创建View对象,//到目前为止它只会创建NotificationStackScrollLayoutif (creationMethod != null) {try {return (View) creationMethod.invoke(mViewInstanceCreatorFactory.build(context, attrs));} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new InflateException("Could not inflate " + name, e);} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {throw new InflateException("Could not inflate " + name, e);}}return null;}@Overridepublic View onCreateView(View parent, String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {return onCreateView(name, context, attrs);}
}
至此,InjectionInflationController的创建View的流程就清晰了.
- 先收集创建View的方法
- 如果Xml文件中的View刚好可以被1中收集的方法创建,则调用1中方法
从上面的阅读中,我们可以看到Dagger2并非适用于所有的情况.其实主要是因为测试的原因
至此,super_status_bar.xml文件的解析,分析完毕
前面,我们详细分析了super_status_bar.xml文件的解析,并知道了它如何一步一步被创建为View,接下来的事情,就是在这个UI上面的操作.
创建合适的CollapsedStatusBarFragment
从上一篇博文(“Android 12 源码分析 —— 应用层 五(SystemUI的StatusBar类的启动过程和三个窗口的创建)http://t.csdn.cn/n3gwH”)中知道,一旦成功创建窗口的顶层View,则会在这个顶层View中添加可以复用的Fragment.添加Fragment的代码就在makeStatusBarView()中.现在我们将有关StatusBar窗口的部分截取如下:
protected void makeStatusBarView(@Nullable RegisterStatusBarResult result) {final Context context = mContext;
//省略不相干的部分//调用FragmaneHostManager得到对应的FragmentHostManager
//然后调用addTagListener设置Fragment创建完成之后的一个监听
//最后调用getFragmentManager()得到FragmentManager开始Fragment的事务
//Fragment事务中,只有replace,将对应的Framgment添加到status_bar_container中FragmentHostManager.get(mPhoneStatusBarWindow).addTagListener(CollapsedStatusBarFragment.TAG, (tag, fragment) -> {/*上一篇博文中已经详细介绍过*/}).getFragmentManager().beginTransaction().replace(R.id.status_bar_container,new CollapsedStatusBarFragment(mOngoingCallController,mAnimationScheduler,mStatusBarLocationPublisher,mNotificationIconAreaController,mFeatureFlags,mStatusBarIconController,mKeyguardStateController,mNetworkController,mStatusBarStateController,this,mCommandQueue),CollapsedStatusBarFragment.TAG).commit();//省略不相干的部分
}
由上面的内容可以知道.Fragment的创建是由如下的步骤完成的:
- 调用FragmaneHostManager得到对应的FragmentHostManager
- 然后调用addTagListener设置Fragment创建完成之后的一个监听,用于Fragment的View创建完成之后的准备工作
- 最后调用getFragmentManager()得到FragmentManager开始Fragment的事务
- Fragment事务中,只有replace,将对应的Framgment添加到status_bar_container中.
那么这里面的FragmentHostManager是做什么的呢?我们先来看看
FragmentHostManager的get()
源码如下:
public static FragmentHostManager get(View view) {try {//调用FragmentService的getFragmentHostManager()方法return Dependency.get(FragmentService.class).getFragmentHostManager(view);} catch (ClassCastException e) {// TODO: Some auto handling here?throw e;}
}
而在FragmentService中,getFragmentHostManager如下:
FragmentService的getFragmentHostManager()
源码如下:
public FragmentHostManager getFragmentHostManager(View view) {//首先获取该View的根ViewView root = view.getRootView();//根据根View,得到对应的FragmengHostState.//FragmentHostState类是一个包装类,它将FragmentHostManager和View包装在一起.//而FragmentHostManager类负责View对应的Fragment的事务,后文详解.FragmentHostState state = mHosts.get(root);//在FragmentService中,将View和FragmentHostState进行缓存,一旦需要则直接返回if (state == null) {//我们现在看到的是StatusBar的第一初始化过程,因此为空,则new一个FragmentHostStatestate = new FragmentHostState(root);mHosts.put(root, state);}//返回state的FragmentHostManager对象return state.getFragmentHostManager();
}
从上面的代码我们可以看到.
- FragmentService,按照View->FragmentHostState的键值对,缓存了相应的对象
- 如果没有这样的保存,则创建FragmentHostState对象.FragmenHostState中封装的一个重要对象是FragmentHostManager.每一个View都有一个FragmentHostManager对象被封装在FragmentHostState中.
FragmenHostState对象非常简单,只做封装,因此不再介绍
接下来我们看看FragmentHostManager对象
FragmentHostManager
FragmentHostManager的源码如下.FragmentHostManager中,只需要知道它的初始化即可,因为剩下的内容,全都在其初始化创建的对象上的简单操作.
public class FragmentHostManager {//省略不相干部分FragmentHostManager(FragmentService manager, View rootView) {//在构造函数中,初始化各个成员mContext = rootView.getContext();mManager = manager;mRootView = rootView;//在创建初期,需要先保存配置,通过applyNewConfig将配置更新到mConfigChanges对象中mConfigChanges.applyNewConfig(mContext.getResources());//调用下面的函数,为Fragment设置生命周期的管理createFragmentHost(null);}private void createFragmentHost(Parcelable savedState) {//FragmentController负责协调Fragment的生命周期//首先,创建FragmentController对象mFragmentsmFragments = FragmentController.createController(new HostCallbacks());//必须先调用attach()方法,该方法负责内部的一些类的成员的初始化,否则无法使用mFragments.attachHost(null);//创建对应的生命周期监听对象mLifecycleCallbacks = new FragmentLifecycleCallbacks() {@Overridepublic void onFragmentViewCreated(FragmentManager fm, Fragment f, View v,Bundle savedInstanceState) {//调用FragmentHostManager中的listener(内容简单略)FragmentHostManager.this.onFragmentViewCreated(f);}@Overridepublic void onFragmentViewDestroyed(FragmentManager fm, Fragment f) {//调用FragmentHostManager中的listener(内容简单略)FragmentHostManager.this.onFragmentViewDestroyed(f);}@Overridepublic void onFragmentDestroyed(FragmentManager fm, Fragment f) {//跟踪Fragment的回收情况Dependency.get(LeakDetector.class).trackGarbage(f);}};//设置监听mFragments.getFragmentManager().registerFragmentLifecycleCallbacks(mLifecycleCallbacks,true);//如果有保存的状态,则负责恢复这个保存的状态if (savedState != null) {mFragments.restoreAllState(savedState, (FragmentManagerNonConfig) null);}//现在将状态保持在resume状态.//关于Fragment的生命周期,见后文补充知识mFragments.dispatchCreate();mFragments.dispatchStart();mFragments.dispatchResume();}public FragmentHostManager addTagListener(String tag, FragmentListener listener) {//根据tag选择对应的listener组ArrayList<FragmentListener> listeners = mListeners.get(tag);//如果没有listener组,则创建一个新的list,用于存放这些listenerif (listeners == null) {listeners = new ArrayList<>();mListeners.put(tag, listeners);}listeners.add(listener);//如果当前已经存在Fragment,那么就直接触发listener的回调//可以思考为什么非要在此处触发?Fragment current = getFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag(tag);if (current != null && current.getView() != null) {listener.onFragmentViewCreated(tag, current);}return this;}//省略简单部分//省略不相干部分
}
FragmenHostManager主要就是负责如下:
- 管理Fragment的生命周期.
- 当触发相应的生命周期之后,会调用FragmentHostManager中的FragmentLifecycleCallbacks对象的相应回调
- 在这些回调方法中,会再次掉到FragmentHostManager中的相应方法,这些方法则会触发FragmentHostManager中的Listener.(也即makeStatusBarView()函数中调用addTagListener()设置的listener)
现在我们知道了FragmentHostManager.那么回到makeStatusBarView()函数中.在调用FragmentHostManager.get(mPhoneStatusBarWindow)之后,得到FragmentHostManager,然后调用addTagListener(TAG,listener)方法.该addTagListener在上面的FragmentHostManager中已经详细介绍过了.
现在我们来回答在listener中留下来的思考-----为什么要马上触发其回调?
答案:Listener的设置可能出现在View的创建之后,如果在其之后,那么就需要主动触发onFragmentViewCreated()方法.
但是这里面没有考虑到的一个问题是,触发线程可能在子线程,所以这里有设计不合理的地方.
有了前面的步骤,就能得到对应的FragmentManager对象了.为了进一步说明其步骤,现将前面的makeStatusBarView()中的过程加以概括:
- 调用FragmaneHostManager得到对应的FragmentHostManager
- 调用addTagListener设置Fragment创建完成之后的一个监听,用于Fragment的View创建完成之后的准备工作
- 最后调用getFragmentManager()得到FragmentManager开始Fragment的事务
- Fragment事务中,只有replace,将对应的Framgment添加到status_bar_container中.
其中,第一步和第二步,我们已经详细分析了.接下来的第三步和第四步,属于Android的Fragment的基本操作了,它先创建CollapsedStatusBarFragment,然后将其放置在id为status_bar_container的容器中.
那么接下来看看CollapsedStatusBarFragment的创建
CollapsedStatusBarFragment的创建
作为一个Fragment,我们按照其生命周期来进行查看,先看其构造函数,如下:
@Inject
//初始化函数乏善可陈,故略之
public CollapsedStatusBarFragment(OngoingCallController ongoingCallController,SystemStatusAnimationScheduler animationScheduler,StatusBarLocationPublisher locationPublisher,NotificationIconAreaController notificationIconAreaController,FeatureFlags featureFlags,StatusBarIconController statusBarIconController,KeyguardStateController keyguardStateController,NetworkController networkController,StatusBarStateController statusBarStateController,StatusBar statusBarComponent,CommandQueue commandQueue
) {//全是成员的赋值,没有什么好看的,略
}
在进行生命周期查看之前,我们先简单列出其生命周期的过程,如下:
Fragment的生命周期:
Fragment被创建:onAttach(): Fragment与Activity关联时调用。onCreate(): Fragment被创建时调用,通常用于初始化成员变量和数据。onCreateView(): 创建Fragment的用户界面视图(布局)。onActivityCreated(): 当Fragment所属的Activity完成其onCreate()方法后调用。
Fragment变得可见:onStart(): Fragment变得可见时调用,可以执行一些初始化或准备工作。onResume(): Fragment完全可见时调用,通常用于启动动画、定时任务等。
Fragment被暂停:onPause(): Fragment即将暂停,通常用于保存数据或释放资源。
Fragment不再可见:onStop(): Fragment不再可见,用于释放更多的资源。
Fragment销毁:onDestroyView(): Fragment的视图被销毁,用于清理视图相关的资源。onDestroy(): Fragment被销毁时调用,通常用于释放资源。onDetach(): Fragment与Activity解除关联时调用。
按照上面的生命周期,结合CollapsedStatusBarFragment的源码,首先查看onCreateView函数,如下:
onCreateView()
源码非常简单,解析status_bar.xml文件.该文件我们已经在"Android 12 源码分析 —— 应用层 四(SystemUI的基本布局设计及其基本概念)http://t.csdn.cn/PSqGS"中介绍过.因此不再继续介绍,接下来我们一步一步,通过图形来说明,图形为手动绘制,为了辅助理解和记忆
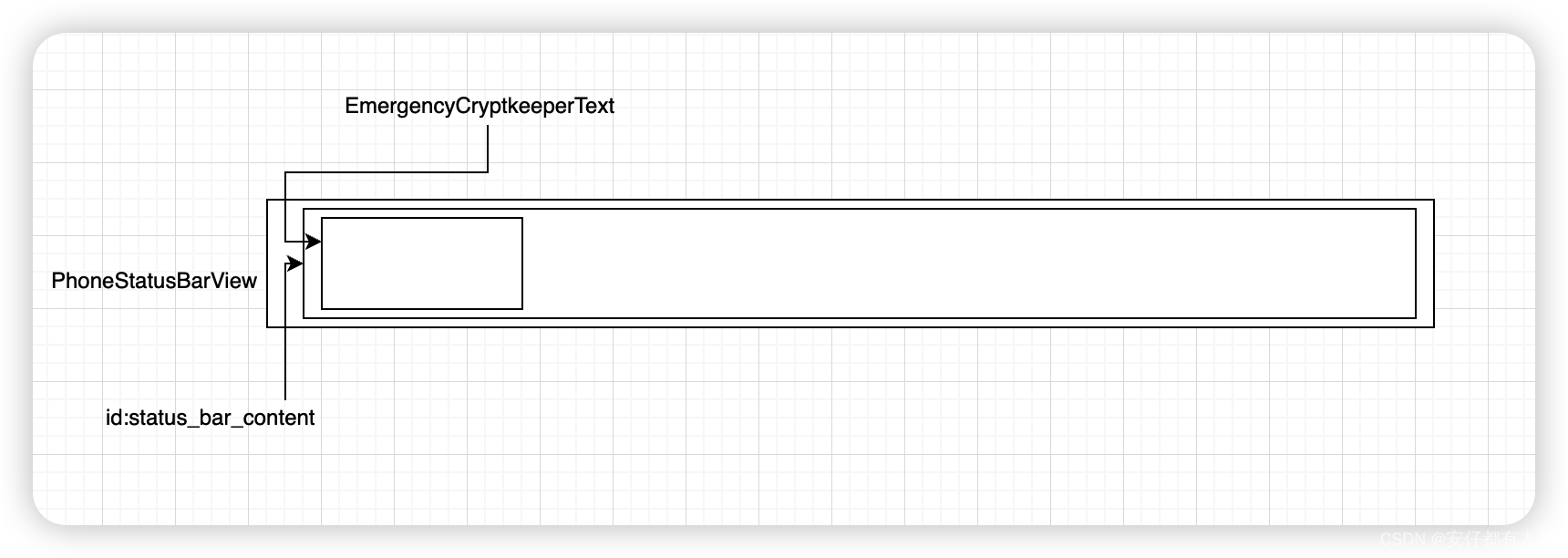
status_bar.xml文件中的内容,省略中间的status_bar_content,则如下;
<com.android.systemui.statusbar.phone.PhoneStatusBarView><ImageView/><!--不会显示为gone--><LinearLayout android:id="@+id/status_bar_contents"><!--省略中间内容,便于说明--></LinearLayout><ViewStubandroid:id="@+id/emergency_cryptkeeper_text"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:layout="@layout/emergency_cryptkeeper_text"/></com.android.systemui.statusbar.phone.PhoneStatusBarView>
画个辅助图如下:
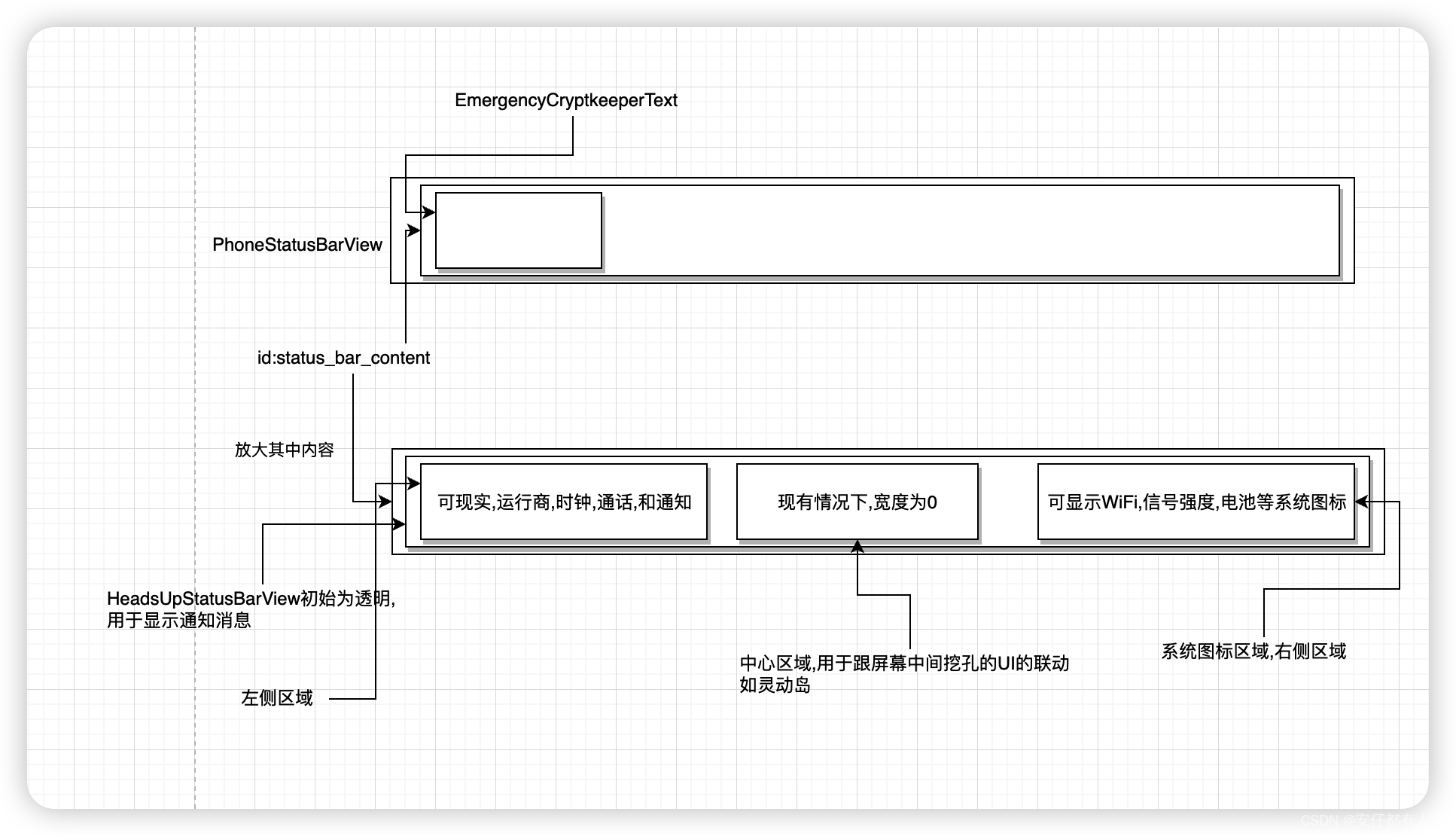
接着,加上中间的status_bar_contents内容变成如下的情况,xml中只列出status_bar_content中的内容
<LinearLayout android:id="@+id/status_bar_contents"><!--左边区域--><FrameLayout><!--左边区域的heads-up区域--><include layout="@layout/heads_up_status_bar_layout" /><!--左边区域的主体内容--><LinearLayout android:id="@+id/status_bar_left_side"><!--左边区域显示运营商名字--><ViewStub android:id="@+id/operator_name" /><!--左边区域显示时钟--><com.android.systemui.statusbar.policy.Clockandroid:id="@+id/clock"/><!--左边区域显示通话--><include layout="@layout/ongoing_call_chip" /><!--左边区域显示通知图标--><com.android.systemui.statusbar.AlphaOptimizedFrameLayoutandroid:id="@+id/notification_icon_area"/></LinearLayout></FrameLayout><!--用于填充空白--><android.widget.Spaceandroid:id="@+id/cutout_space_view"/><!--中心区域--><com.android.systemui.statusbar.AlphaOptimizedFrameLayoutandroid:id="@+id/centered_icon_area"/><!--系统图标区域,也即是右边区域--><com.android.keyguard.AlphaOptimizedLinearLayout android:id="@+id/system_icon_area"><include layout="@layout/system_icons" /></com.android.keyguard.AlphaOptimizedLinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
辅助理解,画图如下:
一旦View创建完成,接下来会触发onViewCreated()函数,如下:
onViewCreated()
onViewCreated()源码如下:
@Override
public void onViewCreated(View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);//view即为onCreateView()函数中解析的status_bar.xml中的顶层View----PhoneStatusBarViewmStatusBar = (PhoneStatusBarView) view;//status_bar_contents内容,负责显示主要的statusbar内容,见上面的示意图View contents = mStatusBar.findViewById(R.id.status_bar_contents);//监听,Layout的改变,一旦发生改变,就调用updateStatusBarLocation()contents.addOnLayoutChangeListener(mStatusBarLayoutListener);//因此需要先调用updateStatusBarLocation()已进行某些值的初始设置updateStatusBarLocation(contents.getLeft(), contents.getRight());//如果需要恢复,则调用restoreHierarchyState进行恢复(此处我们将暂时跳过,因为其内部直接//调用Android View提供标准操作.如果在后面有关于AndroidView的分析,将会进行介绍)if (savedInstanceState != null && savedInstanceState.containsKey(EXTRA_PANEL_STATE)) {mStatusBar.restoreHierarchyState(savedInstanceState.getSparseParcelableArray(EXTRA_PANEL_STATE));}//创建DarkIconManager,负责接收DarkIconDispatcher中的状态变化mDarkIconManager = new DarkIconManager(view.findViewById(R.id.statusIcons), mFeatureFlags);//再设置,不应该被显示的图标mBlockedIcons.add(getString(com.android.internal.R.string.status_bar_volume));mBlockedIcons.add(getString(com.android.internal.R.string.status_bar_alarm_clock));mBlockedIcons.add(getString(com.android.internal.R.string.status_bar_call_strength));//将不应该显示的图标,传递给DarkIconManagermDarkIconManager.setBlockList(mBlockedIcons);//StatusBarIconController负责接收CommandQueue中的回调,同时也跟踪icon的状态//将这些状态分发给需要的类(IconManager)//DarkIconManager继承于IconManager,它需要得到StatusBarIconController中的各种通知.//因此调用addIconGroup将mDarkIconManager传递进去mStatusBarIconController.addIconGroup(mDarkIconManager);//获取系统图标的区域,它在状态栏的最右边,见上面的示意图mSystemIconArea = mStatusBar.findViewById(R.id.system_icon_area);//获取对应的UI,这个是时间图标,见上面示意图mClockView = mStatusBar.findViewById(R.id.clock);//获取对应的通话图标,见上面的示意图mOngoingCallChip = mStatusBar.findViewById(R.id.ongoing_call_chip);//显示系统图标区域,不带动画showSystemIconArea(false);//显示时钟,不带动画showClock(false);//初始化,用于显示电话的状态,如,只能用于紧急呼救initEmergencyCryptkeeperText();//初始化运营商名字,如CMCC中国移动initOperatorName();//初始化通知图标区域initNotificationIconArea();//增加动画的回调,这部分在后面文章中会介绍mAnimationScheduler.addCallback(this);
}
上面的函数主要功能如下:
- 根据id找到View
- 初始化DarkIconManager
- 显示系统图标区域,显示时钟区域,显示通知图标区域
接下来我们看看initEmergencyCryptkeeperText的内容
initEmergencyCryptkeeperText的初始化
源码如下:
private void initEmergencyCryptkeeperText() {//得到对应的ViewStub,见上面的示意图View emergencyViewStub = mStatusBar.findViewById(R.id.emergency_cryptkeeper_text);//判断是否要显示:紧急通话,sim卡状态的文本if (mNetworkController.hasEmergencyCryptKeeperText()) {//如果要,且有对应的View,则inflate它//inflate的内容,即为emergency_cryptkeeper_text.xml,该文件内容简单只有一个类//不做介绍if (emergencyViewStub != null) {((ViewStub) emergencyViewStub).inflate();}//监听网络相关变化,如信号强度,sim卡的更改,飞行模式等等mNetworkController.addCallback(mSignalCallback);} else if (emergencyViewStub != null) {//如果没有,则删除对应的viewViewGroup parent = (ViewGroup) emergencyViewStub.getParent();parent.removeView(emergencyViewStub);}
}
内容简单,见注释,接下来看另外一个初始化函数initOperatorName,如下
initOperatorName的初始化
源码如下:
private void initOperatorName() {//根据配置是否要显示,运营商名字,如中国移动显示CMCCif (getResources().getBoolean(R.bool.config_showOperatorNameInStatusBar)) {//如果需要显示,则inflate其中的Layout,见上面的示意图//当inflate时,解析的文件为:operator_name.xml文件,该文件也只有一个类//相对简单,不再展开ViewStub stub = mStatusBar.findViewById(R.id.operator_name);mOperatorNameFrame = stub.inflate();}
}
内容简单,见注释,接下来看另外一个初始化函数initNotificationIconArea,如下
initNotificationIconArea的初始化
源码如下:
public void initNotificationIconArea() {//获得显示通知图标的父容器(StatusBar的左边区域,见上面的示意图)ViewGroup notificationIconArea = mStatusBar.findViewById(R.id.notification_icon_area);//获取显示通知图标的具体的View,通过mNotificationIconAreaController内部inflate//notification_icon_area.xml文件得到mNotificationIconAreaInner =mNotificationIconAreaController.getNotificationInnerAreaView();//如果通知图标的View有父View,则从中删除,并将其加入notificatonIconArea即左边区域if (mNotificationIconAreaInner.getParent() != null) {((ViewGroup) mNotificationIconAreaInner.getParent()).removeView(mNotificationIconAreaInner);}//加入左边区域notificationIconArea.addView(mNotificationIconAreaInner);//获得显示中心图标的区域的父容器(StatusBar的中心区域)ViewGroup statusBarCenteredIconArea = mStatusBar.findViewById(R.id.centered_icon_area);//获取显示中心图标的具体的View,通过mNotificationIconAreaController内部inflate文件//center_icon_area.xml得到mCenteredIconArea = mNotificationIconAreaController.getCenteredNotificationAreaView();//如果具体的View有父View,则从中删除,并将其加入中心区域if (mCenteredIconArea.getParent() != null) {((ViewGroup) mCenteredIconArea.getParent()).removeView(mCenteredIconArea);}//加入中心区域statusBarCenteredIconArea.addView(mCenteredIconArea);//一切OK之后,还需要根据disable来处理,哪些图标不要显示,关于disable的说明,见上一篇博文updateNotificationIconAreaAndCallChip(mDisabled1, false);
}
在上面的代码中,用于获取具体显示View的代码是通过mNotificationIconAreaController得到,在这个controller内部,它分别inflate两个文件:notification_icon_area.xml和center_icon_area.xml.将他们的顶层View返回给CollapsedStatusBarFragment
注意:为了行文流畅,不再对NotificationIconAreaController的内容inflate做展开,我们将在后面文章中通过分析UI交互(如icon的颜色更改)对其详细介绍.
有了这些准备之后,我们就需要根据disableFlag来判断,哪些需要显示,哪些不需要显示,将会调用updateNotificationIconAreaAndCallChip()函数,如下:
updateNotificationIconAreaAndCallChip决定需要显示的图标
调用updateNotificationIconAreaAndCallChip()函数的参数:mDsiabled1.是通过disbale()接口回调得到,关于这部分内容见上一篇博文中的disabaleFlag内容"Android 12 源码分析 —— 应用层 五(SystemUI的StatusBar类的启动过程和三个窗口的创建)http://t.csdn.cn/YTh8c"
注意:上一篇博文中的disableFlag的分发,会出现在本函数调用之后.但是它并不影响我们对该函数的分析
源码如下:
private void updateNotificationIconAreaAndCallChip(int state1, boolean animate) {//是否要禁止通知图标boolean disableNotifications = (state1 & DISABLE_NOTIFICATION_ICONS) != 0;//是否要禁止通话图标boolean hasOngoingCall = (state1 & DISABLE_ONGOING_CALL_CHIP) == 0;//根据设置,调用showxxx或者hidexxx函数,进行显示或者隐藏//这两个函数,内部通过调用animateShow()或者调用animateHide()进行显示或者隐藏if (disableNotifications || hasOngoingCall) {hideNotificationIconArea(animate);} else {showNotificationIconArea(animate);}//逻辑同通知图标一样boolean showOngoingCallChip = hasOngoingCall && !disableNotifications;if (showOngoingCallChip) {showOngoingCallChip(animate);} else {hideOngoingCallChip(animate);}//通知状态变化mOngoingCallController.notifyChipVisibilityChanged(showOngoingCallChip);
}
上面函数只做了两件事:
- 根据disableFlag来决定要不要显示通知图标
- 根据disableFlag来决定要不要显示通话图标
注意:其中关于动画的显示,会在后文再探disableFlag中进行详细的调用.
至此CollapsedStatusBarFragment的View创建完成,它主要完成例如下的工作:
- 通过id找到对应的View
- 初始化DarkIconManager
- 初始化各种View,如运行商,系统图标区域,通知图标区域,中间图标区域.
总之,该函数负责初始化本Fragment内部的View.而一旦这些View创建完成,就需要进行外部其他Controller之间的初始化.因此,它将会触发另外Fragmenet的另外一个生命周期的回到.也即前文中FragmentHostManager的FragmentLifecycleCallbacks的回调.
CollapsedStatusBarFragment的UI创建完成之后的监听负责进一步的初始化
当所有的UI创建完成之后,将会触发makeStatusBarView()函数中设置的FragmentHostManager的Listener.这部分内容已经在上一篇博文中,详细介绍过了,现在摘录如下:
FragmentHostManager.get(mPhoneStatusBarWindow).addTagListener(CollapsedStatusBarFragment.TAG, (tag, fragment) -> {//将Fragment转换成CollapsedStatusBarFragmentCollapsedStatusBarFragment statusBarFragment =(CollapsedStatusBarFragment) fragment;//先保存以前的PhoneStatusBarViewPhoneStatusBarView oldStatusBarView = mStatusBarView;//再获取新的PhoneStatusBarViewmStatusBarView = (PhoneStatusBarView) statusBarFragment.getView();//对PhoneStatusBarView进行设置,包括注册监听,传递需要的对象等mStatusBarView.setBar(this);mStatusBarView.setPanel(mNotificationPanelViewController);mStatusBarView.setScrimController(mScrimController);mStatusBarView.setExpansionChangedListeners(mExpansionChangedListeners);//如果有一个heads up在顶部,则需要调整为正确的状态if (mHeadsUpManager.hasPinnedHeadsUp()) {//主要是通知各个监听器,更新各自的状态mNotificationPanelViewController.notifyBarPanelExpansionChanged();}//初始化PhoneStatusBarView中的Bouncer//Bouncer界面就是,解锁时要求输入pin,密码等的界面//新创建的PhoneStatusBarView中的Bouncer默认是没有打开的。因此要根据//当前实际进行更新mStatusBarView.setBouncerShowing(mBouncerShowing);//如果以前的StatusBar已经展开了一部分,则要求新的StatusBar也展开同样的大小//因为新创建的PhoneStatusBar,默认展开是0if (oldStatusBarView != null) {float fraction = oldStatusBarView.getExpansionFraction();boolean expanded = oldStatusBarView.isExpanded();mStatusBarView.panelExpansionChanged(fraction, expanded);}//重新创建HeadsUpAppearanceController//它负责控制在StatusBar中要显示的headsup的图标,主要是heads_up_status_bar_view//的操作,见上文示意图HeadsUpAppearanceController oldController = mHeadsUpAppearanceController;if (mHeadsUpAppearanceController != null) {mHeadsUpAppearanceController.destroy();}//重新创建一个新的HeadsUpAppearanceController对象mHeadsUpAppearanceController = new HeadsUpAppearanceController(mNotificationIconAreaController, mHeadsUpManager,mStackScroller.getController(),mStatusBarStateController, mKeyguardBypassController,mKeyguardStateController, mWakeUpCoordinator, mCommandQueue,mNotificationPanelViewController, mStatusBarView);//从旧对象中读取值赋值给新对象mHeadsUpAppearanceController.readFrom(oldController);//建立LightsOutNotificationController和对应View的关系//LightsOutNotificationController负责处理SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LOW_PROFILE中的//图标的消失和隐藏,负责显示小圆点//SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LOW_PROFILE:这个属性的能力是让SystemBar在视觉上变得模糊,//具体表现是状态栏图标仅保留电量时间关键图标,并且变暗。导航栏图标变成三个点或者变暗mLightsOutNotifController.setLightsOutNotifView(mStatusBarView.findViewById(R.id.notification_lights_out));//将StatusBar窗口的view,放入NotificationShade窗口的控制器中mNotificationShadeWindowViewController.setStatusBarView(mStatusBarView);//检查是否要进行StatusBar的模式切换,如果要切换则会形成一个过渡动画//关于StatusBar模式切换的细节,我们在介绍完StatusBarWindow的整个初始化过程之后,//另外的文章进一步介绍.此处我们关注整个启动过程checkBarModes();}).getFragmentManager().beginTransaction().replace(R.id.status_bar_container,new CollapsedStatusBarFragment(mOngoingCallController,mAnimationScheduler,mStatusBarLocationPublisher,mNotificationIconAreaController,mFeatureFlags,mStatusBarIconController,mKeyguardStateController,mNetworkController,mStatusBarStateController,this,mCommandQueue),CollapsedStatusBarFragment.TAG).commit();
上面的代码,是View创建完成之后,进行相应对象的创建和初始化.这些对象的创建和初始化,主要是为了分离CollapsedStatusBarFragment本身,因此将其放在一个独立的Listener中.
注意:对于上面的Listener回调中的内容不能理解,也没有关系,我们将会在后面慢慢介绍到各个类的时候,详细介绍其功能.其中涉及到具体的UI交互
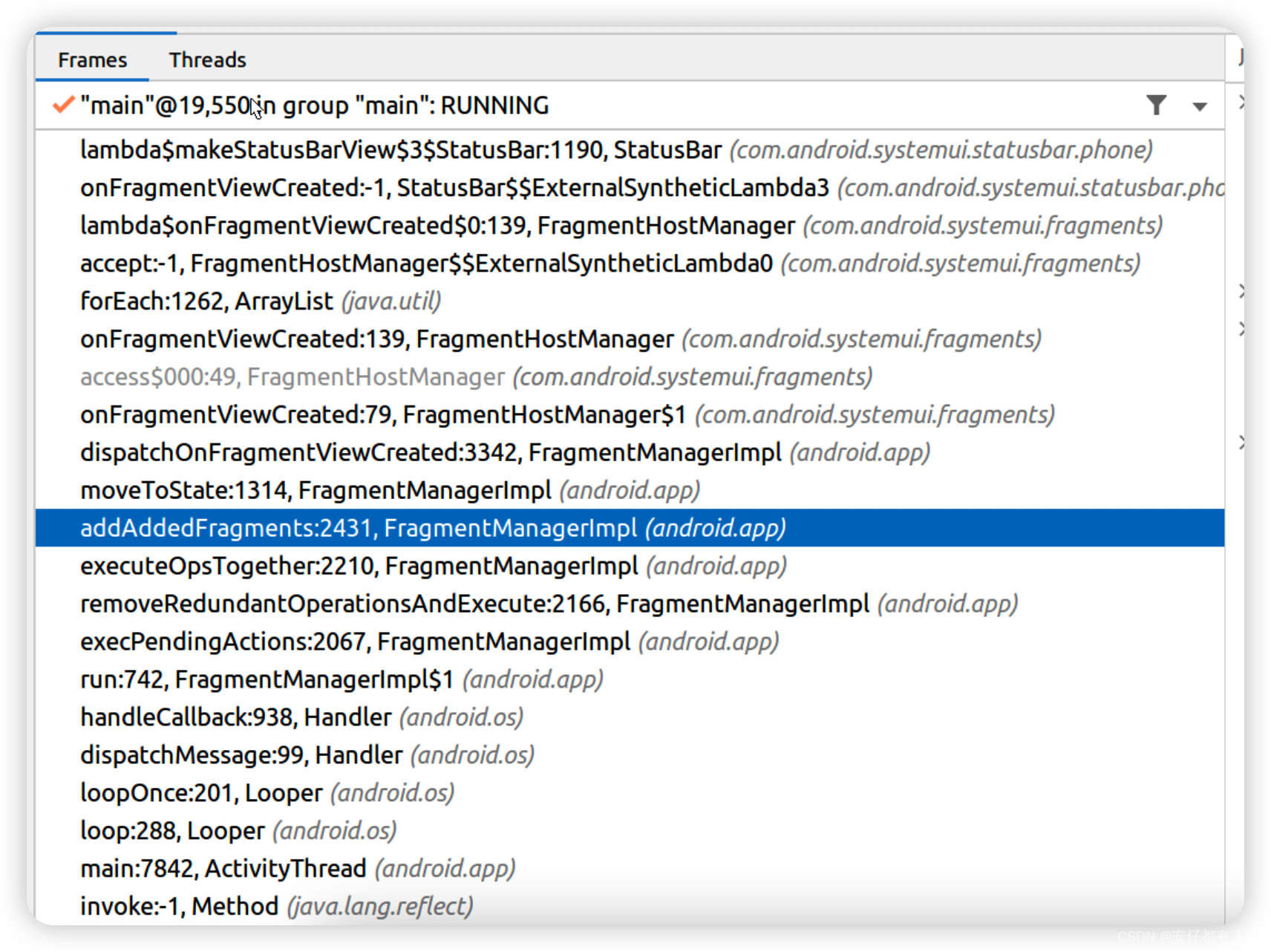
同时,为了能够理解这个Listener的触发,此处贴上一个调用栈图片.之所以不对其进行进一步的分析是因为这部分不属于SystemUI中的内容,而是Android Fragment中的内容.
那么一切准备妥当,整个UI显示,将会是下面这个样子:

至此,将会进入下一个生命周期函数onResume中.
onResume
在完成了整个View之后,接下里就会触发其onResume函数()如下:
@Override
public void onResume() {super.onResume();//接收CommandQueue中的命令,CommandQueue,见上一篇博文 mCommandQueue.addCallback(this);//接收StatusBarState的改变,StatusBarState,见上一篇博文的介绍mStatusBarStateController.addCallback(this);//初始化化通话图标initOngoingCallChip();
}
mCommandQueue.addCallback()需要注意的细节
在addCallback()中,做了一个非常不起眼但却很重要的操作,如下:
@Override
public void addCallback(@NonNull Callbacks callbacks) {mCallbacks.add(callbacks);//主动调用disable(),其实此处调用disable()跟前文中,主动调用onFragmentViewCreated一样.for (int i = 0; i < mDisplayDisabled.size(); i++) {int displayId = mDisplayDisabled.keyAt(i);int disabled1 = getDisabled1(displayId);int disabled2 = getDisabled2(displayId);//这将触发CollapsedStatusBarFragment的disable函数被调用callbacks.disable(displayId, disabled1, disabled2, false /* animate */);}
}
上面函数很简单:
- 保存回调
- 触发回调的disable
他将触发CollapsedStatusBarFragment的disable()函数,如下:
在探disableFlags的处理
disable()函数源码如下:
//其中的state1就是disable1Flag
//state2就是disable2Flag
@Override
public void disable(int displayId, int state1, int state2, boolean animate) {//是否是同一个逻辑屏幕,如果不是则会返回if (displayId != getContext().getDisplayId()) {return;}//需要对传入的state1做一下调整,在这个调整函数中,它会主动调用各个Controller判断//要不要显示某些UI,然后将相应的标志位设置好,最终将其返回.该函数较简单,不再展开state1 = adjustDisableFlags(state1);//下面是一些位操作,用于得到哪些位被改变了final int old1 = mDisabled1;final int diff1 = state1 ^ old1;final int old2 = mDisabled2;final int diff2 = state2 ^ old2;mDisabled1 = state1;mDisabled2 = state2;if ((diff1 & DISABLE_SYSTEM_INFO) != 0 || ((diff2 & DISABLE2_SYSTEM_ICONS) != 0)) {if ((state1 & DISABLE_SYSTEM_INFO) != 0 || ((state2 & DISABLE2_SYSTEM_ICONS) != 0)) {//隐藏,animate表示是否使用动画,此处传递过来为falsehideSystemIconArea(animate);hideOperatorName(animate);} else {showSystemIconArea(animate);showOperatorName(animate);}}//依然更新相应的图标要不要显示,他们依然是调用show/hidexxxx()完成,其中xxx表示的是某个Viewif (((diff1 & DISABLE_ONGOING_CALL_CHIP) != 0)|| ((diff1 & DISABLE_NOTIFICATION_ICONS) != 0)) {updateNotificationIconAreaAndCallChip(state1, animate);}//下面的代码,依然使用show/hidexxx()函数完成,其中xxx表示的是某个Viewif ((diff1 & DISABLE_CLOCK) != 0 || mClockView.getVisibility() != clockHiddenMode()) {if ((state1 & DISABLE_CLOCK) != 0) {hideClock(animate);} else {showClock(animate);}}
}
上面的函数也很简单:
- 从diableFlag中得到对应的位
- 根据位判断是否要显示或者隐藏某个View
- 显示或者隐藏全部通过show/hidexxx()函数完成
接下来我们看看show/hidexxx()函数的具体过程.我们以onVIewCreated()函数中的第一个showSystemIconArea()为例.如下:
showSystemIconArea()
源码如下:
private void showSystemIconArea(boolean animate) {//先判断动画的状态,现在还在初始的流程中,state为IDEL//在下一篇文章中,将会介绍AnimationScheduler的作用int state = mAnimationScheduler.getAnimationState();if (state == IDLE || state == SHOWING_PERSISTENT_DOT) {//调用animateShow()函数,是否要通过动画显示,此处为传递的值为falseanimateShow(mSystemIconArea, animate);}}
上面的函数完成:
- 是否要调用animateShow()函数,该函数会负责动画
在接着看animateShow()函数之前,有必要检查一下其他的show/hidexxx()函数是不是也是一样的.幸运的是,几乎所有的show/hidexxx()函数,最终都会调用到animateShow()或者animateHiddenStatte().
接下来我们看看animateShow()函数
animateShow()
animateShow()函数负责在show一个View的时候,是否要配合动画
private void animateShow(View v, boolean animate) {//先取消View中的动画v.animate().cancel();//再设置View位可见v.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);//如果不需要动画,则直接将透明度设置为1,并返回if (!animate) {v.setAlpha(1f);return;}//如果需要动画v.animate().alpha(1f)//设置最终透明度为1.setDuration(FADE_IN_DURATION)//动画运行时间.setInterpolator(Interpolators.ALPHA_IN)//设置插值器.setStartDelay(FADE_IN_DELAY)//延迟多久开始动画.withEndAction(null);//动画结束完成执行的动作,此处为空,历史原因才有这句话//如果锁屏的消失动画正在运行,则可以将两个动画,联合起来//重新设置对应的duration,startdelay//然后start()if (mKeyguardStateController.isKeyguardFadingAway()) {v.animate().setDuration(mKeyguardStateController.getKeyguardFadingAwayDuration()).setInterpolator(Interpolators.LINEAR_OUT_SLOW_IN).setStartDelay(mKeyguardStateController.getKeyguardFadingAwayDelay()).start();}
}
上面的函数也非常简单,只做一件事:
- 设置透明度的属性动画.
同样的animateHiddenState()函数则为这个函数的逆过程,它也是设置透明度的属性动画,再此就不做展开.
我们继续接着onResume()剩下的内容查看,对于增加mStatusBarStateController的回调非常简单,因此我们接着看下一句,initOngoingCallChip.如下:
initOngoingCallChip的初始化
源码如下,整个源码非常简单.给对应的控制器增加监听和View
private void initOngoingCallChip() {mOngoingCallController.addCallback(mOngoingCallListener);mOngoingCallController.setChipView(mOngoingCallChip);
}
该函数也很简单,没有什么可以详细介绍的.
至此,整个Fragment的创建和初始化的生命周期走完.
接下来就是将相应的Window加入屏幕中
将UI加入屏幕中
在前面的分析中,我们只是创建了整个UI体系,但是还没有将其加入屏幕中,加入屏幕,也是在StatusBar的createAndAddWindwos()函数中,如下
public void createAndAddWindows(@Nullable RegisterStatusBarResult result) {//创建对应的UImakeStatusBarView(result);//将NotificationShadeWindow加入屏幕mNotificationShadeWindowController.attach();//将StatusBarWinidow加入屏幕mStatusBarWindowController.attach();
}
对于StatusBar窗口,在是调用mStatusBarWindowController.attach();将其加入屏幕上.其代码内容为:
public void attach() {//创建对应的WindowManager.LayoutParams对象//该对象用于描述窗口的属性和参数//在这里,我们要求其宽度为:MATCH_PARENT//高度,为一个固定值:即mBarHeight//Window类型为:TYPE_STATUS_BAR,这是抓们为StatusBar设计的窗口类型//window的标志有:不能被聚焦,支持窗口之外的触摸,支持自己绘制SystemBar背景//像素格式为:PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT它有更多的bit用来存放透明信息mLp = new WindowManager.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,mBarHeight,WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_STATUS_BAR,WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SPLIT_TOUCH| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_DRAWS_SYSTEM_BAR_BACKGROUNDS,PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT);mLp.privateFlags |= PRIVATE_FLAG_COLOR_SPACE_AGNOSTIC;//然后一个窗口都需要一个Binder作为tokenmLp.token = new Binder();mLp.gravity = Gravity.TOP;mLp.setFitInsetsTypes(0 /* types */);//窗口的名字mLp.setTitle("StatusBar");mLp.packageName = mContext.getPackageName();mLp.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS;//调用WindowManager的addView从此刻开始,就能在屏幕中看到对应的UI了mWindowManager.addView(mStatusBarView, mLp);//保存旧的Window参数,用于在后面参数更改之后,进行对比mLpChanged.copyFrom(mLp);//下面两句的内容,我们将会在下一篇文章的StatusBar的UI交互中进行介绍,现在不需要知道mContentInsetsProvider.addCallback(this::calculateStatusBarLocationsForAllRotations);calculateStatusBarLocationsForAllRotations();
}
上面的函数也很简单,完成一件事情:
- 将对应的View添加到屏幕中.
至此,整个StatusBar的UI的创建过程介绍完毕.对于StatusBar的UI的逆过程,也即StatusBar的销毁,或者重建,几乎就是上面内容的逆过程,或者说是重复过程,没有再次介绍的必要.
下一篇文章将会介绍StatusBar中UI的交互
PS:文中,难免有错误之处,如果发现,请批评指正


![[maven] scopes 管理 profile 测试覆盖率](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3379879de5154a1da1e6033ad9eb8f42.png)

![[设计模式] 浅谈SOLID设计原则](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f845bb46162944a4b7f3f8e7292cf2aa.png)