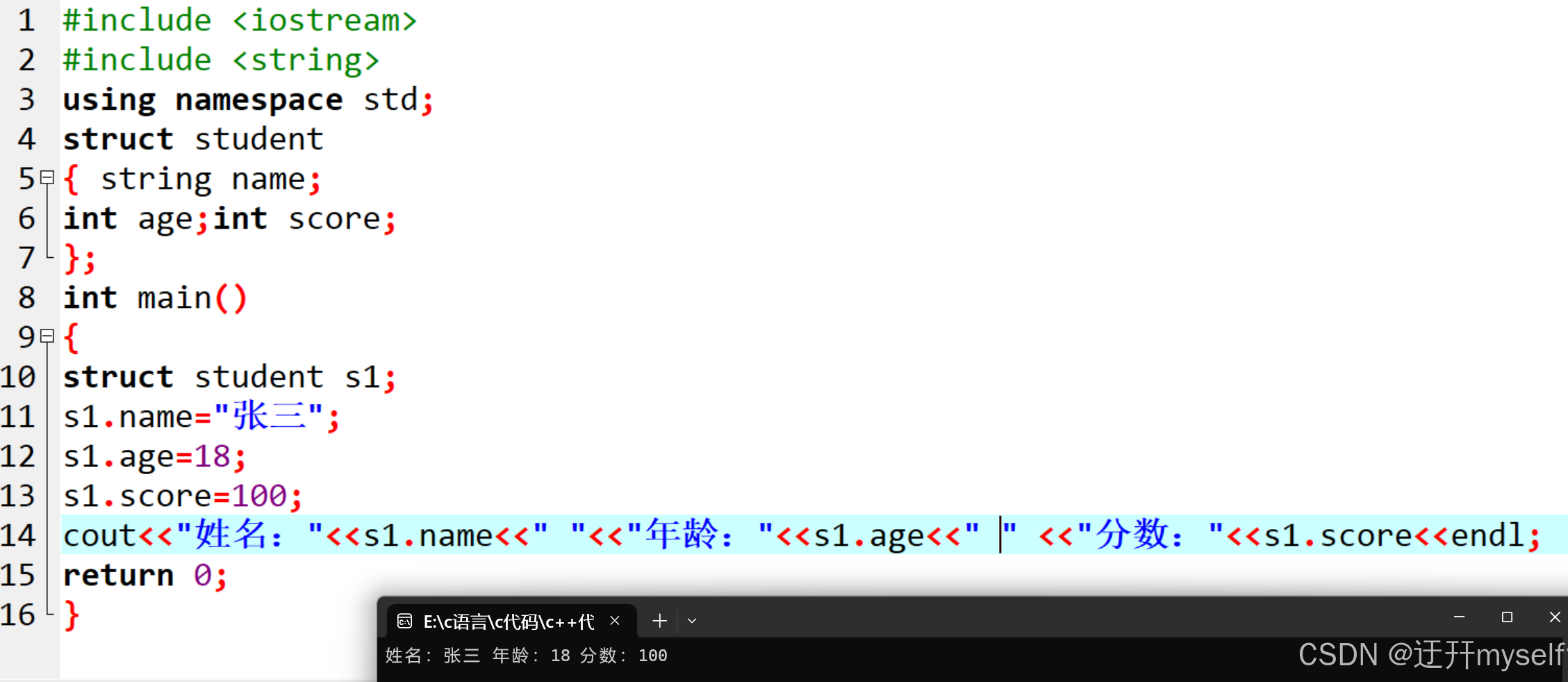
/*结构体属于用户自定义的数据类型, 允许用户存储不同的数据类型,
语法:struct 结构体名{结构体成员列表} ;*/
//struct 结构体名 变量名
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct student
{ string name;
int age;int score;
};
int main()
{
struct student s1;
s1.name="张三";
s1.age=18;
s1.score=100;
cout<<"姓名:"<<s1.name<<" "<<"年龄:"<<s1.age<<" " <<"分数:"<<s1.score<<endl;
return 0;
}
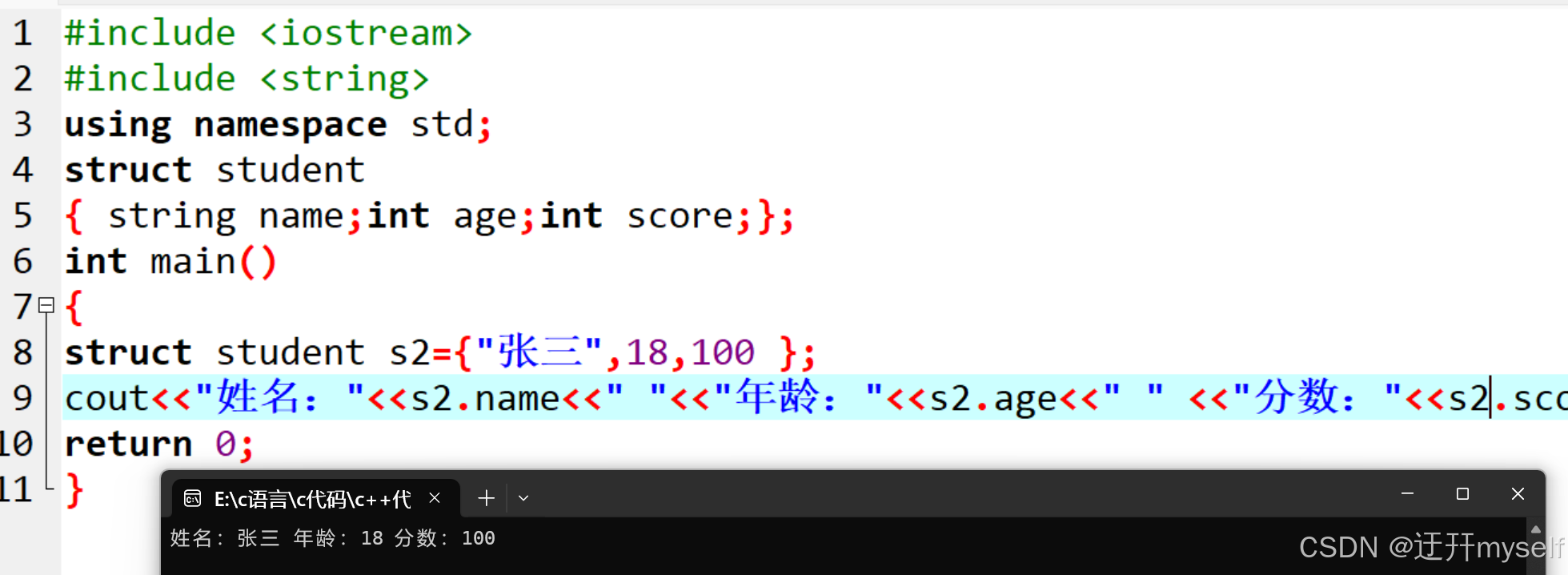
//struct 结构体名 变量名={成员1值,成员2值...}
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct student
{ string name;int age;int score;};
int main()
{
struct student s2={"张三",18,100 };
cout<<"姓名:"<<s2.name<<" "<<"年龄:"<<s2.age<<" " <<"分数:"<<s2.score<<endl;
return 0;
}
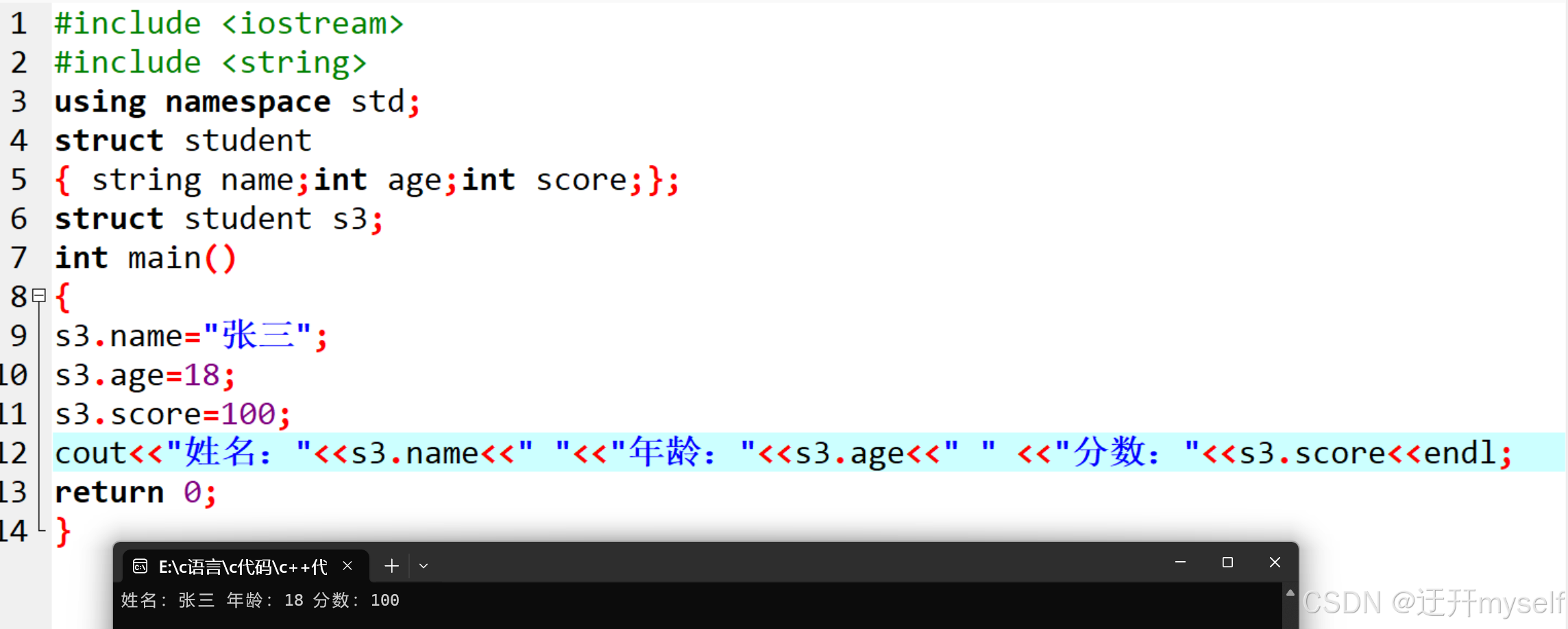
//定义结构体时顺便创建变量
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct student
{ string name;int age;int score;};
struct student s3;
int main()
{
s3.name="张三";
s3.age=18;
s3.score=100;
cout<<"姓名:"<<s3.name<<" "<<"年龄:"<<s3.age<<" " <<"分数:"<<s3.score<<endl;
return 0;
}
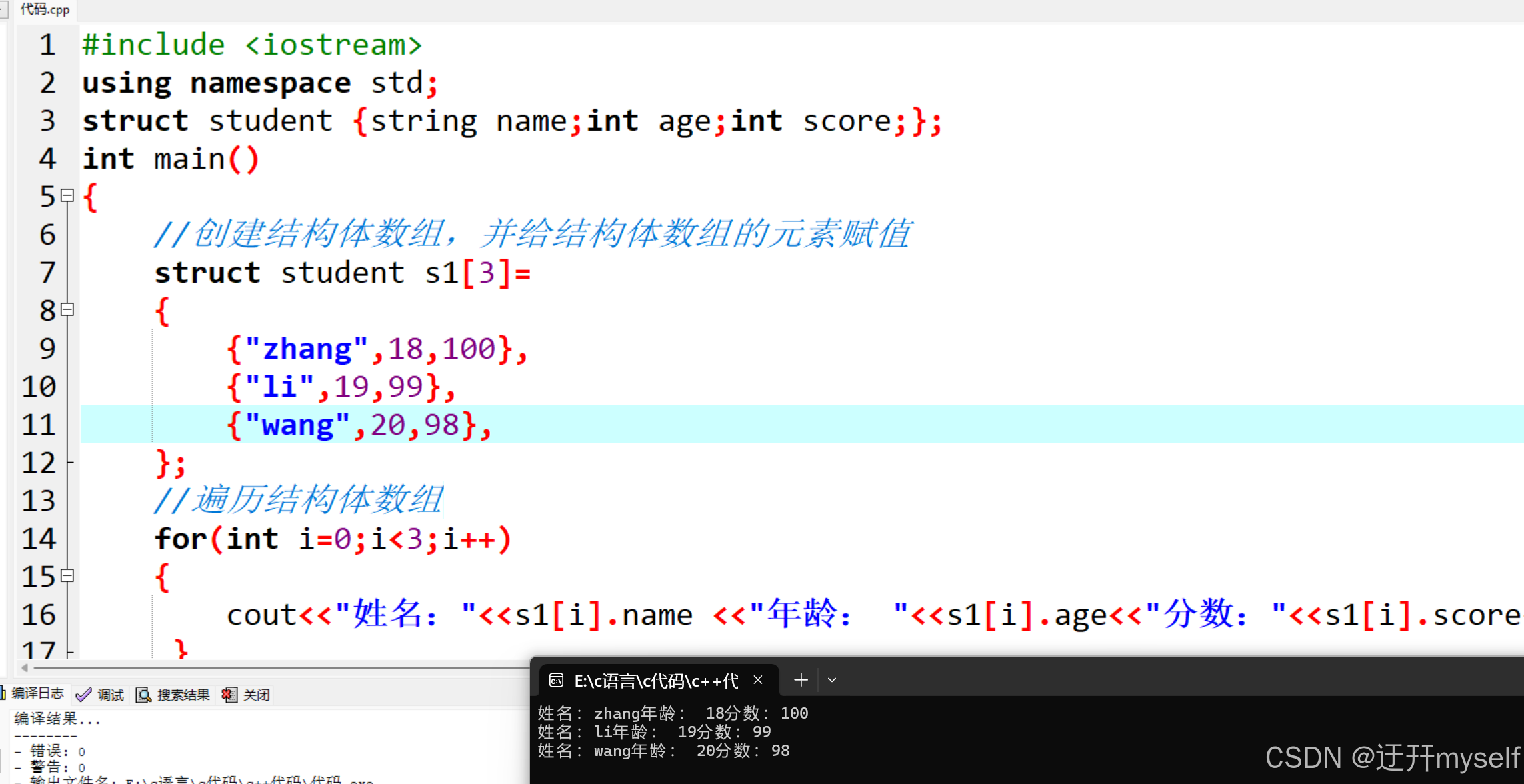
//结构体数组
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct student {string name;int age;int score;};
int main()
{
//创建结构体数组,并给结构体数组的元素赋值
struct student s1[3]=
{
{"zhang",18,100},
{"li",19,99},
{"wang",20,98},
};
//遍历结构体数组
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
cout<<"姓名:"<<s1[i].name <<"年龄: "<<s1[i].age<<"分数:"<<s1[i].score<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
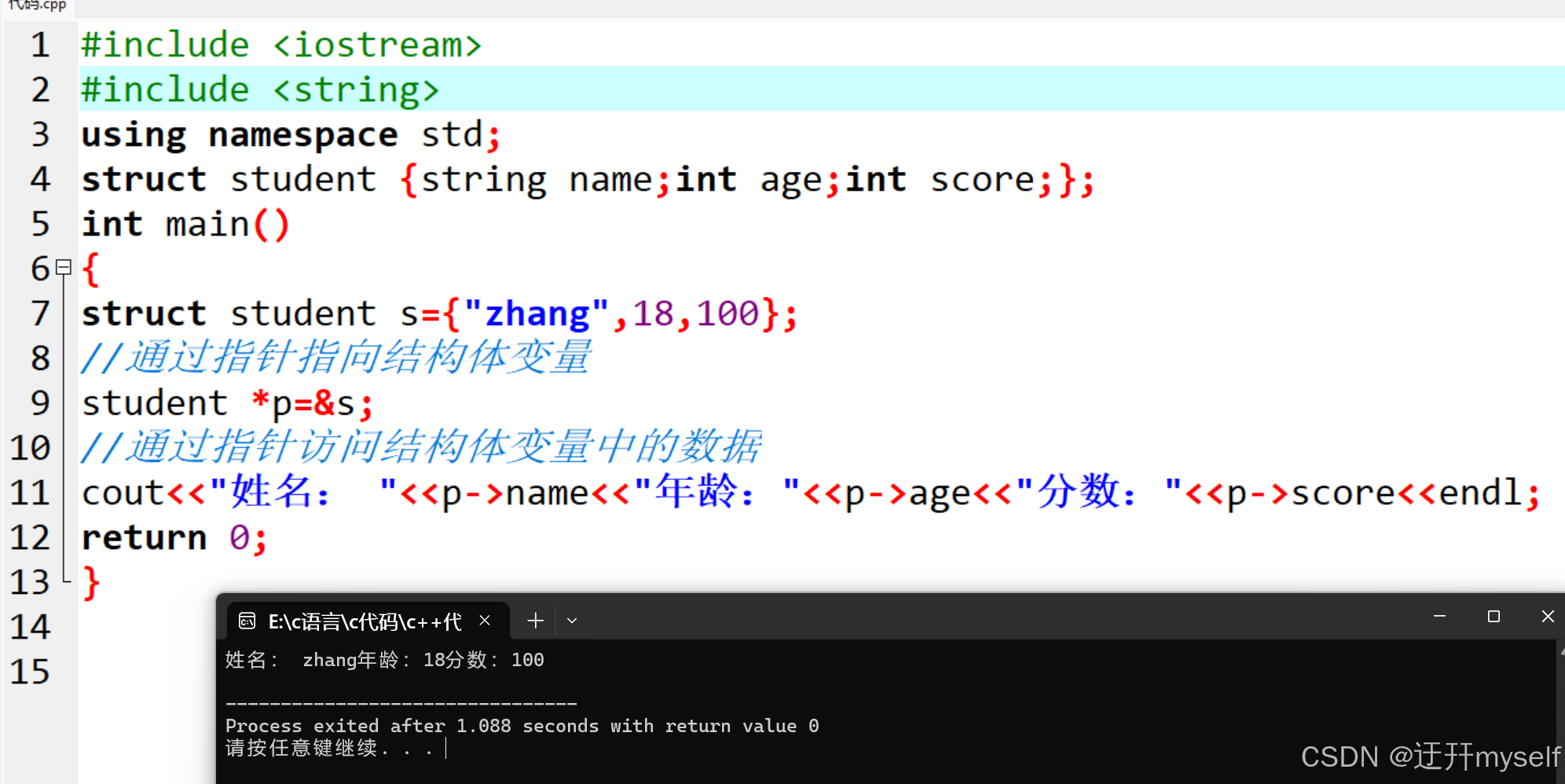
//结构体指针
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct student {string name;int age;int score;};
int main()
{
struct student s={"zhang",18,100};
//通过指针指向结构体变量
student *p=&s;
//通过指针访问结构体变量中的数据
cout<<"姓名: "<<p->name<<"年龄:"<<p->age<<"分数:"<<p->score<<endl;
return 0;
}
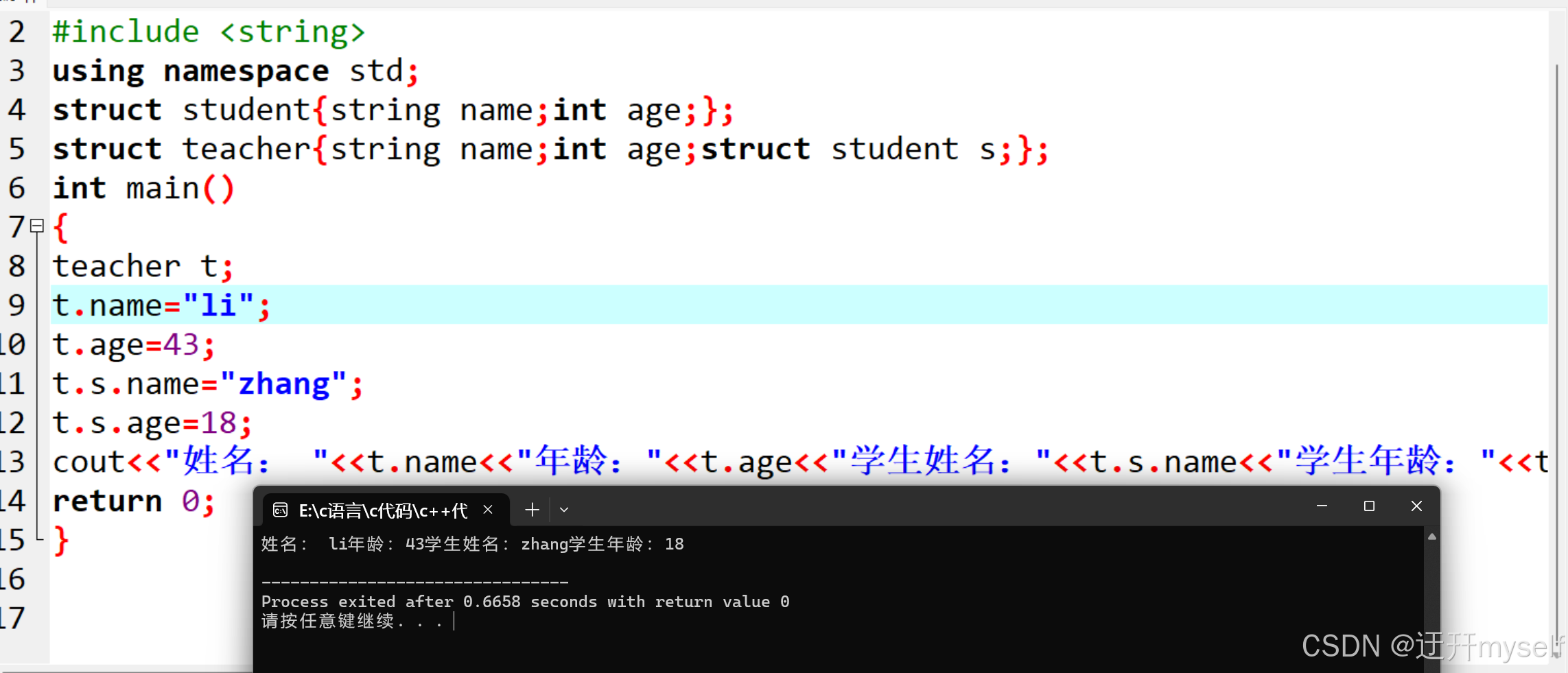
//结构体嵌套结构体
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct student{string name;int age;};
struct teacher{string name;int age;struct student s;};
int main()
{
teacher t;
t.name="li";
t.age=43;
t.s.name="zhang";
t.s.age=18;
cout<<"姓名: "<<t.name<<"年龄:"<<t.age<<"学生姓名:"<<t.s.name<<"学生年龄:"<<t.s.age<<endl;
return 0;
}
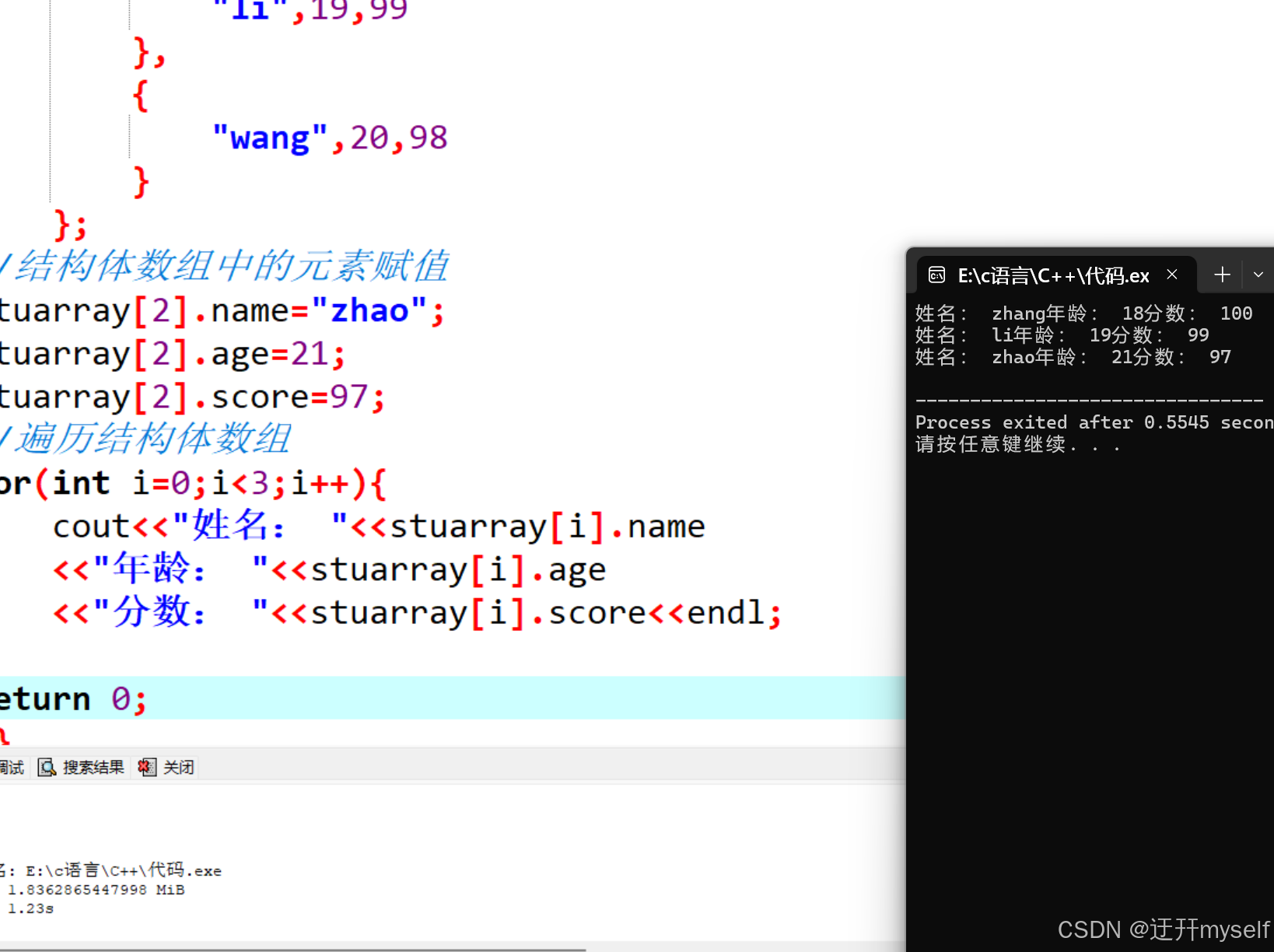
//结构体数组
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//结构体数组——定义结构体数组
struct student{
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
//创建结构体数组
int main()
{
struct student stuarray[3]={
{
"zhang",18,100
},
{
"li",19,99
},
{
"wang",20,98
}
};
//结构体数组中的元素赋值
stuarray[2].name="zhao";
stuarray[2].age=21;
stuarray[2].score=97;
//遍历结构体数组
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
cout<<"姓名: "<<stuarray[i].name
<<"年龄: "<<stuarray[i].age
<<"分数: "<<stuarray[i].score<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
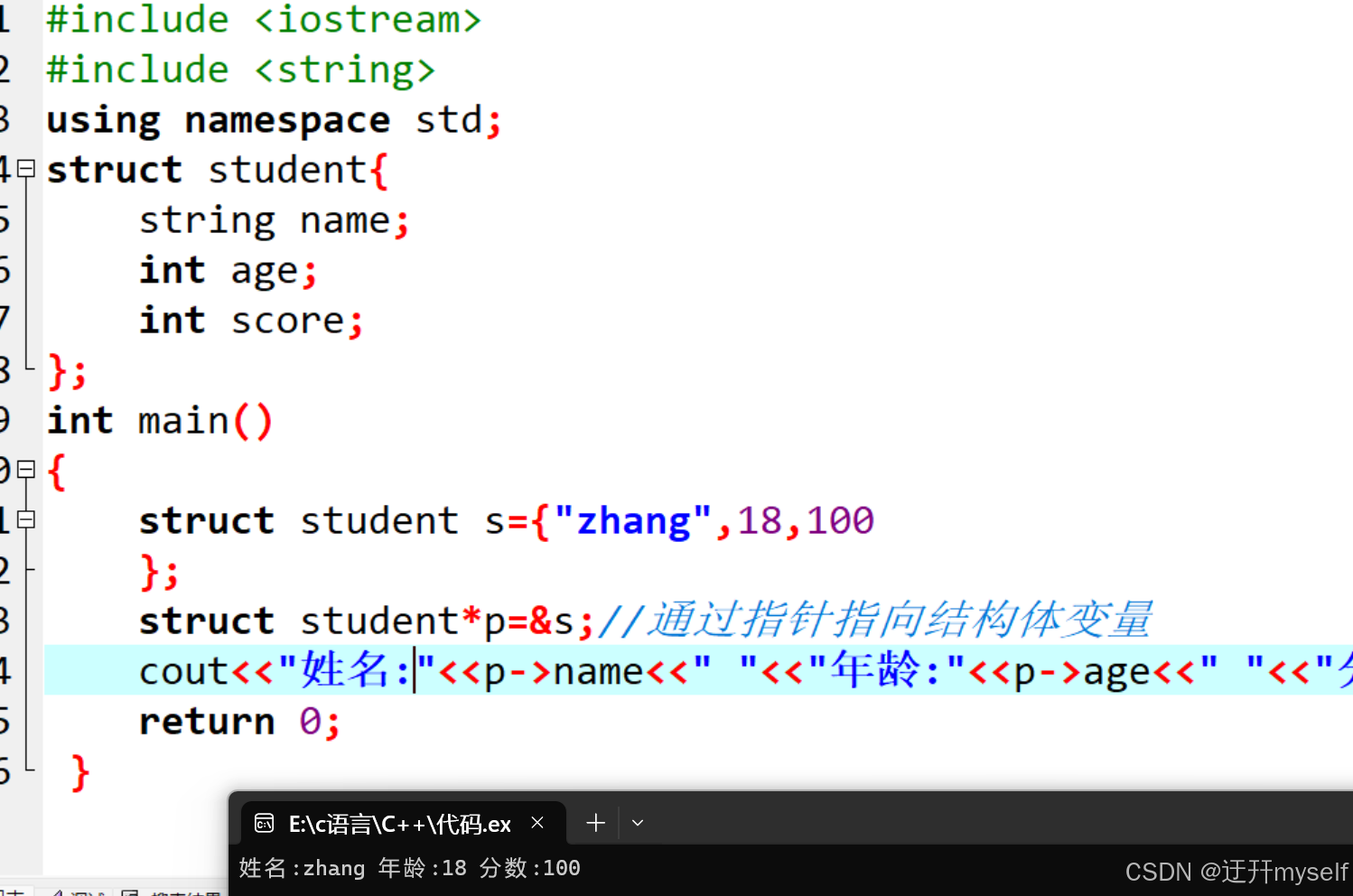
//结构体指针
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct student{
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main()
{
struct student s={"zhang",18,100
};
struct student*p=&s;//通过指针指向结构体变量
cout<<"姓名:"<<p->name<<" "<<"年龄:"<<p->age<<" "<<"分数:"<<p->score<<endl;
return 0;
}
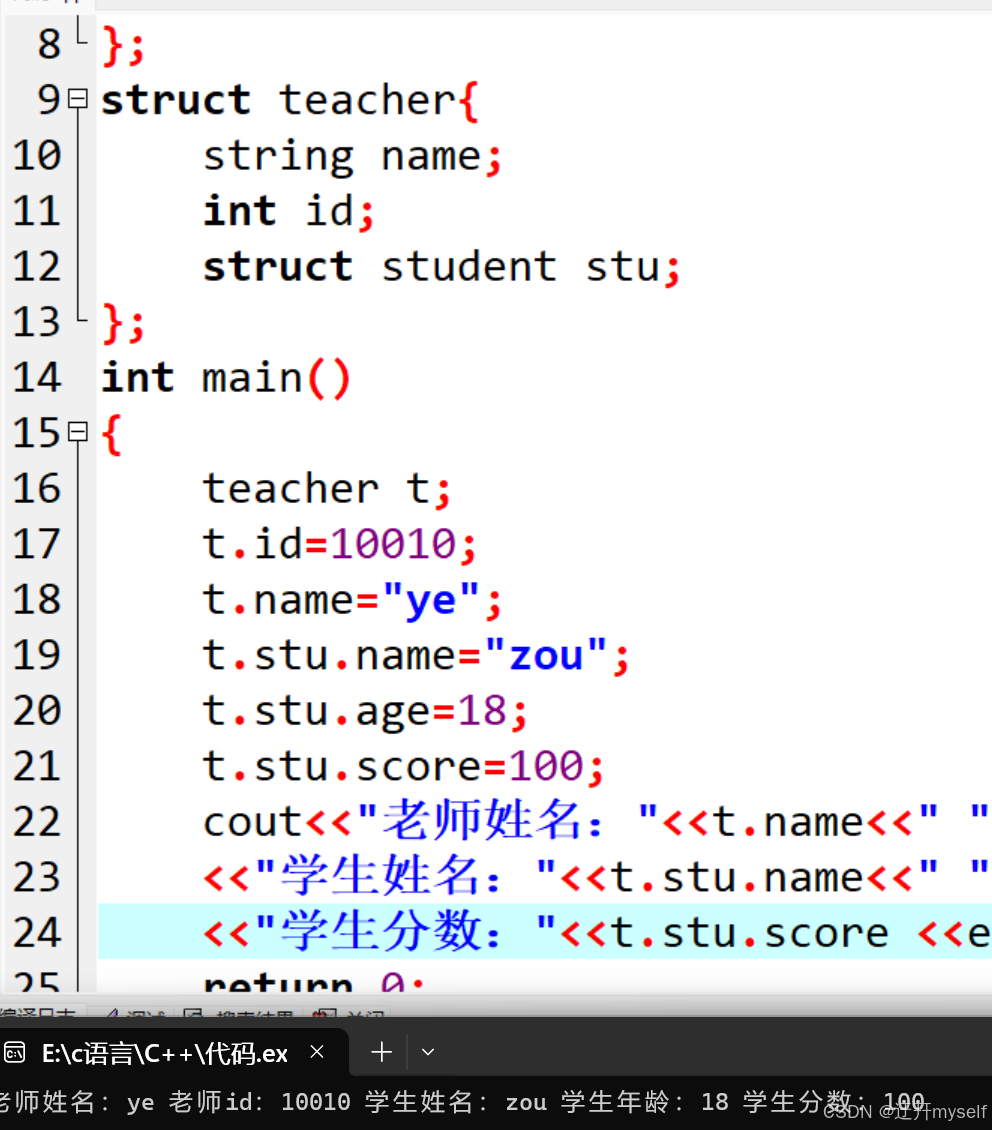
//结构体嵌套结构体
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct student{
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
struct teacher{
string name;
int id;
struct student stu;
};
int main()
{
teacher t;
t.id=10010;
t.name="ye";
t.stu.name="zou";
t.stu.age=18;
t.stu.score=100;
cout<<"老师姓名:"<<t.name<<" "<<"老师id:"<<t.id<<" "
<<"学生姓名:"<<t.stu.name<<" "<<"学生年龄:"<<t.stu.age<<" "
<<"学生分数:"<<t.stu.score <<endl;
return 0;
}
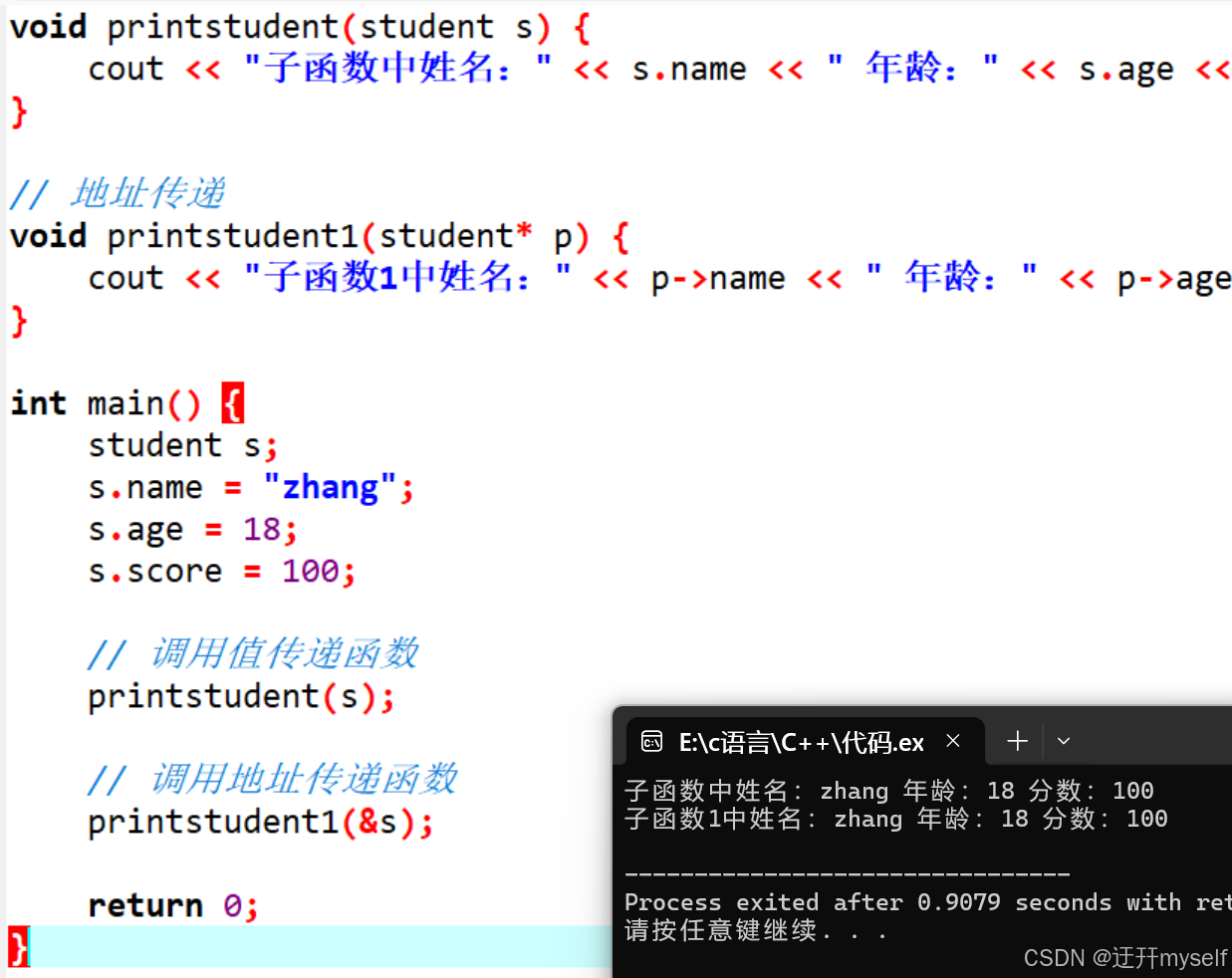
//结构体做函数参数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
// 值传递
void printstudent(student s) {
cout << "子函数中姓名:" << s.name << " 年龄:" << s.age << " 分数:" << s.score << endl;
}
// 地址传递
void printstudent1(student* p) {
cout << "子函数1中姓名:" << p->name << " 年龄:" << p->age << " 分数:" << p->score << endl;
}
int main() {
student s;
s.name = "zhang";
s.age = 18;
s.score = 100;
// 调用值传递函数
printstudent(s);
// 调用地址传递函数
printstudent1(&s);
return 0;
}
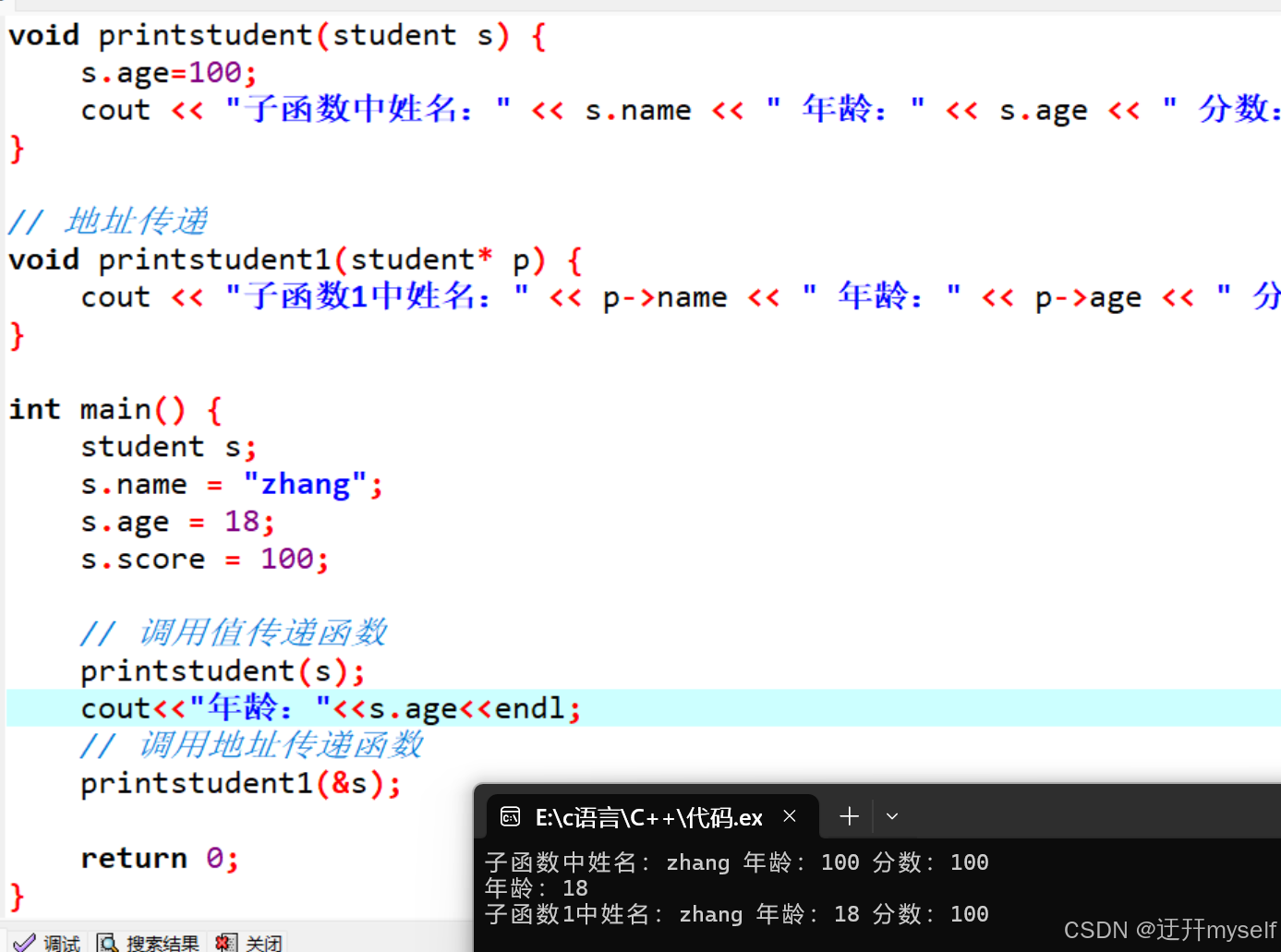
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
// 值传递
void printstudent(student s) {
s.age=100;//值传递修饰形参,实参不会改变
cout << "子函数中姓名:" << s.name << " 年龄:" << s.age << " 分数:" << s.score << endl;
}
// 地址传递
void printstudent1(student* p) {
cout << "子函数1中姓名:" << p->name << " 年龄:" << p->age << " 分数:" << p->score << endl;
}
int main() {
student s;
s.name = "zhang";
s.age = 18;
s.score = 100;
// 调用值传递函数
printstudent(s);
cout<<"年龄:"<<s.age<<endl;
// 调用地址传递函数
printstudent1(&s);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
// 值传递
void printstudent(student s) {
cout << "子函数中姓名:" << s.name << " 年龄:" << s.age << " 分数:" << s.score << endl;
}
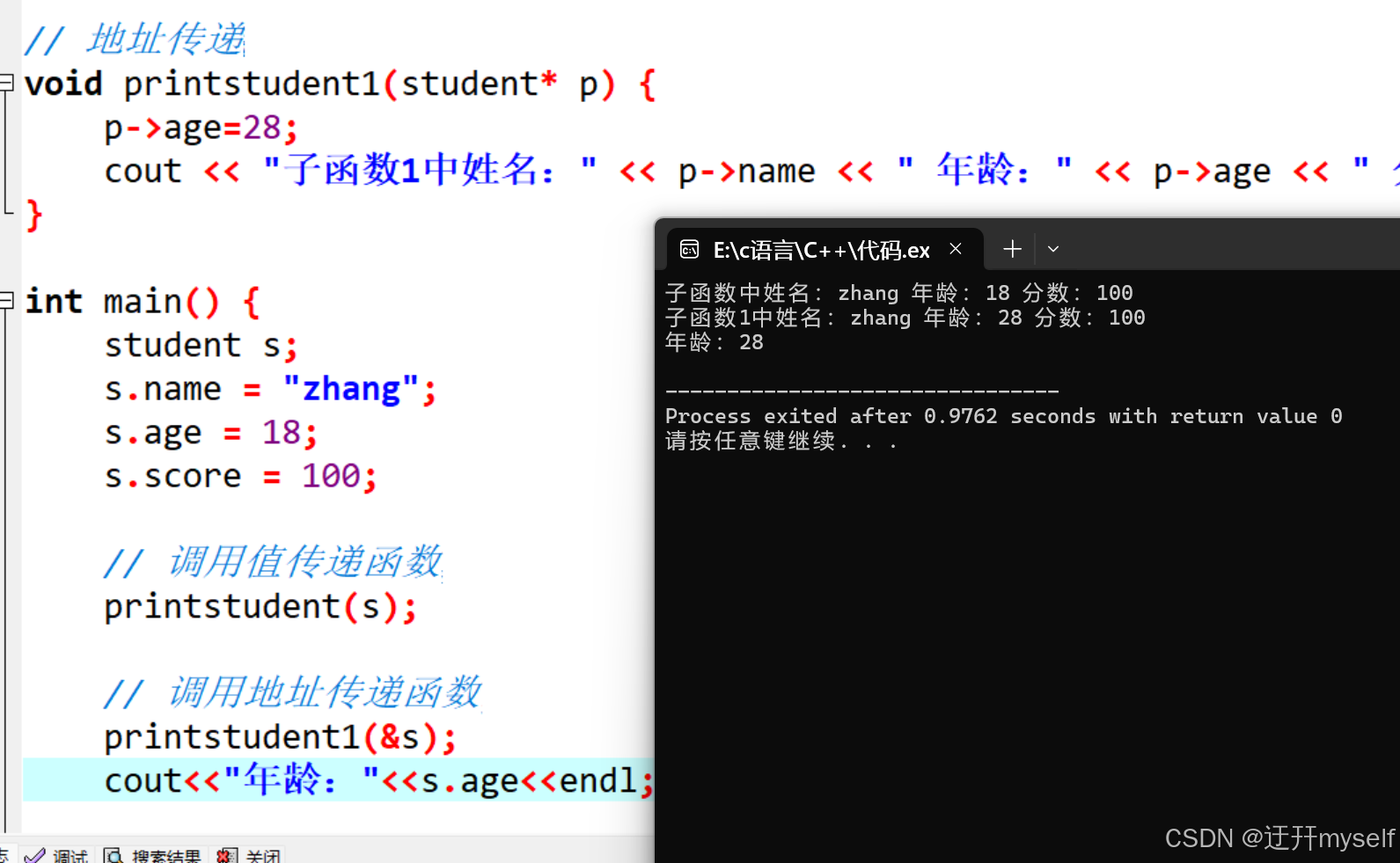
// 地址传递
void printstudent1(student* p) {
p->age=28;
cout << "子函数1中姓名:" << p->name << " 年龄:" << p->age << " 分数:" << p->score << endl;
}
int main() {
student s;
s.name = "zhang";
s.age = 18;
s.score = 100;
// 调用值传递函数
printstudent(s);
// 调用地址传递函数
printstudent1(&s);
cout<<"年龄:"<<s.age<<endl;
return 0;
}
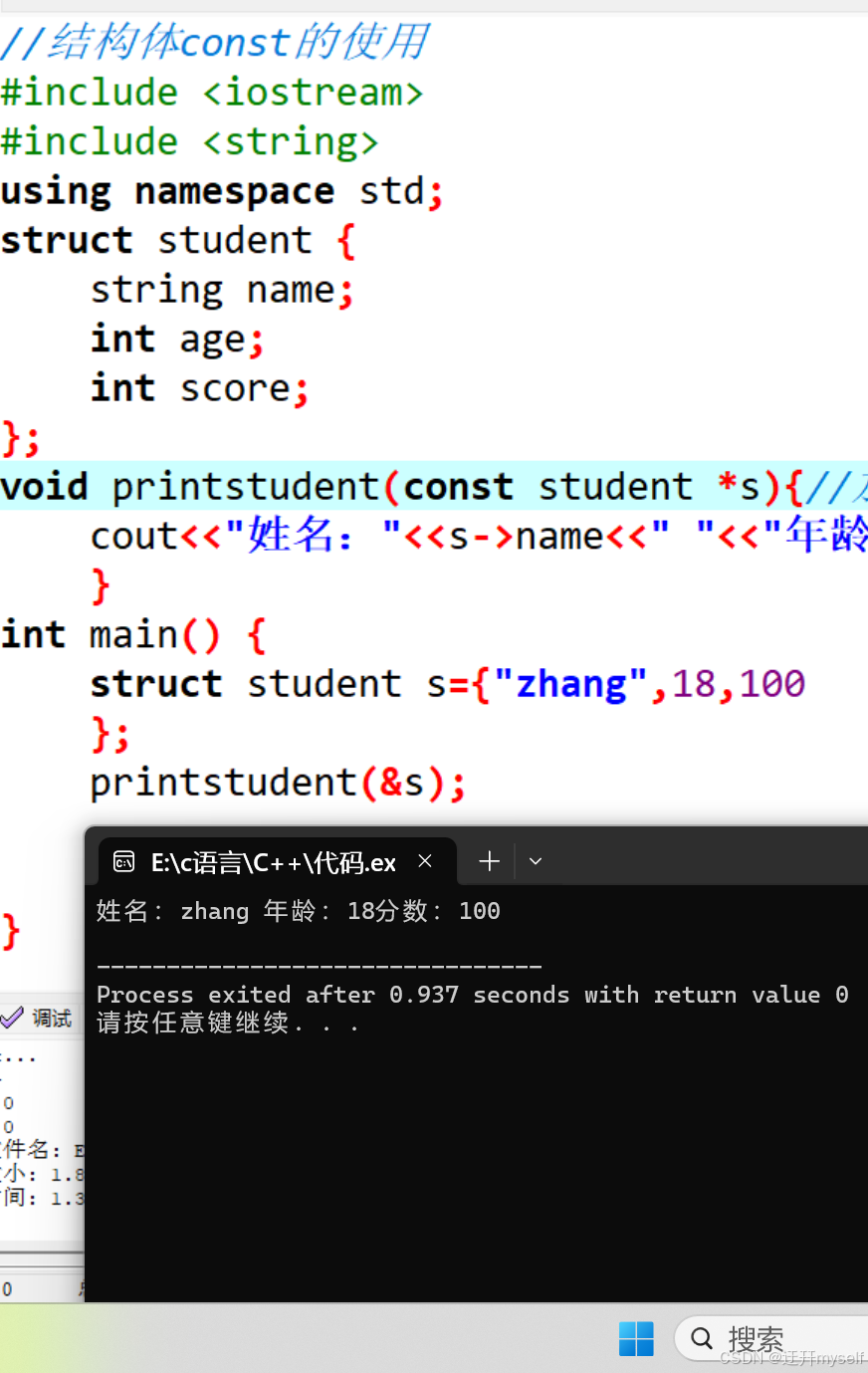
//结构体const的使用
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
void printstudent(const student *s){//加入const之后,一旦有修改的操作就会报错,防止误操作
cout<<"姓名:"<<s->name<<" "<<"年龄:"<<s->age<<"分数:"<<s->score<<endl;
}
int main() {
struct student s={"zhang",18,100
};
printstudent(&s);
return 0;
}